| González Gil-Pazó GP-1 | |
|---|---|
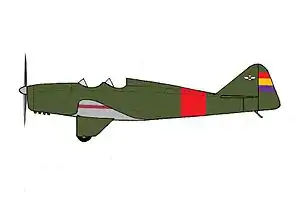 | |
| González Gil-Pazó GP-1 trainer of the Spanish Republican Air Force. | |
| Role | Two-seat trainer |
| National origin | Spain |
| Designer | Arturo González Gil y Santibañez and José Pazó |
| First flight | June 1934 |
| Number built | c.40 |
The González Gil-Pazó GP-1 was a single-engine, two-seat open cockpit training aircraft, built in Spain in the 1930s to compete for a government contract. Declared the winner, production was curtailed by the Spanish Civil War. Two cabin variants, the González Gil-Pazó GP-2 and GP-4, were also built.
Design and development
The first aircraft produced from the collaboration between Arturo González Gil y Santibañez and José Pazó was the Gil-Pazó No.1. It was, like all of their aircraft, a low-wing cantilever monoplane. It was built of wood and metal with plywood skinning, seated two and had an unfaired conventional undercarriage. Reportedly similar to the Miles Hawk, it was powered by an ADC Cirrus engine. Almost no specifications are known, apart from a loaded weight of 778 kg (1715 lb). It first flew in June 1932 and was last recorded at Cuatro Vientos, Madrid in July 1936.[1]
In 1934 the Director General de Aeronáutica issued a specification for a two-seat trainer and Gil-Pazó's response was the GP-1. This "supremely elegant" aircraft, with two open cockpits and a trousered undercarriage was reportedly somewhat like the Miles Hawk Major in appearance. Its wings, of semi-elliptic plan, had a wooden structure and a stressed plywood skin. Flaps were fitted. The fuselage was a steel tube structure, fabric covered at the rear with dural skinning forward. For its first flight in June 1934 it was powered by the same Cirrus engine as the No.1 but this was replaced by a 145 kW (195 hp) Walter Junior inverted inline engine for the trainer contract competition.[1]
The competitive trials, against the Loring X, the Hispano HS-34 and the Adaro 1.E.7, assessed the Gil-Pazó GP-1 as the clear winner, so in 1936 González Gil and Pazó received an order for 100 aircraft. These were to be built by AISA, the former Talleres Loring factory at Carabanchel Alto, Madrid. None of these had been completed by July 1936 at the start of the Spanish Civil War, and with rebel forces approaching Madrid in October, AISA retreated to Alicante. About forty GP-1s were built there during the war in a collaboration with Hispano-Suiza.[1]
In 1935-6 the open cockpit GP-1 was developed into two cabin types, the González Gil-Pazó GP-2 and GP-4. Both had raised rear fuselages faired into the cabin tops. The GP-2 was powered by a 97 kW (130 hp) de Havilland Gipsy Major engine and had two seats in tandem. Only one two-seater was built. A second GP-2 was built as a single-seater with one, rather than two, cabin side windows on each side. The GP-4 was powered by a 97 kW (130 hp) Walter Major engine and carried four people. Only one GP-4 was constructed.[1]
Operational history
Two notable flights were made before the Civil War. In January 1936 Ramón Torres and Carlos Coll set a record with their flight from Barcelona to Agadir, Morocco in the two-seat GP-2. The single-seat GP-2 was flown by Lorenzo Richi in March 1936 from Madrid to Bata in what was then Spanish Guinea at an average speed of 187 km/h (116 mph).[1]
About thirty of the forty GP-1s built at Alicante were captured by the Nationalist forces, given military serials and incorporated into Grupo 30. After the war at least twelve of these were given Spanish civil registrations; one remained on the register until 1961.[1]
One GP-2 and the sole GP-4 were also on the Spanish civil register until about 1960. The GP-4 had been flown into Nationalist hands by Pazó in September 1936, where it was used for liaison and transport duties.[1]
Variants

- Gil-Pazó No.1
- GP-1 precursor
- GP-1
- Open cockpit trainer; Walter Junior powered. About forty built.
- GP-2
- Enclosed cabin for one or two; Gipsy Major powered. Two or three built.
- GP-4
- Enclosed cabin for four; Walter Major powered. One built.
Operators
Specifications (GP-1)
Data from Howson[1]
General characteristics
- Capacity: two
- Length: 8.5 m (27 ft 11 in)
- Wingspan: 11.6 m (38 ft 1 in)
- Wing area: 18 m2 (190 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 525 kg (1,157 lb)
- Gross weight: 880 kg (1,940 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Walter Junior 4-cylinder air cooled inverted in-line piston, 145 kW (195 hp)
- Propellers: 2-bladed
Performance
- Maximum speed: 212 km/h (132 mph, 114 kn)
- Stall speed: 69 km/h (43 mph, 37 kn)
- Range: 1,000 km (620 mi, 540 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 7,500 m (24,600 ft)
See also
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
Related lists