| County of Flanders Comté de Flandre | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 862–1791 | |||||||||
 Flag
 Coat of arms
| |||||||||
.svg.png.webp) French Flanders in France (1789 borders) | |||||||||
| Capital | Lille | ||||||||
| Government | |||||||||
| • Type | Province | ||||||||
| King of West Francia / King of France | |||||||||
• 862–877 | Charles II | ||||||||
• 1774–1791 | Louis XVI | ||||||||
| Governor of Flanders and Hainaut | |||||||||
• 1694–1711 | Louis-François de Boufflers | ||||||||
• 1787–1791 | Charles Eugène Gabriel de La Croix | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• County created | 862 | ||||||||
• Disestablished | 1791 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | France | ||||||||
French Flanders (French: La Flandre française, pronounced [flɑ̃dʁə fʁɑ̃sɛz])[1] is a part of the historical County of Flanders, where Flemish—a Low Franconian dialect cluster of Dutch—was (and to some extent, still is) traditionally spoken. The region lies in the modern-day northern French region of Hauts-de-France, and roughly corresponds to the arrondissements of Lille, Douai and Dunkirk on the northern border with Belgium. Together, with French Hainaut and Cambrésis, it makes up the French Department of Nord.

Geography
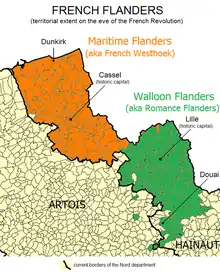
French Flanders consists, mostly, of flat marshlands in the coal-rich regions just south of the North Sea. It comprises two areas:
- French Westhoek to the northwest, lying between the river Lys and the North Sea, roughly the same area as the Arrondissement of Dunkirk;
- Walloon Flanders (French: La Flandre wallonne; Dutch: Waals Vlaanderen), to the southeast, south of the Lys and now the Arrondissements of Lille and Douai.
History
Once a part of ancient and medieval Francia from the inception of the Frankish kingdom (descended from the Empire of Charlemagne) under the Merovingian monarchs such as Clovis I, who was crowned at Tournai, Flanders gradually fell under the control of the English and then Spanish, becoming part of the Spanish Netherlands and retained by Spain at the end of the Eighty Years' War. When French national military power returned under the Bourbons with King Louis XIV "The Sun King" (1638–1715), a part of historically French Flanders was returned to the Kingdom.
The region now called "French Flanders" was once part of the feudal state County of Flanders, then part of the Southern Netherlands. It was separated from the county (part of Habsburgs' Burgundian inheritance) in 1659 due to the Peace of the Pyrenees, which ended the French-Spanish conflict in the Thirty Years War (1618–1648), and other parts of the region were added in successive treaties in 1668 and 1678. The region was ceded to the Kingdom of France, and became part of the province of Flanders and Hainaut. The bulk became part of the modern French administrative Nord department, although some western parts of the region, which separated in 1237 and became the County of Artois before the cession to the French, are now part of Pas-de-Calais.
During World War II, 'French Flanders' referred to all of Nord-Pas de Calais, which was first attached to the military administration of German-occupied Belgium, then part of Belgien-Nordfrankreich under a Reichskommissar, and finally part of a theoretical Reichsgau of Flanders.
Rich in coal, facing the North Sea, bordered by usually powerful neighbors, French Flanders has been fought over numerous times in the thousand years between the Middle Ages and World War II.
Language
The traditional language of northern French Flanders (Westhoek), related to the Dutch language, is known as West Flemish, specifically, a subdialect known as French Flemish, spoken by around 20,000 daily speakers and 40,000 occasional users.[2] The traditional language of Walloon Flanders (part of Romance Flanders) is Picard (and its dialects, such as Ch'ti or Rouchi). Many schools in this region teach Flemish to schoolchildren, partially in an effort to revive the language.[3]
Culture
In 2008, the success of the movie Bienvenue chez les Ch'tis illuminated this part of France to a wide audience.
See also
Sources and references
- ↑ Dutch: Frans-Vlaanderen; West Flemish: Frans-Vloandern
- ↑ http://www.uoc.edu/euromosaic/web/document/neerlandes/an/i1/i1.html
- ↑ Lambrechts, Toon. "French Flemish: group defends a dying language". Flanders Today. Archived from the original on 1 January 2021.
- Nouveau Petit Larousse Illustré, 1952.
- French Flanders
- Ethnologue Report for West Flemish
- Flemish in France
External links
- The Extent of Flemish in France in 1970, contains language maps Archived 29 September 2007 at the Wayback Machine