The graduated majority judgment (GMJ), sometimes called the usual judgment or continuous-time Bucklin voting, is a single-winner electoral system first suggested as an improvement on majority judgment by Jameson Quinn,[1] and later independently by the French social scientist Adrien Fabre in 2019.[2] It is a highest median voting method, a system of cardinal voting in which the winner is decided by the median rating rather than the mean.[2]
Highest medians
The elector rates each candidate on a common scale, such as:
| Awful | Bad | Tolerable | Neutral | Acceptable | Good | Excellent | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Candidate A | X | ||||||
| Candidate B | X | ||||||
| Candidate C | X | ||||||
| Candidate D | X |
When counting the votes, we calculate the share of each grade for each of the votes cast. This is the candidate's "merit profile":
| Candidate | Awful | Bad | Tolerable | Neutral | Acceptable | Good | Excellent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2% | 15% | 21% | 20% | 9% | 18% | 15% |
| B | 2% | 17% | 19% | 13% | 13% | 12% | 24% |
| C | 1% | 9% | 10% | 15% | 15% | 25% | 25% |
For each candidate, we determine the median or majority grade as the grade where a majority of voters would oppose giving the candidate a higher grade, but a majority would also oppose giving a lower grade.[3] This rule means that the absolute majority of the electors judge that a candidates merits at least its median grade, while half the electors judge that he deserves at most its median grade.[4]
If only one candidate has the highest median grade, they are elected (as in all highest median voting rules). Otherwise, the election uses a tie-breaking procedure.
Tie-breaking
Graduated majority judgment uses a simple line-drawing method to break ties.[2] This rule is easier to explain than others such as majority judgment, and also guarantees continuity.
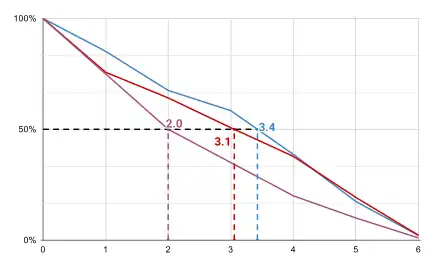
Graphically, we can represent this by drawing a plot showing the share of voters who assign an approval less than the given score, then draw lines connecting the points on this graph. The place where this plot intersects 50% is each candidate's score.
Example
Consider the same election as before, but relabeling the verbal grades as numbers on a scale from 0 to 6.
Grade Candidate |
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2% | 15% | 21% | 20% | 9% | 18% | 15% |
| 2% | 17% | 39% | 58% | 68% | 85% | 100% | |
| B | 2% | 17% | 19% | 13% | 13% | 12% | 24% |
| 2% | 19% | 38% | 51% | 64% | 76% | 100% | |
| C | 1% | 9% | 10% | 15% | 15% | 25% | 25% |
| 1% | 10% | 20% | 35% | 50% | 75% | 100% |
Candidates A and B both receive a median grade between 2 or 3 (i.e. their median falls between 2 and 3), so we must invoke the tiebreaking procedure. When we do, we find that the median grades for candidates A, B, and C are 3.4, 3.1, and 2.0 respectively. Thus, Candidate A is declared the winner.
Race analogy
The tiebreaking rule can be explained using an analogy where every candidate is in a race. Each candidate takes 1 minute to run from one grade to the next, and they run at a constant speed when moving from one grade to the next. The winner is the first candidate to cross the finish line at 50% of the vote.[1]
Mathematical description
Say the median grade of a candidate is (when there is a tie, we define the median as halfway between the neighboring grades). Let (the share of proponents) refer to the share of electors giving a score strictly better than the median grade. The share of opponents of , written , is the share of grades falling below the median. Then the complete score for GMJ is given by the following formula:[2]
Additional tie-breaking
In the unusual situation where the tie-breaking formula above does not determine a single winner (if several candidates have exactly the same score), ties can be broken by binning together the 3 grades closest to the median, then repeating the tiebreaking procedure.[2] In the example above, we would combine all "Good," "Fair," and "Passable" grades into a new "Passable to Good" grade, then apply the same tie-breaking formula as before. This process can be repeated multiple times (binning more and more grades) until a winner is found. If no winner is found, this implies two candidates have received exactly the same number of votes of every grade, an extremely unlikely situation.
Properties and advantages
Advantages and disadvantages common to highest-median rules
As an electoral system, the graduated majority judgment shares most of its advantages with other highest-median voting rules such as majority judgment, including its resistance to tactical voting. It also shares most of its disadvantages (for example, it fails the participation criterion, and can fail the majority criterion arbitrarily badly).
Specific advantages of graduated majority judgment
The tie-breaking formula of the graduated majority judgment presents specific advantages over the other highest-median voting rules.
Continuity
The function defined by the graduated majority judgment tie-breaking formula is a continuous function (as well as being almost-everywhere differentiable), whereas the functions of majority judgment and typical judgment are discontinuous.[2] In other words, a small change in the number of votes for each candidate is unlikely to change the winner of the election, because small changes in vote shares result in only small changes in the overall rating.
This property makes the graduated majority judgment a more robust voting method in the face of accusations of fraud or demands of a recount of all votes. As small differences of votes are less likely to change the outcome of the election, candidates are less likely to contest results.[2]
Rare ties
The additional tiebreaking procedures of graduated majority judgment mean that tied elections become extremely unlikely (far less likely than systems such as plurality). Whereas plurality votes, ranked voting, and approval voting can result in ties when working with small elections, the only way for two candidates to tie with usual judgment is to have all candidates receive exactly the same number of votes in every grade category, implying the chances of an undetermined election fall exponentially with the number of grades.
See also
References
- 1 2 Smith, Warren D. "On Balinski & Laraki's "majority judgment" median-based range-like voting scheme". RangeVoting.org. Center for Range Voting. Retrieved 2024-01-02.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Fabre, Adrien (2021). "Tie‐breaking the highest median: alternatives to the majority judgment". Social Choice and Welfare. 56: 101–124. doi:10.1007/s00355-020-01269-9. S2CID 226196615 – via Springer Link.
- ↑ "Le jugement majoritaire". lechoixcommun.fr (in French). Retrieved 2021-02-08.
- ↑ Leray, Marjolaine; Hogg, Carol. "A little more democracy? Cartoons by Marjolaine Leray on the topic of Majority Judgment" (PDF). Le Choix commun.