
Fresh Wharf was a wharf located in the City of London close to London Bridge, on the north bank of the River Thames.[1] The site was used as a quay in Roman times and later as an unloading place for Anglo-Saxon boats. A wharf was constructed there at some point in the medieval period and appears to have acquired its name from its customary usage as a landing place for fresh fish. In the 16th century, Fresh Wharf was made a "Legal Quay" authorised for the import of certain goods during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I of England. It expanded as London's river-borne trade grew in the 18th and 19th centuries, with large warehouses being established immediately behind the wharf. In the 20th century, the wharf's owners took over the adjoining wharves immediately upstream and downstream, built a new ten-storey warehouse and renamed the site New Fresh Wharf. By the end of the 1960s, however, London's docks had fallen into disuse with the advent of containerization, for which they were not suited, and the wharf was closed down in 1970. An office block was built on the site of the warehouse in 1977 and the former quayside is now part of a public footpath along the Thames.
Early history

A quay existed on the site as long ago as the Roman period,[2] but there is no evidence that it was used after 260 AD.[3] Its construction illustrated the effects of climate change in the Roman era. Due to a period of colder temperatures that led to more water being locked up in the polar icecaps, the sea level and thus the level of the Thames fell considerably in the centuries after Roman Londinium was founded. A revetment had been constructed at Fresh Wharf in the second century AD but by the third century the high water mark had dropped so much that the river wharves had to project much further out into the river to maintain the same depth of water. In the case of the timber quay at Fresh Wharf, it was constructed 8.25 metres (27.1 ft) in front of the earlier revetment.[4]
The date of establishment of Fresh Wharf is not known. In late Anglo-Saxon times (10th–11th century), the site of Fresh Wharf appears to have been merely a beach on which ships were grounded for off-loading.[5] A wharf was built there at some subsequent point during the medieval period; its name was first recorded as Fresshffysshewharfe in 1363, which was probably related to its appointment as one of the places authorised for the unloading of fish.[6] On the landward side, the wharf was accessed via Lower Thames Street a short distance down from the church of St Magnus-the-Martyr.[7] Excavations of 1974–5 on the site revealed much about the medieval buildings. [8]
It became one of the twenty "Legal Quays" of the City of London in 1559 with state authorisation to serve as one of the official landing and loading points for traders.[9] The wharf was listed as being "for fyshe and eele shippers".[10] During the Great Fire of London in September 1666, which started a short distance to the north in Pudding Lane, Fresh Wharf and all of the other Legal Quays were destroyed. They were quickly rebuilt and were all back in operation by the mid-1670s.[11] Another fire on 18 April 1760 resulted in the wharf and some of the surrounding area burning down.[12] The ownership of the wharf changed hands several times during the century, with its most notable owner being the famous actor David Garrick, who invested in a £1,500 mortgage (equivalent to £215,000 today) on the wharf in 1776. However, the investment turned out to be a financial disaster for Garrick when the debtor absconded to the Far East.[13]
Nineteenth century
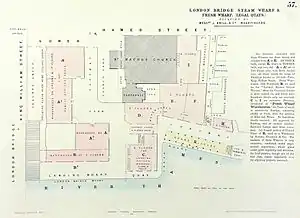
The 1824 Accounts Relating to the Port of London listed Fresh Wharf as having a river frontage of 137 ft (42 m), making it the second largest of the Legal Quays after Custom House Quay.[14] All of the Legal Quays, including Fresh Wharf, were compulsorily purchased by the government in 1805[15] but in 1827 the wharfinger John Knill was assigned the lease at a yearly rent of £1,555 after purchasing the fee simple from the Crown.[16]
By the 1840s, the wharf was being used by schooners transporting fruit from the Canary Islands, Azores and Mediterranean regions. As many as a dozen ships at a time would unload simultaneously, bringing six million oranges a year to London.[17] The wharf's trade was "exclusively Foreign, consisting chiefly of Fruit, with the addition of Silk and Wines"; it did not accept hazardous goods. It was run in conjunction with London Bridge Wharf, which was used by coasters and steamships.[18]
Fresh Wharf was described around this time as "covering an immense space of ground, and consisting of a great number of lofty warehouses, containing, in the whole, property valued at considerably over a million [pounds] sterling" (equivalent to £106,566,000 today).[19] All but one of the warehouses were of recent vintage and constructed of brick, other than the "very old" timber Crane House that adjoined Cox & Hammond's Quay.[18] It was severely damaged by fire again on 21 June 1858, causing the destruction of an estimated £100,000 of property stored in the wharf's warehouses.[19]
The Knills continued to run Fresh Wharf for the rest of the century and became a family of considerable note. They acquired a baronetcy that continues to this day; the second of the Knill baronets, Sir John Stuart Knill, became the first Roman Catholic Lord Mayor of London in 1892.[20]
Twentieth century
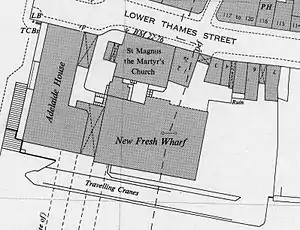
At the turn of the century, Fresh Wharf was a busy and profitable enterprise, dealing with 300,000 tons of cargo and over quarter of a million passengers a year.[21] The Fresh Wharf Company expanded its operations in the 1930s by leasing the whole of the river frontage from London Bridge Wharf, in front of the 1925 Adelaide House, to its neighbour immediately to the south, Cox and Hammond's Quay, which had originally been two separate quays of equally ancient vintage to Fresh Wharf and had likewise been named as Legal Quays in 1559. The combined wharves, now known as New Fresh Wharf, had two berths. The larger of the two measured 455 feet (139 m) and could accommodate vessels of up to 7,000 tons.[1] The position of Fresh Wharf made it the closest steamer wharf and associated warehouses to the centre of the City of London.[22] By 1937, New Fresh Wharf had 28 cranes and had diversified to handle a variety of general cargoes, green fruit and canned goods.[23] A new quay was constructed in front of the wharf in the 1930s and the existing jetty at London Bridge Wharf was extended.[1]

As well as handling goods, New Fresh Wharf was also used by passenger steamships. These were operated by the Queen Line of the New Medway Steam Packet Company, which ran daily services to Southend-on-Sea, Herne Bay, Margate and Ramsgate on one route, and to Southend, Clacton-on-Sea, Walton-on-the-Naze and Felixstowe on its other route. The Company moved its operations to Tower Pier from around 1935 onwards.[24] Passenger services also ran twice weekly to Amsterdam under the auspices of the Holland Steamship Company.[25]
The wharf narrowly escaped destruction during the Second World War when its southern neighbour, Nicholson's Wharf, was flattened by a V-1 flying bomb.[26] A regular passenger and cargo service between the wharf and the Canary Islands was maintained for a number of years after the war by the 10,123-ton MV Monte Ulia[1] and its 7,723-ton sister ship MV Monte Urquiola, operated by Naviera Aznar SA.[27] Such vessels were among the largest merchant ships ever to visit the Pool of London.[28] Writing in 1963, James Harold Bird observed how "during his lunch-hour the pale-faced London office worker can lean on the downstream parapet of London Bridge and watch Canary Island produce being unloaded to New Fresh Wharf below from vessels up to 500 feet long and delivered to a ten-storey warehouse."[29] The warehouse was constructed in 1953[30] and provided four million cubic feet of storage space. By this time the wharf had five travelling cranes and two conveyors, capable of transporting loads of up to five tons. Its river frontage measured 585 feet (178 m).[31]
Closure and redevelopment

Only a few years after Bird's description of the fruit ships unloading alongside London Bridge, the inner London docks fell into disuse as a result of trade moving to the container port downriver at Tilbury Docks. New Fresh Wharf closed for good in 1970[32] and in 1973 the warehouse was demolished.[30] Archaeological excavations on the site between 1974 and 1978 uncovered the remains of the Roman quay and revetment.[2] The demolished warehouse was eventually replaced by St Magnus House, an office building designed by Richard Seifert that was constructed in 1978.[1]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Ellmers, Chris; Werner, Alex (2000). London's Riverscape Lost and Found. London's Found Riverscape Partnership. p. 2. ISBN 1-874044-30-9.
- 1 2 Louise Miller; John Schofield; Michael Rhodes (1986). The Roman Quay at St. Magnus House, London: Excavations at New Fresh Wharf, Lower Thames Street, London, 1974-78. London & Middlesex Archaeological Society. ISBN 9780903290326.
- ↑ Brown, Nicholas Waldemar; Reed, Graham (2003). London's Waterfront: The Thames from Battersea to the Barrier. Burke's Peerage & Gentry. p. 64. ISBN 978-0-9711966-3-6.
- ↑ Sargent, Andrew (21 November 2013). The Story of the Thames. Amberley Publishing Limited. ISBN 978-1-4456-1201-0.
- ↑ Steane, John (30 October 2014). The Archaeology of Medieval England and Wales. Routledge. p. 133. ISBN 978-1-317-59994-4.
- ↑ Henry A Harben, 'Foxton Inn - Fresh Wharf Gateway', in A Dictionary of London (London, 1918), https://www.british-history.ac.uk/no-series/dictionary-of-london/foxton-inn-fresh-wharf-gateway (accessed 2 March 2015).
- ↑ Lockie, John (1810). Topography of London: Giving a Concise Local Description Of, and Accurate Direction To, Every Square, Street, Lane, Court, Dock, Wharf, Inn, Public Office, &c. in the Metropolis and Its Environs ... G. and W. Nicol.
- ↑ J Schofield, L Blackmore and J Pearce, London's Waterfront 1100-1666 (2018) passim.
- ↑ James Elmes (1831). A Topographical Dictionary of London and Its Environs: Containing Descriptive and Critical Accounts of All the Public and Private Buildings, Offices, Docks, Squares, Streets, Lanes, Wards, Liberties, Charitable, Scholastic and Other Establishments, with Lists of Their Officers, Patrons, Incumbents of Livings, &c. &c. &c. in the British Metropolis. Whittaker, Treacher and Arnot. p. 269.
- ↑ Rule, Fiona (2012). London's Docklands: A History of the Lost Quarter. Ian Allan Publishing. p. 97. ISBN 978-0-7110-3716-8.
- ↑ Rule (2012), pp. 13, 129
- ↑ John Timbs (1867). Curiosities of London: Exhibiting the Most Rare and Remarkable Objects of Interest in the Metropolis, with Nearly Sixty Years' Personal Recollections. Virtue. p. 341.
- ↑ McCusker, John J.; Morgan, Kenneth (2000). The Early Modern Atlantic Economy. Cambridge University Press. p. 81. ISBN 978-0-521-78249-4.
- ↑ House of Commons (1824). Parliamentary Papers, House of Commons and Command. H.M. Stationery Office.
- ↑ McCusker & Morgan (2000), p. 67
- ↑ Britain, Great (1827). The Public General Acts. Proprietors of the Law Journal Reports.
- ↑ John Leather (7 November 2013). The Gaff Rig Handbook: History, Design, Techniques, Developments. A&C Black. p. 181. ISBN 978-1-4081-2161-0.
- 1 2 Loveday, James Thomas (1857). Loveday's London Waterside Surveys: For the Use of Fire Insurance Companies, Showing Wharves and Granaries with the Buildings Connected on the Banks of the Thames from London Bridge to Rotherhithe [and] Tower Dock. The Author. p. 57.
- 1 2 Edmund Burke (1859). The Annual Register of World Events: A Review of the Year. Longmans, Green. p. 103.
- ↑ Fox-Davies, Arthur Charles (1895). Armorial Families: A Complete Peerage, Baronetage, and Knightage, and a Directory of Some Gentlemen of Coat-armour, and Being the First Attempt to Show which Arms in Use at the Moment are Borne by Legal Authority. Jack. p. 578.
- ↑ Report from the Joint Select Committee of the House of Lords and the House of Commons on the Port of London Bill. HMSO. 1903. p. 99.
- ↑ James Harold Bird (1957). The Geography of the Port of London. Hutchinson University Library. p. 137.
- ↑ "Port Cities: The working Thames - The riverside wharves". www.portcities.org.uk. Retrieved 26 April 2019.
- ↑ Andrew Gladwell (29 August 2013). River Medway Pleasure Steamers. Amberley Publishing Limited. ISBN 978-1-4456-2394-8.
- ↑ Ward, Lock; Company, ltd (1929). Handbook to Holland. Ward, Lock. p. 22.
- ↑ London County Council (2005). The London County Council bomb damage maps, 1939-1945. London Topographical Society. ISBN 9780902087514.
- ↑ Thurman, Chris (2002). London's River. Tempus. p. 32. ISBN 9780752423791.
- ↑ "PortCities London: The working Thames". National Maritime Museum. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ↑ James Harold Bird (1963). The major seaports of the United Kingdom. Hutchinson. p. 399.
- 1 2 Ken Steedman; Tony Dyson; John Schofeld; A. G. Vince; Jennifer Hillam (1992). The Bridgehead and Billingsgate to 1200. London & Middlesex Archaeological Society. p. 21.
- ↑ Port of London Guide. Coram Publishers. 1957. p. 181.
- ↑ Christmas, Linda (3 April 1972). "Running out of steam". The Guardian. p. 10.
External links
![]() Media related to Fresh Wharf at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Fresh Wharf at Wikimedia Commons