 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Butanoyl-4-[[3-butanoyl-5-[(5-butanoyl-2,6-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-4-oxocyclohexa-1,5-dien-1-yl)methyl]-2,4,6-trihydroxyphenyl]methyl]-3,5-dihydroxy-6,6-dimethylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one | |
| Other names
Filixic acid BBB; Filixic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.022.516 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C36H44O12 | |
| Molar mass | 668.736 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Filicin is a chemical compound that has been isolated from ferns of the genus Dryopteris. It has been isolated from the male fern (Dryopteris filix-mas).[1] Filicin has been studied for its anthelmintic activity.[2]
Related compounds
A variety of chemically related compounds, sometimes referred to collectively as filicins, have also been isolated from ferns. Chemical analysis of filicins in fern extracts can assist in determining taxonomy.[3] Examples of filicins include:
| Name(s) | Chemical structure | Molecular formula | Molecular weight (g/mol) | CAS number | PubChem | Notes and references |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
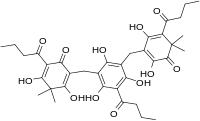
| Filixic acid ABA | 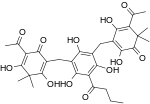 |
C32H36O12 | 612.63 | 38226-84-5 | CID 15081408 from PubChem | First isolated from Dryopteris dickinsii[4] |
| Filixic acid ABP | 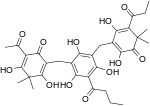 |
C33H38O12 | 626.66 | 57765-54-5 | CID 73672225 from PubChem | [5] |
| Filixic acid ABB | 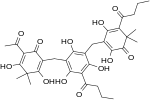 |
C34H40O12 | 640.68 | 37318-24-4 | CID 102574620 from PubChem | Found in Dryopteris sieboldii[6] |
| Filixic acid PBP | 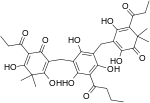 |
C34H40O12 | 640.68 | 51005-85-7 | CID 20055092 from PubChem | Found in Dryopteris sieboldii[6] and Dryopteris filix-mas |
| Filixic acid PBB | 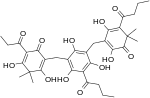 |
C35H42O12 | 654.71 | 49582-09-4 | CID 20055091 from PubChem | [5] |
| Flavaspidic acid BB; Toxifren; Polystichocitrin; Glavaspidic acid | 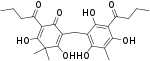 |
C24H30O8 | 446.49 | 114-42-1 | CID 8237 from PubChem | Isolated from Dryopteris abbreviata[7] |
References
- ↑ "Filicin". TOXNET. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Heikinheimo, R (1963). "Effect of filicin administered as an anthelmintic on the coagulation factors of the blood". Annales Medicinae Internae Fenniae. 52: 93–6. PMID 13953368.
- ↑ Euw, J. v.; Lounasmaa, M.; Reichstein, T.; Widén, C.J. (1980). "Chemotaxonomy in Dryopteris and related fern genera". Studia Geobotanica. 1: 275–311.
- ↑ Hisada, Sueo; Shiraishi, Koichi; Inagaki, Isao (1972). "Pharmaceutical studies on Japanese ferns containing phloroglucinol derivatives. 9 Constituents of Dryopteris dickinsii". Yakugaku Zasshi. 92 (9): 1124–1128. doi:10.1248/yakushi1947.92.9_1124.
- 1 2 Widén, C. J; Lounasmaa, M; Sarvela, J (1975). "Phloroglucinol derivatives of eleven Dryopteris species from Japan". Planta Medica. 28 (2): 144–64. PMID 1197418.
- 1 2 Hisada, Sueo; Inoue, O.; Inagak, Isao (1973). "Phloroglucinol derivatives of Dryopteris sieboldii". Phytochemistry. 12 (8): 2055. doi:10.1016/s0031-9422(00)91535-8.
- ↑ Coşkun, Maksut; Sakushima, Akiyo; Nishibe, Sansei; Hisada, Sueo; Tanker, Nevin (1982). "A phloroglucinol derivative of Dryopteris abbreviata". Phytochemistry. 21 (6): 1453. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(82)80168-4.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.