| Extensor carpi radialis brevis | |
|---|---|
 Posterior surface of the left forearm. Superficial muscles. The partially obscured extensor carpi radialis brevis is shown in blue. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | humerus at the anterior of lateral epicondyle (common extensor tendon)[1] |
| Insertion | Posterior base of the 3rd metacarpal[1] |
| Artery | radial artery |
| Nerve | deep branch of the radial nerve |
| Actions | extensor and abductor of the hand at the wrist joint[1] |
| Antagonist | Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus extensor carpi radialis brevis |
| TA98 | A04.6.02.041 |
| TA2 | 2499 |
| FMA | 38497 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
In human anatomy, extensor carpi radialis brevis is a muscle in the forearm that acts to extend and abduct the wrist. It is shorter and thicker than its namesake extensor carpi radialis longus which can be found above the proximal end of the extensor carpi radialis brevis.
Origin and insertion
It arises from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, by the common extensor tendon; from the radial collateral ligament of the elbow-joint; from a strong aponeurosis which covers its surface; and from the intermuscular septa between it and the adjacent muscles.[2]
The fibres end approximately at the middle of the forearm in the form of a flat tendon, which is closely connected with that of the extensor carpi radialis longus, and accompanies it to the wrist; it passes beneath the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis, beneath the extensor retinaculum, and inserts into the lateral dorsal surface of the base of the third metacarpal bone, with a few fibres inserting into the medial dorsal surface of the second metacarpal bone.[2]
Relations
Under the extensor retinaculum the tendon lies on the back of the radius in a shallow groove, to the ulnar side of that which lodges the tendon of the extensor carpi radialis longus, and separated from it by a faint ridge.[2]
Innervation
Like all the muscles in the posterior forearm, ECR brevis is supplied by a branch of the radial nerve.
Function
It is an extensor, and an abductor of the hand at the wrist joint. That is, it serves to manipulate the wrist so that the fingers moves away from the palm. The muscle, like all extensors of the forearm, can be strengthened by exercise that resist its extension; Reverse wrist curls with dumbbells can be performed.
Additional images
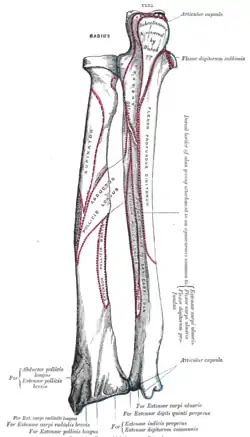 Bones of left forearm. Posterior aspect.
Bones of left forearm. Posterior aspect.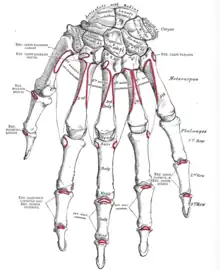 Bones of the left hand. Dorsal surface.
Bones of the left hand. Dorsal surface.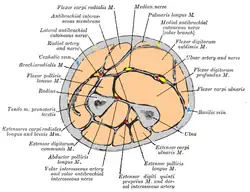 Cross-section through the middle of the forearm.
Cross-section through the middle of the forearm.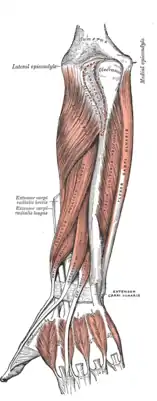 Posterior surface of the forearm. Deep muscles.
Posterior surface of the forearm. Deep muscles.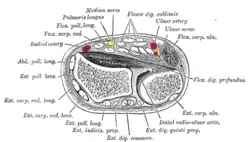 Transverse section across distal ends of radius and ulna.
Transverse section across distal ends of radius and ulna.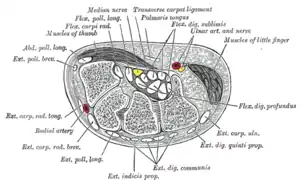 Transverse section across the wrist and digits.
Transverse section across the wrist and digits.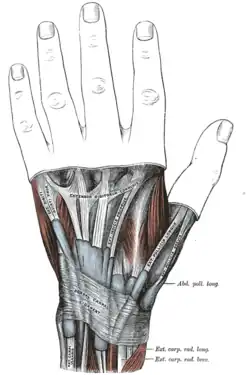 The mucous sheaths of the tendons on the back of the wrist.
The mucous sheaths of the tendons on the back of the wrist.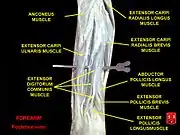 Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle
Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle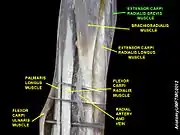 Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle
Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle
Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle
Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle
Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 452 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 452 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- 1 2 3 Origin, insertion and nerve supply of the muscle at Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine
- 1 2 3 Gray's Anatomy 1918, see infobox