 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
fluoroamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
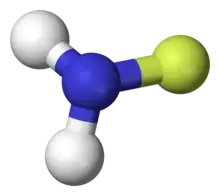
| NH2F | |
| Molar mass | 35.021 g/mol |
| Appearance | unstable gas |
| Density | 1.431 g/L |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Fluoroamine is a chemical compound with formula NH2F. It is analogous to monochloramine, but seldom studied.
The term fluoroamine usually refers to amines with fluorinated substituents, an example being perfluorotributylamine (N(C4F9)3) and perfluoromethyldiethylamine (C2F5)2(CF3)N.[2]
References
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. pp. 4–73. ISBN 0-8493-0594-2.
- ↑ Michael G. Costello; Richard M. Flynn; John G. Owens (2001). "Fluoroethers and Fluoroamines". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. Weinstein: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0612211506122514.a01.pub2. ISBN 0-471-23896-1.
External links
- WebBook page for NH2F
- Monofluoroamine (PubChem page at U.S. National Library of Medicine)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.