 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| ATCvet code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.907 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
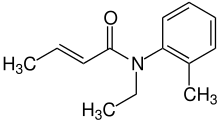
| Formula | C13H17NO |
| Molar mass | 203.285 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Crotamiton is a drug that is used both as a scabicidal (for treating scabies) and as a general antipruritic (anti-itching drug). It is a prescription, lotion-based medicine that is applied to the whole body to get rid of the scabies mite that burrows under the skin and causes itching.
Use
For treating scabies, crotamiton should be applied to the whole body rather than a localized area. It is applied two or three times, with a 24-hour delay between applications, and the patient is asked to take a shower no sooner than after 48 hours. For children under 3 years, it is applied once daily. It can also be used to treat itching stemming from other causes, e.g. insect bites, in which case it is applied to the itching areas only, and repeated if necessary after 4 to 8 hours. Use near the eyes, or breaks in the skin, should be avoided.
Pharmacology
Crotamiton is toxic to the scabies mite.[1] It probably acts as a general antipruritic by inhibition of TRPV4, a sensory ion channel that is expressed in the skin and primary sensory neurons.[2]
Pharmacokinetics
After topical application, crotamiton is absorbed systemically. It has an elimination half-life of 30.9 hours and 4.8-8.8% is excreted in the urine.[3]
Side effects
The most common side effect of crotamiton is skin irritation.
Trade name
Crotamiton is marketed under the trade names Eurax, which is manufactured by Ranbaxy Laboratories in the United States, and GlaxoSmithKline in the United Kingdom, and Euracin, which is manufactured by Green Cross in South Korea. In Germany, it is marketed under the brand name Crotamitex. In India, it is sold as Eurax by Ranbaxy Laboratories.
References
- ↑ "Crotamiton: mechanism of action". Medscape Drug Information.
- ↑ Kittaka H, Yamanoi Y, Tominaga M (October 2017). "Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) channel as a target of crotamiton and its bimodal effects". Pflügers Archiv. 469 (10): 1313–1323. doi:10.1007/s00424-017-1998-7. PMID 28612138. S2CID 4059914.
- ↑ "Crotamiton: pharmacokinetics". Medscape Drug Information.