The Gotland Basin is the large central basin in the Baltic Sea between Sweden and the Baltic countries. It is subdivided into the Gdansk Deep (or Gdansk Basin),[1][2] the Western Gotland Basin, and the Eastern Gotland Basin. Within the Eastern Gotland Basin is the Gotland Deep (249 metres deep) which is an anoxic basin. The Western Gotland Basin contains Landsort Deep, which is the deepest spot of the Baltic sea (459 metres deep).
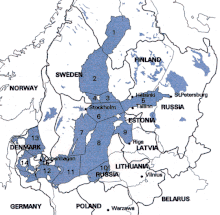
The Gotland Basin is marked by the numbers 7, 8 and 10 in this map of the area's marine environment.
The sediments in the Gotland Basin are important for studying the climate changes in northern Europe over the past 5,000 years.
Further reading
- Emeis, K.C.; Neumann, T.; Endler, R.; Struck, U.; Kunzendorf, H.; Christiansen, C. (1998) “Geochemical records of sediments in the Gotland Basin - products of sediment dynamics in a not so stagnant basin?” Applied Geochemistry 13, No. 3: 349-358 ;
- Hille, Sven; Nausch, Gunther; and Leipe, Thomas (2005) "Sedimentary deposition and reflux of phosphorus (P) in the Eastern Gotland Basin and their coupling with P concentrations in the water column" Oceanologia 47(4): pp. 663–679 ;
References
- ↑ Matti Leppäranta; Kai Myrberg (20 March 2009). Physical Oceanography of the Baltic Sea. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 145. ISBN 978-3-540-79703-6.
- ↑ Jacek Bełdowski; Robert Been; Eyup Kuntay Turmus (18 September 2017). Towards the Monitoring of Dumped Munitions Threat (MODUM): A Study of Chemical Munitions Dumpsites in the Baltic Sea. Springer Netherlands. p. 199. ISBN 978-94-024-1153-9.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.