 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
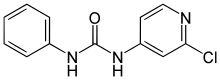
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-(2-Chloropyridin-4-yl)-N′-phenylurea | |
| Other names
N-(2-Chloro-4-pyridyl)-N'-phenylurea; CPPU; 4PU30 cpd | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.109.509 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H10ClN3O | |
| Molar mass | 247.68 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Density | 1.3839 at 25 deg C |
| Melting point | 165-170 deg C |
| 39 mg/L (pH 6.4, 21 deg C) | |
| Solubility in methanol | 119 g/L |
| Solubility in ethanol | 149 g/L |
| Solubility in acetone | 127 g/L |
| Solubility in chloroform | 2.7 g/L |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Forchlorfenuron is a plant growth regulator.[2] It has been approved for use on kiwifruit and grapes in the United States,[3] and it has been associated with news of watermelons exploding in China.[4]
References
- "TOXNET". toxnet.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 2018-05-31.
- ↑ "Commission Directive 2006/10/EC of 27 January 2006 amending Council Directive 91/414/EEC to include forchlorfenuron and indoxacarb as active substances. Official Journal of the European Union 2006-1-28". Archived from the original on 2012-10-08. Retrieved 2011-05-17.
- ↑ "Pesticide Fact Sheet for new chemical: Forchlorfenuron; issued: September 2004. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances (7501C)" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2011-06-26. Retrieved 2011-05-18.
- ↑ "Exploding watermelons! Acres of crops erupt - World news - Weird news - NBC News". NBC News. Retrieved 2011-05-17.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.