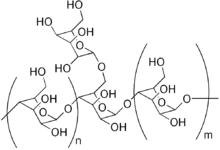
Galactomannans are polysaccharides consisting of a mannose backbone with galactose side groups, more specifically, a (1-4)-linked beta-D-mannopyranose backbone with branchpoints from their 6-positions linked to alpha-D-galactose, (i.e. 1-6-linked alpha-D-galactopyranose).
In order of increasing number of mannose-to-galactose ratio:[1]
- fenugreek gum, mannose:galactose ~1:1
- guar gum, mannose:galactose ~2:1
- tara gum, mannose:galactose ~3:1
- locust bean gum or carob gum, mannose:galactose ~4:1
- cassia gum, mannose:galactose ~5:1
Galactomannans are often used in food products to increase the viscosity of the water phase.
Guar gum has been used to add viscosity to artificial tears, but is not as stable as carboxymethylcellulose.[2]
Food use
Galactomannans are used in foods as stabilisers. Guar and locust bean gum (LBG) are commonly used in ice cream to improve texture and reduce ice cream meltdown. LBG is also used extensively in cream cheese,[3] fruit preparations and salad dressings. Tara gum is seeing growing acceptability as a food ingredient but is still used to a much lesser extent than guar or LBG. Guar has the highest usage in foods, largely due to its low and stable price.
Clinical use
Galactomannan is a component of the cell wall of the mold Aspergillus[4] and is released during growth. Detection of galactomannan in blood is used to diagnose invasive aspergillosis infections in humans. This is performed with monoclonal antibodies in a double-sandwich ELISA; this assay from Bio-Rad Laboratories was approved by the FDA in 2003 and is of moderate accuracy.[5] The assay is most useful in patients who have had hemopoietic cell transplants (stem cell transplants). False positive Aspergillus Galactomannan test have been found in patients on intravenous treatment with some antibiotics or fluids containing gluconate or citric acid such as some transfusion platelets, parenteral nutrition or PlasmaLyte.[6][7]
References
- ↑ Peter A. Williams; Glyn O. Phillips (2004). Gums and Stabilisers for the Food Industry 12. Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 311. ISBN 978-0-85404-891-5.
- ↑ Simmons, P.A. (May 2004). "Modeling of Ocular Viscosity for Mid–viscosity Artificial Tear Preparations". Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 45 (13): 3893.
- ↑ "CAROB AND LOCUST BEAN GUM - LBG PROPERTIES". CyberColloids Ltd.
- ↑ Bart-Delabesse E, Basile M, Al Jijakli A, et al. (October 2005). "Detection of Aspergillus galactomannan antigenemia to determine biological and clinical implications of beta-lactam treatments". J. Clin. Microbiol. 43 (10): 5214–20. doi:10.1128/JCM.43.10.5214-5220.2005. PMC 1248458. PMID 16207986.
- ↑ Pfeiffer CD, Fine JP, Safdar N (2006). "Diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis using a galactomannan assay: a meta-analysis". Clin Infect Dis. 42 (10): 1417–27. doi:10.1086/503427. PMID 16619154.
- ↑ Martin-Rabadan, P.; Gijon, P.; Alonso Fernandez, R.; Ballesteros, M.; Anguita, J.; Bouza, E. (18 May 2012). "False-positive Aspergillus Antigenemia Due to Blood Product Conditioning Fluids". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 55 (4): e22–e27. doi:10.1093/cid/cis493. PMID 22610929.
- ↑ Spriet, Isabel; Lagrou, Katrien; Maertens, Johan; Willems, Ludo; Wilmer, Alexander; Wauters, Joost; Warnock, D. W. (March 2016). "Plasmalyte: No Longer a Culprit in Causing False-Positive Galactomannan Test Results". Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 54 (3): 795–797. doi:10.1128/JCM.02813-15. PMC 4767971. PMID 26719444.