 | |
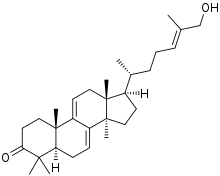
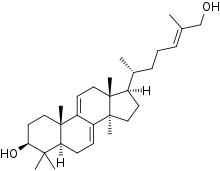 Ganoderol A (top) and ganoderol B | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H46O2 (A) C30H48O2 (B) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Ganoderols are triterpenes isolated from Ganoderma lucidum.[1][2]
References
- ↑ Fatmawati, S; Shimizu, K; Kondo, R (2011). "Ganoderol B: A potent α-glucosidase inhibitor isolated from the fruiting body of Ganoderma lucidum". Phytomedicine. 18 (12): 1053–5. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2011.03.011. PMID 21596546.
- ↑ Liu, J; Shimizu, K; Konishi, F; Kumamoto, S; Kondo, R (2007). "The anti-androgen effect of ganoderol B isolated from the fruiting body of Ganoderma lucidum". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 15 (14): 4966–72. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2007.04.036. PMID 17499997.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.