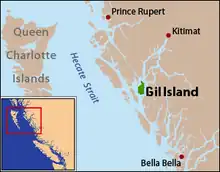
Gil Island is an island on the North Coast of British Columbia, Canada, located on the west side of Whale Channel in the entrance to Douglas Channel, one of the main coastal inlets, on the route of the Inside Passage between Pitt Island and Princess Royal Island. It is 26 km (16 mi) long, with a width ranging from 6 to 13 km (4 to 8 mi), and an area of 231 km2 (89 sq mi). The only named summit on the mountainous island is Mount Gil, which faces the opening of Douglas Channel.[1]
Name origin
"Named in 1792 by Lieutenant Commander Jacinto Caamaño of the Spanish corvette Aranzazu, while searching along the coast under orders from the viceroy of Mexico for the mythical 'Rio de Reyes'. This strait or river, supposed to connect the Pacific with the Atlantic, was claimed to have been discovered in 1640 by Admiral Pedro Bartolome de Fonti, in command of a fleet of 4 vessels, his flagship being named the Holy Ghost (Greenhow's Oregon, 1844, p.84.) The ensign-bearer of the San Martin, flagship of the Duke of Medina Sidonia in the Spanish Armada, was named Juan Gil. (Laughton, The Spanish Armada, Navy Records, II, p.355.) Caamaño sailed from Nootka 13 June 1792, steered northwards, and after examining Port Bucareli (Alaska) anchored in Dixon Entrance, probably under Rose Spit, on the 20 July. He then coasted southward along the continental shore, passing through Principe Channel into Nepean and Whale Sounds and out again near Surf Inlet and thence southward through Laredo Channel. In making the examination along this coastline for Fonti's strait, Caamaño bestowed several names, among others being the channels he passed through, and Campania Island, Campania Sound, and Aristazabal Island, all of which Vancouver adopted on his chart. Caamaño arrived at Nootka from his cruise 7 September 1972...."[2]
Indian reserves
Indian reserves on the island are under the jurisdiction of the Hartley Bay Indian Band, and are:
- Kunhunoan Indian Reserve No. 13, on Small Bay on the west side of the island, at 53°13′00″N 129°18′00″W / 53.21667°N 129.30000°W, 2.30 ha. (5.7 acres).[3]
- Maple Point Indian Reserve No. 11 at the point of the same name 53°06′00″N 129°12′00″W / 53.10000°N 129.20000°W, 50.20 ha. (124.0 acres).[4]
- Turtle Point Indian Reserve No. 12, at the point of the same name, which is Gil Island's northernmost tip, 51.80 ha. (128.0 acres).53°19′00″N 129°16′00″W / 53.31667°N 129.26667°W[5]
Wreck of the Queen of the North
The M/V Queen of the North was a Canadian RORO ferry operated by BC Ferries, which sank on March 22, 2006 after hitting Gil Island on a southbound voyage during the night. All but two passengers were rescued by the people of nearby Hartley Bay.
References
- ↑ "Gil, Mount". BC Geographical Names.
- ↑ Walbran, John T; British Columbia Coast Names, 1592-1906: their origin and history; Ottawa, 1909 (republished for the Vancouver Public Library by J.J. Douglas Ltd, Vancouver, 1971)
- ↑ BC Names/GeoBC entry "Kunhunoan 13 (Indian reserve)"
- ↑ BC Names/GeoBC entry "Maple Point 11 (Indian reserve)"
- ↑ BC Names/GeoBC entry "Turtle Point 12 (Indian reserve)"
External links
- "Gil Island" article in The Columbia Gazetteer of North America. Columbia University Press, 2000.
- "Gil Island". BC Geographical Names.