| Excalibosaurus Temporal range: Early Jurassic, | |
|---|---|
%252C_Lyme_Regis%252C_England%252C_Early_Jurassic_-_Royal_Ontario_Museum_-_DSC09979.JPG.webp) | |
| Fossil, Royal Ontario Museum | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Excalibosaurus McGowan, 1986 |
| Binomial name | |
| Excalibosaurus costini McGowan, 1986 | |
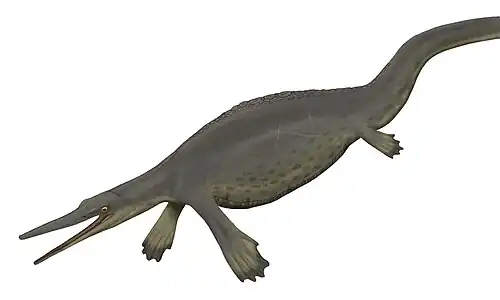
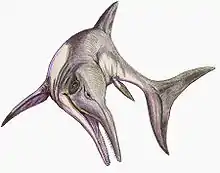
Excalibosaurus (meaning "Excalibur's lizard") is a monotypic genus of marine prehistoric reptiles (ichthyosaurs) that lived during the Sinemurian stage (approximately 196.5 ± 2 Ma to 190.8 ± 1.0 Ma (million years ago)) of the Early Jurassic period in what is now England. It is characterized by the extreme elongation of the rostrum, with the lower jaw about three-quarters the length of the upper jaw, giving the animal a swordfish-like look. The only known species is Excalibosaurus costini.
History of research

This relatively rare animal is known from two skeletons. The holotype, discovered in 1984 near a beach on the Somerset coast, consists of the skull, forefin, part of the pectoral girdle and some vertebrae and ribs. It has been described in 1986 by Christopher McGowan.[2] The fossil is hosted in the Bristol City Museum and Art Gallery. The second specimen is an almost complete skeleton collected in the same area in 1996, and was purchased by the Royal Ontario Museum. It was described again by McGowan in 2003.[3]
Description
The holotype specimen has a skull length of 78.5 cm (2 ft 6.9 in), while the largest specimen has a skull length of 1.54 m (5 ft 1 in).[3] The larger specimen has a total length of 6.528 metres (21.42 ft).[4]
Classification
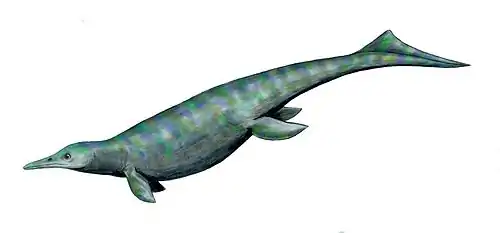
Excalibosaurus is related to two other genera of ichthyosaurs, Leptonectes from the Rhaetian (Late Triassic) to the Sinemurian (Early Jurassic) of England and Eurhinosaurus from the Toarcian (Early Jurassic) of Germany. The three genera are grouped in the family Leptonectidae.[5][6][3] It was once thought that Excalibosaurus was a junior synonym of Eurhinosaurus,[7] but the description of the 1996 specimen show many morphological differences such as the shape of the forefin (much shorter and broader in Excalibosaurus), the slender shape of the body, that clearly differentiate the two genera.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ "Excalibosaurus at Fossilworks". Paleobiology Database. Fossilworks. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- ↑ McGowan, C. (1986). "A putative ancestor for the swordfish-like ichthyosaur Eurhinosaurus". Nature. 322 (6078): 454–456. Bibcode:1986Natur.322..454M. doi:10.1038/322454a0. S2CID 4255439.
- 1 2 3 4 McGowan, C. (2003). "A new Specimen of Excalibosaurus from the English Lower Jurassic". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 23 (4): 950–956. doi:10.1671/1860-20. S2CID 129236415.
- ↑ Martin, J.E.; Vincent, P.; Suan, G.; Sharpe, T.; Hodges, P.; William, M.; Howells, C.; Fischer, V. (2015). "A Mysterious Giant Ichthyosaur from the Lowermost Jurassic of Wales". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. Institute of Paleobiology, Polish Academy of Sciences. 60 (4): 837–842. doi:10.4202/app.00062.2014. S2CID 13714078. Supplementary Information
- ↑ Maisch, M. W. (1998). "A new ichthyosaurian genus from the Posidonia Shale (Lower Toarcian, Jurassic) of Holzmaden, SW-Germany, with comments on the phylogeny of post-Triassic ichthyosaurs". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie, Abhandlungen. 209 (1): 47–78. doi:10.1127/njgpa/209/1998/47.
- ↑ Motani, R. (1999). "Phylogeny of the Ichthyopterygia". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 19 (3): 473–496. doi:10.1080/02724634.1999.10011160.
- ↑ Michael W. Maisch & Andreas T. Matzke (2000). "The Ichthyosauria". Stuttgarter Beiträge zur Naturkunde. Serie B. 298: 1–159.