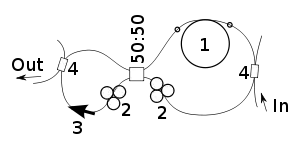
A figure-8 laser is a fiber laser with a figure-8-shaped ring resonator. It is used for making pico- and femtosecond soliton pulses. The typical spectrum of such a laser consists of a wide central peak and a few narrow lateral peaks that are placed symmetrically around it. The amplitudes of the narrow peaks are the same as or less than that of the central peak.[1]
Both loops of the resonator work as Sagnac loops. The active medium of the laser is optical fiber with its core doped with rare-earth ions. It is placed asymmetrically with respect to the resonator loops to make a nonlinear difference in phase between opposite waves, ensuring mode locking.[2] In 1992 a figure-8 laser was built with a smaller loop length of 1.6 m and a larger loop length of 60.8 m for generation of 315 fs pulses with repetition rate 125 MHz.[3]
References
- ↑ Fermann, Galvanauskas & Sucha 2002, pp. 102–103.
- ↑ Agrawal 2008, pp. 181–182.
- ↑ Agrawal 2008, p. 215.
Literature
- Agrawal, G. P. (2008). Applications of nonlinear fiber optics. Optics and Photonis Series. Vol. 10 (2nd ed.). Academic Press. p. 508. ISBN 978-0-12-374302-2.
- Fermann, M. E.; Galvanauskas, A.; Sucha, G., eds. (2002). Ultrafast Lasers: Technology and Applications. CRC Press. p. 800. ISBN 978-0-8247-4349-9.
External links
- "Mode-locked Fiber Lasers: 1.5-μm Femtosecond Erbium Fiber Lasers". Encyclopedia of Laser Physics and Technology. RP Photonics. Retrieved 2011-08-12.
- M. K. Islam & P. L. Chu. "Stability Analysis of Mode Locked Figure-eight Fiber Laser" (PDF). Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium. Retrieved 2011-08-13.