 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
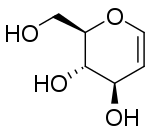
| IUPAC name
1,5-Anhydro-2-deoxy-D-arabino-hex-1-enitol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3S,4R)-2-(Hydroxymethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-3,4-diol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.032.949 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10O4 | |
| Molar mass | 146.1412 |
| Melting point | 58 to 60 °C (136 to 140 °F; 331 to 333 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Glucal is the glycal formed from glucose.[2] It is a chemical intermediate in the synthesis of a variety of oligosaccharides.[3]
Glucal and its derivatives can be converted to other chemically useful sugars using the Ferrier rearrangement.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.