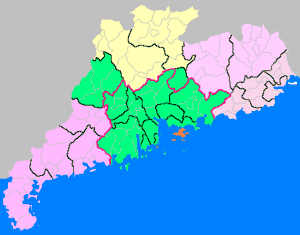
Gaoyao
高要区 Koyiu | |
|---|---|
 | |
.png.webp) Location of Gaoyao (red) within Zhaoqing City and Guangdong province | |
 Gaoyao Location of the seat in Guangdong | |
| Coordinates: 23°02′N 112°27′E / 23.033°N 112.450°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Guangdong |
| Prefecture-level city | Zhaoqing |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,206 km2 (852 sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Gaoyao, Zhaoqing | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 高要 | ||||||||||
| Postal | Koyiu | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Gaoyao, alternately romanized as Koyiu, is an urban district of Zhaoqing in western Guangdong, China. Population: 706,000.
Name
Gaoyao—literally "high-&-wanting"—is a former name of the Lingyang Gorge on the Xi River. It was originally the name of the surrounding land but came to be used for the area's seat of government. Gaoyao is the pinyin romanization of the Chinese name, based on its Mandarin pronunciation; the former Chinese Postal Map spelling was based on the local Cantonese pronunciation of the same name. Gaoyao has also sometimes been romanized as Kaou Yaou.[1]
Geography
Gaoyao is located on the southern bank of the Xi River, opposite central Zhaoqing. Both are about 100 kilometers (62 mi) away from Guangzhou, the provincial capital.
Climate
| Climate data for Gaoyao (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 28.3 (82.9) |
31.4 (88.5) |
32.4 (90.3) |
34.4 (93.9) |
34.9 (94.8) |
37.9 (100.2) |
38.5 (101.3) |
38.1 (100.6) |
36.9 (98.4) |
35.8 (96.4) |
33.1 (91.6) |
30.0 (86.0) |
38.5 (101.3) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 18.9 (66.0) |
20.9 (69.6) |
23.5 (74.3) |
27.9 (82.2) |
31.3 (88.3) |
33.2 (91.8) |
34.2 (93.6) |
33.9 (93.0) |
32.3 (90.1) |
29.6 (85.3) |
25.6 (78.1) |
20.8 (69.4) |
27.7 (81.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 13.9 (57.0) |
16.0 (60.8) |
19.2 (66.6) |
23.4 (74.1) |
26.5 (79.7) |
28.2 (82.8) |
28.9 (84.0) |
28.6 (83.5) |
27.2 (81.0) |
24.2 (75.6) |
19.9 (67.8) |
15.2 (59.4) |
22.6 (72.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 10.6 (51.1) |
12.7 (54.9) |
16.1 (61.0) |
20.3 (68.5) |
23.3 (73.9) |
25.1 (77.2) |
25.6 (78.1) |
25.3 (77.5) |
23.9 (75.0) |
20.3 (68.5) |
16.0 (60.8) |
11.5 (52.7) |
19.2 (66.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 3.1 (37.6) |
3.9 (39.0) |
6.1 (43.0) |
10.7 (51.3) |
16.8 (62.2) |
20.4 (68.7) |
22.9 (73.2) |
22.6 (72.7) |
18.8 (65.8) |
13.4 (56.1) |
5.3 (41.5) |
1.7 (35.1) |
1.7 (35.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 51.8 (2.04) |
43.9 (1.73) |
76.2 (3.00) |
130.3 (5.13) |
189.2 (7.45) |
212.3 (8.36) |
189.1 (7.44) |
188.8 (7.43) |
150.6 (5.93) |
56.6 (2.23) |
41.9 (1.65) |
37.8 (1.49) |
1,368.5 (53.88) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 7.9 | 10.3 | 14.8 | 14.9 | 18.0 | 19.7 | 16.8 | 16.0 | 11.8 | 5.0 | 5.5 | 5.9 | 146.6 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 78 | 79 | 81 | 80 | 81 | 81 | 79 | 80 | 79 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 79 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 99.7 | 75.9 | 58.2 | 77.2 | 124.5 | 147.0 | 191.8 | 183.8 | 173.3 | 182.9 | 156.3 | 140.5 | 1,611.1 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 30 | 24 | 16 | 20 | 30 | 36 | 46 | 46 | 47 | 51 | 48 | 42 | 36 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[2][3] | |||||||||||||
History
Gaoyao was a county of the Qin and Han and its eponymous county seat was the principal settlement of the area. Under the Sui, the administration relocated across the river to Duanzhou, which was renamed Zhaoqing under the Song. Gaoyao continued as a separate county in Zhaoqing Commandery.[1] It was promoted to a county-level city in 1993 and later to urban district status.
Tourism
Places of interest include the Red Mansion and Gaoyao Xuegong Pavilion. There are also 3 pagodas that can be seen in Gaoyao.
Image gallery
Administrative divisions
Gaoyao has jurisdiction over one subdistrict and several towns:
| Name | Chinese (S) | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2010)[4] | Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nan'an Subdistrict | 南岸街道 | Nán'àn Jiēdào | 81,886 | 36.5 |
| Hetai town | 河台镇 | Hétái Zhèn | 33,660 | 150 |
| Lecheng town | 乐城镇 | Lèchéng Zhèn | 24,337 | 94 |
| Shuinan town | 水南镇 | Shuǐnán Zhèn | 11,598 | 126 |
| Lubu town (Lukpo) | 禄步镇 | Lùbù Zhèn | 63,488 | 254 |
| Xiaoxiang town | 小湘镇 | Xiǎoxiāng Zhèn | 30,964 | 200 |
| Dawan town | 大湾镇 | Dàwān Zhèn | 34,535 | 108 |
| Xinqiao town | 新桥镇 | Xīnqiáo Zhèn | 39,265 | 41.8 |
| Baizhu town | 白诸镇 | Báizhū Zhèn | 36,977 | 128 |
| Liantang town | 莲塘镇 | Liántáng Zhèn | 58,429 | 125 |
| Huodao town | 活道镇 | Huódào Zhèn | 41,358 | 228 |
| Jiaotang town | 蛟塘镇 | Jiāotáng Zhèn | 33,060 | 130 |
| Huilong town | 回龙镇 | Huílóng Zhèn | 25,426 | 124.25 |
| Baitu town | 白土镇 | Báitǔ Zhèn | 71,430 | 108.4 |
| Jindu town | 金渡镇 | Jīndù Zhèn | 43,623 | 101.23 |
| Jinli town | 金利镇 | Jīnlì Zhèn | 93,792 | 141.3 |
| Xiangang town | 蚬岗镇 | Xiǎngǎng Zhèn | 29,292 | 96.6 |
Miscellaneous
- Gaoyao is closely connected with the Duanzhou District of Zhaoqing City, geographically as well as culturally. The two urban districts are connected by two road bridges and a railway bridge.
- Gaoyao is also a known hometown for many Overseas Chinese. There is a large community from Gaoyao in Sydney, Australia.[5][6]
some notable figures:
- Liang Han Chao (梁寒操): historian, educator, and also founder of Kwangtung cultural and history periodical.
- Herbert Chow Ciu Lung (周小龍): founder of chickeeduck clothing, also a Hong Kong social activist.
- Joshua Wong Chi-fung (黃之鋒): Hong Kong male politician
- Fong Lai Ying (方麗盈): Hong Kong experienced female singer
References
Citations
- 1 2 Bolton & al. (1941), p. 262.
- ↑ 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 28 May 2023.
- ↑ 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 28 May 2023.
- ↑ shi, Guo wu yuan ren kou pu cha ban gong; council, Guo jia tong ji ju ren kou he jiu ye tong ji si bian = Tabulation on the 2010 population census of the people's republic of China by township / compiled by Population census office under the state; population, Department of; statistics, employment statistics national bureau of (2012). Zhongguo 2010 nian ren kou pu cha fen xiang, zhen, jie dao zi liao (Di 1 ban. ed.). Beijing Shi: Zhongguo tong ji chu ban she. ISBN 978-7-5037-6660-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ Heritage Council of NSW: Yiu Ming Temple
- ↑ Choi, C.Y., , Sydney University Press, Sydney, 1975
Bibliography
- Bolton, Kingsley; et al. (1941), Triad Societies, Vol. 5, Abingdon: Routledge, reprinted 2000.
- Choi, C.Y. (1975), Chinese Migration and Settlement in Australia, Sydney: Sydney University Press
External links
- http://www.gaoyao.gov.cn (in Chinese)