| Signed | January 10, 1941 |
|---|---|
| Location | Moscow, Russian SFSR, Soviet Union |
| Signatories | |
| Languages | German, Russian |
The German–Soviet Border and Commercial Agreement, signed on January 10, 1941, was a broad agreement which settled border disputes, and continued raw materials and war machine trade between the Soviet Union and Nazi Germany. The agreement continued the countries' relationship that started in 1939 with the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, which contained secret protocols that divided Eastern Europe between the Soviet Union and Germany. The relationship had continued with the subsequent invasions by Germany and the Soviet Union of that territory. The agreement contained additional secret protocols, settling a dispute regarding land in Lithuania, which had been split between both countries. The agreement continued the German–Soviet economic relations that had been expanded by the 1939 German–Soviet Commercial Agreement and the more comprehensive 1940 German–Soviet Commercial Agreement.
The agreement proved to be short-lived. Just six months after it was signed, Germany invaded the Soviet Union, which ended economic relations between them. The raw materials imported by Germany from the Soviet Union between 1939 and 1941 played a major role in supporting the German war effort against the Soviet Union after 1941.
Background
Resource requirements
Germany lacked natural supplies of several key raw materials needed for economic and military operations. German planners in mid-1939 determined that the nation possessed only two to three months' supply of rubber stocks and three to six months of oil stocks.[1] They estimated that, after a planned German attack on Poland and the expected subsequent allied naval blockade, the Soviet Union would become the only potential supplier for many key raw materials needed for a war.[1]
Soviet-German 1939 agreements and the division of Eastern Europe

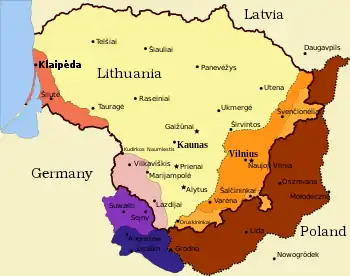
On August 19, 1939, the Soviet Union and Germany entered German–Soviet Commercial Agreement (1939) providing for the trade of certain German military and civilian equipment in exchange for Soviet raw materials.[2][3] On August 23, they entered the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, which contained secret protocols dividing the states of Northern and Eastern Europe into German and Soviet "spheres of influence."[4]
One week after the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact's signing, the partition of Poland commenced with the German invasion of western Poland,[5] followed by the Soviet Union's invasion of Eastern Poland on September 17, which included coordination with German forces.[6] Three Baltic States described by the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, were given no choice but to sign a "Pact of defense and mutual assistance" which permitted the Soviet Union to station troops in them.[7]
Eleven days after the Soviet invasion of Eastern Poland, the parties modified the secret protocol of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact in an agreement called the German–Soviet Boundary and Friendship Treaty[8] that contained a "Secret Additional Protocol." Among other things, the agreement allotted Germany a larger part of Poland and transferred Lithuania to the Soviets.[7] However, one piece of Lithuania referred to as the "Lithuania Strip", the left bank of river Scheschupe, was to remain a German territory.[7]
1940 German–Soviet Economic Relationship

Hitler's press for a German invasion of Poland in 1939 placed tremendous strain on the German military, which was not scheduled to be ready for total war until 1942 or 1943.[9] In addition, Germany faced critical shortages in oil, rubber and other materials needed to prosecute even just a western offensive.[10] The only remaining state capable of supplying Germany with the requisite raw materials was the Soviet Union.[10] At the same time, the Soviets' demands for manufactured goods, such as German machines, were increasing while its ability to import those goods from outside decreased when many countries ceased trading relations after the Soviet entry into the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact.[11] On February 11, 1940, Germany and the Soviet Union entered into the German–Soviet Commercial Agreement, an intricate trade pact in which the Soviet Union would send Germany 650 million Reichsmark in raw materials in exchange for 650 million Reichsmark in machinery, manufactured goods and technology.[12][13] The trade pact helped Germany to surmount the British blockade of Germany.[2] The Soviet Union became a major supplier of vital materials to Germany, including oil, copper, nickel, chrome, platinum, lumber and grain.[14]
The Baltics and Bessarabia
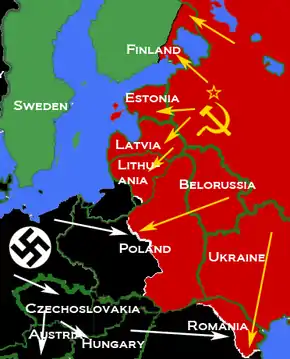

In mid-June 1940, Soviet NKVD troops raided border posts in Lithuania, Estonia and Latvia, resulting in those states' annexation into the Soviet Union, including the whole of Lithuania, including the Scheschupe area, which was to be given to Germany.[7][15] On June 26, the Soviet Union issued an ultimatum demanding Bessarabia, Bukovina, and the Hertsa region from Romania. After the Soviets agreed with Germany that they would limit their claims in Bukovina to northern Bukovina, Germany urged Romania to accept the ultimatum.[16] With France no longer in a position to be the guarantor of the status quo in Eastern Europe, and the Third Reich pushing Romania to make concessions to the Soviet Union, the Romanian government gave in, following Italy's counsel and Vichy France's recent example. After the Soviet occupation of Bessarabia, around 100,000 Volksdeutsche living in Bessarabia began immigrating to Germany.[16]
That summer, Germany grew even more dependent on Soviet imports.[17] German acquisitions of France, the Netherlands, and Belgium created additional demand while decreasing avenues for indirect supply.[17]
Last Soviet attempts to join the Axis
Hitler had been considering war with the Soviet Union since July 1940.[13] However, after Germany entered the Axis Pact with Japan and Italy, in October 1940, the Soviet Union explored a possible entry into the Axis themselves.[18] After long discussions and proposals, Germany presented the Soviets with a draft written Axis pact agreement defining the world spheres of influence of the four proposed Axis powers (Japan, Germany, Soviet Union, Italy).[19][20][21] Eleven days later,[22] the Soviets presented a Stalin-drafted written counterproposal where they would accept the four power pact, but it included Soviet rights to Bulgaria and a world sphere of influence focus on the area around modern Iraq and Iran.[23] The Soviet offer came concurrently with massive economic efforts to Germany.[24] The Soviets promised by May 11, 1941, the delivery of 2.5 million tons of grain—1 million tons above its current obligations.[23] They also promised full compensation for the Volksdeutsche property claims.[23]
Shortly thereafter, Hitler issued a secret directive on the eventual attempts to invade the Soviet Union.[22][25] Stalin's written draft counter-proposal was ignored,[26][27] which worsened tensions between the countries.[28]
Negotiations



In October 1940, German officials estimated that their raw material supplies could comfortably last only though the summer of 1941.[28] The situation was much more dire for rubber, the use for which in boots and tires was vital for any mobile army.[28] German stocks had fallen to only 1,500 tons.[28] The secret protocols had also caused Hitler to be in the humiliating position of having to hurriedly evacuate ethnic German families, the Volksdeutsche, who had lived in Finland and the Baltic countries for centuries, while officially condoning the invasions.[29][30] The Soviet annexations in Romania caused further strain.[31] While Germany had given the Soviets Bessarabia in the secret protocols, it had not given them Bukovina.[31] Germany wanted the 100,000 tons of grain for which they had previously contracted with Bessarabia, guarantees of German property safety, guarantees for 125,000 Volksdeutsche in Bessarabia and Bukovina, and reassurance that the train tracks carrying Romanian oil would be left alone.[30]
While Hitler planned for war in the east, he wanted an additional economic deal to get what he could from the Soviet Union before the invasion, while other German officials wanted such a deal in the hopes that it could change the current anti-Soviet direction of German policy.[28] Meanwhile, because of delivery difficulties and other issues, doubts began to arise about whether the German–Soviet Commercial Agreement would continue to be effective.[28]
Furthermore, talks became heated around the issue of the "Lithuanian Strip".[32] When the Soviets occupied the whole of Lithuania on June 15, this included the Strip, which had been promised to Germany in the "Secret Additional Protocols" German–Soviet Boundary and Friendship Treaty modifying the secret protocols of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact.[33]
Negotiations began in Moscow on October 30.[34] German military economic negotiators had hoped for success in the negotiations, in part, because they felt this would strengthen their arguments against Hitler's then increasingly anti-Soviet policy.[34] The parties came closer to agreements on German 38-cm turrets, but the Soviets continued to resist demands for a full reimbursement of Volksdeutsche property.[34] Instead of permitting full indemnification, the Soviets put restrictions on the wealth that the Volksdeutsche could take with them and limited the totals that the Soviets would apply to the Reich's clearing accounts.[35] In November, negotiations proceeded well for Germany on potential modifications for year two of the German-Soviet Commercial Agreement, with the Soviets first increasing their grain offer from 1.2 million tons to 1.5 million, and then up to Germany's demand for 2.5 million tons.[36] Negotiations regarding the "Lithuanian Strip" required Hitler's direct intervention, so negotiations were briefly suspended on November 29 awaiting his actions.[36]
The parties further negotiated over the percentage of nickel each would receive from a Finnish nickel mine at Petsamo[36] and the amount that the Soviets would compensate Germany for their property claims in the Baltics, now occupied by the Soviet Union.[32] Progress was made on the Volksdeutsche property front, with total compensation between 200 million and 350 million Reichsmarks, while the Soviets requested 50 million Reichsmarks for their property claims in German-occupied territories.[37] They reached general agreement on German shipments of 10.5-cm flak cannons, gold, machinery and other items.[37]
Hitler desired an arrangement because German planners were estimating that German food, oils and nonferrous metals would run out in 1941, and German rubber supplies could run out almost immediately, especially if Trans-Siberian or blockade-breaker shipments failed to arrive.[38] German allies, such as Italy, were in even worse shape for key raw materials.[38]
Knowing they were preparing for an invasion of the Soviet Union, German negotiators pushed to delay the delivery of German goods beyond the summer of 1941.[32] Suspicious of German delays, in December, the Soviets demanded that all questions pending between the countries be resolved before an agreement could be made.[32] Tensions had already built after Germany had ignored Stalin's letter regarding Axis membership, with negotiators almost coming to blows at one point.[32]
The Agreement


On January 10, 1941, the German ambassador to Moscow von Schulenburg and Commissar for Foreign Affairs Vyacheslav Molotov signed agreements in Moscow to settle all of the open disputes that the Soviets had demanded.[32]
The agreement included relatively few substantially new economic elements.[32] It extended trade regulation of the 1940 German–Soviet Commercial Agreement until August 1, 1942, and increased deliveries above the levels of year one of that agreement to 620 to 640 million Reichsmark.[39][40] The agreement also finalized issues over transit costs for shipped goods, settled issues over the delivery schedules for goods shipped in year two of the German-Soviet Commercial Agreement, settled trading rights in the Baltics and Bessarabia and calculated the compensation for German property interests in the Baltic States now occupied by the Soviets.[32]
Because of a stronger German negotiation position, German Foreign Ministry official Karl Schnurre concluded that, in economic terms, the agreement was "the greatest Germany ever concluded, going well beyond the previous year's February agreement."[41] The agreement included Soviet commitments to 2.5 million tons of grain shipments and 1 million tons of oil shipments, as well as large amounts of nonferrous and precious metals.[41] German Special Ambassador Karl Ritter, in a state of near-euphoria over Germany's achievement, wrote a directive to all German embassies that "While Britain and the United States have up to now been unsuccessful in their efforts to come to an agreement with the Soviet Union in any field, the Soviet Union has concluded with Germany, the largest contract ever between two states."[42]
The agreement further covered the migration to Germany within two and a half months of Volksdeutsche, ethnic Germans and German citizens in Soviet-held Baltic and Balkan territories, and the migration to the Soviet Union of ethnic Russians, Baltic and "White Russian" "nationals" in German-held territories.[39] In many cases, the resulting population transfers of Volksdeutsche were to land previously held by ethnic Poles or others in Nazi-occupied territories.
The agreement also formally set the border between Germany and the Soviet Union between the Igorka river and the Baltic Sea.[39]
Secret protocols in the new agreement stated that Germany would renounce its claims to the Lithuanian Strip in the "Secret Additional Protocols" of the German–Soviet Boundary and Friendship Treaty and that the territory would be regarded as within the Soviet sphere of influence, for which Germany would be paid 7.5 million dollars (31.5 million Reichsmark).[32] Because of currency fluctuation issues, the parties used American dollar demarcations for compensation totals.[32]
On January 17, 1941, Molotov asked German officials whether the parties could then work out an agreement for entry into the Axis pact.[43] Molotov expressed astonishment at the absence of any answer to the Soviets' November 25 offer to join the Pact.[43] They never received an answer.[43] Germany was already planning its invasion of the Soviet Union. On December 18, 1940, Hitler had signed War Directive No. 21 to the German high command for an operation now codenamed Operation Barbarossa stating: "The German Wehrmacht must be prepared to crush Soviet Russia in a quick campaign."[44] Hitler directed Raeder that Germany would have to take Polyanry and Murmansk at that time to cut off access to aid that would come to the Soviet Union.[45]
Total trade
During both the first period of the 1940 German–Soviet Commercial Agreement (February 11, 1940, to February 11, 1941) and the second (February 11, 1941, until the Pact was broken), Germany received massive quantities of raw materials, including over:[46][47]
- 1,600,000 tons of grains
- 900,000 tons of oil
- 200,000 tons of cotton
- 140,000 tons of manganese
- 200,000 tons of phosphates
- 20,000 tons of chrome ore
- 18,000 tons of rubber
- 100,000 tons of soybeans
- 500,000 tons of iron ores
- 300,000 tons of scrap metal and pig iron
- 2,000 kilograms of platinum
Large amounts of crude oil were delivered, with German documents in July 1940 already indicating that the Soviets had delivered crude oil at a rate of 150,000 tons a month for five months in 900 German tank cars exclusively reserved for it.[48]
The trade pact helped Germany to surmount the British blockade of Germany.[2] By June 1940, Soviet imports comprised over 50% of Germany's total imports, and often exceed 70% of total German imports before Hitler broke the pact in June 1941.[49]
Hitler breaks the Pact
On June 22, 1941, Germany began Operation Barbarossa, the invasion of the Soviet Union through the territories that the two countries had previously divided.[5] Despite fears causing the Soviet Union to enter deals with Germany in 1939, that Germany came so close to destroying the Soviet Union was due largely to Soviet actions taken from 1939 to 1941.[50] Without Soviet imports, German stocks would have run out in several key products by October 1941, within three and a half months.[51] Germany would have already run through their stocks of rubber and grain before the first day of the invasion were it not for Soviet imports:[51]
Tot USSR
importsJune 1941
German StocksJune 1941 (w/o
USSR imports)Oct 1941
German StocksOct 1941 (w/o
USSR imports)Oil Products 912 1350 438 905 -7 Rubber 18.8 13.8 -4.9 12.1 -6.7 Manganese 189.5 205 15.5 170 -19.5 Grain 1637.1 1381 -256.1 761 -876.1 *German stocks in thousands of tons (with and without USSR imports-Oct 1941 aggregate)
Without Soviet deliveries of these four major items, Germany could barely have attacked the Soviet Union, let alone come close to victory, even with more intense rationing.[52]
Three years later, Friedrich Werner von der Schulenburg was later executed as one of the conspirators in the July 20, 1944, Plot to assassinate Adolf Hitler.[53]
See also
Notes
- 1 2 Ericson 1999, p. 54
- 1 2 3 Shirer 1990, p. 668
- ↑ Ericson 1999, p. 57
- ↑ Text of the Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact, executed August 23, 1939
- 1 2 Roberts 2006, p. 82
- ↑ Roberts 2006, p. 43
- 1 2 3 4 Wettig, Gerhard, Stalin and the Cold War in Europe, Rowman & Littlefield, Landham, Md, 2008, ISBN 0-7425-5542-9, page 20-21
- ↑ "German–Soviet Boundary and Friendship Treaty". Archived from the original on 2016-08-20. Retrieved 2009-02-02.
- ↑ Ericson 1999, pp. 63–4
- 1 2 Ericson 1999, pp. 61–71
- ↑ Ericson 1999, p. 66
- ↑ Ericson 1999, p. 103
- 1 2 Weeks, Albert L., Stalin's Other War: Soviet Grand Strategy, 1939–1941, Rowman & Littlefield, 2003, ISBN 0-7425-2192-3, page 74–75
- ↑ Moss, Walter, A History of Russia: Since 1855, Anthem Press, 2005, ISBN 1-84331-034-1, page 291
- ↑ Senn, Alfred Erich, Lithuania 1940: Revolution from Above, Amsterdam, New York, Rodopi, 2007 ISBN 978-90-420-2225-6
- 1 2 Nekrich, Ulam & Freeze 1997, p. 181
- 1 2 Ericson 1999, pp. 127–128
- ↑ Roberts 2006, p. 58
- ↑ Nekrich, Ulam & Freeze 1997, p. 201
- ↑ Roberts 200645
- ↑ Brackman 2001, p. 343
- 1 2 Nekrich, Ulam & Freeze 1997, pp. 202–205
- 1 2 3 Nekrich, Ulam & Freeze 1997, p. 203
- ↑ Weinberg 1995, p. 201
- ↑ Roberts 2006, p. 59
- ↑ Donaldson, Robert H. and Joseph L. Nogee, The Foreign Policy of Russia: Changing Systems, Enduring Interests, M.E. Sharpe, 2005, ISBN 0-7656-1568-1, pages 65–66
- ↑ Churchill, Winston, The Second World War, Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 1953, ISBN 0-395-41056-8, pages 520–521
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Ericson 1999, p. 146
- ↑ Shirer 1990, p. 665
- 1 2 Ericson 1999, p. 134
- 1 2 Shirer 1990, p. 794
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Ericson 1999, pp. 150–53
- ↑ Weinberg, Gerhard L., Germany, Hitler, and World War II: Essays in Modern German and World History, Cambridge University Press, 1996, ISBN 0-521-56626-6, page 178
- 1 2 3 Ericson 1999, p. 144
- ↑ Ericson 1999, p. 138
- 1 2 3 Ericson 1999, pp. 147–8
- 1 2 Ericson 1999, p. 149
- 1 2 Ericson 1999, p. 151
- 1 2 3 Johari, J.C., Soviet Diplomacy 1925–41: 1925–27, Anmol Publications PVT. LTD., 2000, ISBN 81-7488-491-2 pages 134–137
- ↑ Ericson 1999, p. 238
- 1 2 Wegner 1997, p. 108
- ↑ Wegner 1997, p. 109
- 1 2 3 Weinberg 1995, p. 202
- ↑ Brackman 2001, p. 344
- ↑ Philbin III 1994, p. 51
- ↑ Ericson 1999, pp. 195–9
- ↑ Philbin III 1994, p. 47
- ↑ Philbin III 1994, p. 48
- ↑ Ericson 1999, pp. 208–9
- ↑ Ericson 1999, p. 181
- 1 2 Ericson 1999, pp. 202–205
- ↑ Ericson 1999, p. 182
- ↑ Shirer 1990, p. 1392
References
- Brackman, Roman (2001), The Secret File of Joseph Stalin: A Hidden Life, Frank Cass Publishers, ISBN 0-7146-5050-1
- Ericson, Edward E. (1999), Feeding the German Eagle: Soviet Economic Aid to Nazi Germany, 1933–1941, Greenwood Publishing Group, ISBN 0-275-96337-3
- Hehn, Paul N. (2005), A Low Dishonest Decade: The Great Powers, Eastern Europe, and the Economic Origins of World War II, 1930–1941, Continuum International Publishing Group, ISBN 0-8264-1761-2
- Nekrich, Aleksandr Moiseevich; Ulam, Adam Bruno; Freeze, Gregory L. (1997), Pariahs, Partners, Predators: German–Soviet Relations, 1922–1941, Columbia University Press, ISBN 0-231-10676-9
- Philbin III, Tobias R. (1994), The Lure of Neptune: German-Soviet Naval Collaboration and Ambitions, 1919–1941, University of South Carolina Press, ISBN 0-87249-992-8
- Roberts, Geoffrey (2006), Stalin's Wars: From World War to Cold War, 1939–1953, Yale University Press, ISBN 0-300-11204-1
- Shirer, William L. (1990), The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich: A History of Nazi Germany, Simon and Schuster, ISBN 0-671-72868-7
- Wegner, Bernd (1997), From Peace to War: Germany, Soviet Russia, and the World, 1939–1941, Berghahn Books, ISBN 1-57181-882-0
- Weinberg, Gerhard L. (1995), A World at Arms: A Global History of World War II, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-55879-4