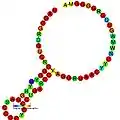
Gag/pol translational readthrough site (or Retroviral readthrough element) is a cis-regulatory element found in retroviruses.[1] The readthrough site facilitates the mechanism of translation readthrough of the stop codon at the gag-pol junction producing the gag and pol fusion protein in certain retroviruses. Retroviruses whose gag and pol genes are in the same reading frame often depend upon approximately 5% read-through of the gag UAG termination codon to form the gag-pol polyprotein. This readthrough is usually dependent on a pseudoknot located eight nucleotides downstream of the stop codon (UAG). Sequence conservation is found in the second pseudoknot loop.
References
- ↑ Wills NM, Gesteland RF, Atkins JF (September 1994). "Pseudoknot-dependent read-through of retroviral gag termination codons: importance of sequences in the spacer and loop 2". EMBO J. 13 (17): 4137–4144. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06731.x. PMC 395336. PMID 8076609.
- ↑ Family RF01073. Derived from Pseudobase PKB00047 PKB00078 PKB00079 PKB00088 PKB00098 PKB00099
- ↑ Family RF01092. Derived from Pseudobase PKB00048
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.