Lymphoid-specific helicase (Lsh) is a member of the SNF2 helicase family of chromatin remodeling proteins that in humans is encoded by the HELLS gene.
The HELLS gene has proved to play critical roles in DNA methylation, chromatin packaging, control of Hox genes, stem cell proliferation, and developing lymphoid tissue.
In a developing embryo, epigenetic programming is controlled through the mechanisms of DNA methylation and chromatin organization. These processes are the master regulators that determine which genes are turned on or off throughout development. Lsh, a protein encoded by the HELLS gene is a major regulator of methylation patterns and thus crucial to normal fetal development.
Mutations and knockouts of the HELLS gene severely disrupts the process of fetal programming. In mice, knockout of HELLS gene resulted in death of embryos at birth and caused embryonic growth retardation. In humans, hypomethylation caused by a mutation in the HELLS gene is linked to Immunodeficiency-centromeric instability-facial anomalies syndrome 4 (ICF4). This is a rare disease that causes immunodeficiency, facial anomalies, growth retardation, failure to thrive, and psychomotor retardation. The adverse effects due to the absence and mutation of the HELLS gene is a result of the extensive loss of genomic wide methylation and the abnormal expression of repeat sequences. The disruption in methylation patterns can cause the silencing of genes or the over-expression of genes, leading to abnormal and in some cases fatal developmental consequences.
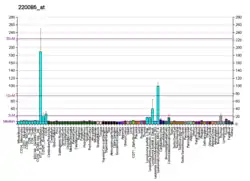
This gene encodes a lymphoid-specific helicase. Other helicases function in processes involving DNA strand separation, including replication, repair, recombination, and transcription. This protein is thought to be involved with cellular proliferation and may play a role in leukemogenesis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described, but their biological validity has not been determined.[5]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000119969 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000025001 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: HELLS helicase, lymphoid-specific".
Further reading
- Ohira M, Morohashi A, Nakamura Y, Isogai E, Furuya K, Hamano S, et al. (July 2003). "Neuroblastoma oligo-capping cDNA project: toward the understanding of the genesis and biology of neuroblastoma". Cancer Letters. 197 (1–2): 63–8. doi:10.1016/S0304-3835(03)00085-5. PMID 12880961.
- Andersson B, Wentland MA, Ricafrente JY, Liu W, Gibbs RA (April 1996). "A "double adaptor" method for improved shotgun library construction". Analytical Biochemistry. 236 (1): 107–13. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0138. PMID 8619474.
- Hillier LD, Lennon G, Becker M, Bonaldo MF, Chiapelli B, Chissoe S, et al. (September 1996). "Generation and analysis of 280,000 human expressed sequence tags". Genome Research. 6 (9): 807–28. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.807. PMID 8889549.
- Yu W, Andersson B, Worley KC, Muzny DM, Ding Y, Liu W, et al. (April 1997). "Large-scale concatenation cDNA sequencing". Genome Research. 7 (4): 353–8. doi:10.1101/gr.7.4.353. PMC 139146. PMID 9110174.
- Sun LQ, Lee DW, Zhang Q, Xiao W, Raabe EH, Meeker A, et al. (May 2004). "Growth retardation and premature aging phenotypes in mice with disruption of the SNF2-like gene, PASG". Genes & Development. 18 (9): 1035–46. doi:10.1101/gad.1176104. PMC 406293. PMID 15105378.
- Yano M, Ouchida M, Shigematsu H, Tanaka N, Ichimura K, Kobayashi K, et al. (October 2004). "Tumor-specific exon creation of the HELLS/SMARCA6 gene in non-small cell lung cancer". International Journal of Cancer. 112 (1): 8–13. doi:10.1002/ijc.20407. PMID 15305370. S2CID 9416948.
- Xi S, Zhu H, Xu H, Schmidtmann A, Geiman TM, Muegge K (September 2007). "Lsh controls Hox gene silencing during development". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (36): 14366–71. Bibcode:2007PNAS..10414366X. doi:10.1073/pnas.0703669104. PMC 1955459. PMID 17726103.
- Fan T, Hagan JP, Kozlov SV, Stewart CL, Muegge K (February 2005). "Lsh controls silencing of the imprinted Cdkn1c gene". Development. 132 (4): 635–44. doi:10.1242/dev.01612. PMID 15647320.
- Dennis K, Fan T, Geiman T, Yan Q, Muegge K (November 2001). "Lsh, a member of the SNF2 family, is required for genome-wide methylation". Genes & Development. 15 (22): 2940–4. doi:10.1101/gad.929101. PMC 312825. PMID 11711429.
External links
- "HELLS (Helicase, Lymphoid-Specific)". Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology. Archived from the original on 2021-09-03. Retrieved 2020-07-01.