 | ||
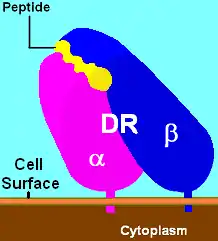
major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR53 | ||
| Haplotypes | DRA*01:DRB4*0101 DRA*01:DRB4*0102 DRA*01:DRB4*0103 DRA*01:DRB4*0104 | |
| Structure (See HLA-DR) | ||
| Identifiers | alpha *0101 | |
| Symbol(s) | HLA-DRA | |
| EBI-HLA | DRA*0101 | |
| Identifiers | beta 4 *0101 *0102 *0103 *0104 | |
| Symbol(s) | HLA-DRB4 | |
| EBI-HLA | DRB4*0101 | |
| EBI-HLA | DRB4*0102 | |
| EBI-HLA | DRB4*0103 | |
| EBI-HLA | DRB4*0104 | |
| Shared data | ||
| Locus | chr.6 6p21.31 | |
HLA-DR53 is an HLA-DR serotype that recognizes gene products of HLA-DRB4 locus. There are 13 alleles at this locus that encode 7 proteins.
DRB3, DRB4, and DRB5 are minor DR beta encoding loci, they have been recognized as having distinct evolution.[1] and the DRB4 locus presence is linked to HLA-DR7 seropositivity. The DRB4*locus was apparently duplicated from an ancestor of the DRB1-DRB4 common locus around 5 million years ago.[2]
DRB4 locus is only apparent in a small subset of DQ haplotypes, and most individuals lack DRB4. In addition the level of normal expression is 8 fold lower than the DRB1 in cells which can express both.[3] and lowered because of both transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation.[4]
Alleles
| DRB4* | DR53 | ? | Sample |
| allele | % | % | size (N) |
| 0101 | 95 | 38 | |
| 0103 | 89 | 49 | |
DR53 reactive alleles: DRB4*0101, *0103
Unknown reactivity: *0102, *0104 to *0107
Null alleles: *0101102N, *01030102N, *0201N, *0301N
Associated diseases
DRB4*01 is positively associated with Erythema multiforme,[6] Crohn's disease,[7] myasthenia gravis,[8] rheumatoid arthritis[9] Hashimoto's thyroiditis,[10] vitiligo,[11] primary biliary cirrhosis,[12] clozapine-induced agranulocytosis,[13] Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada disease,[14]
HLA-DRB1 linkage
HLA-DR53 serotypes (HLA-DRB4) is linked to the following HLADR serotypes (HLA-DRB1) allele groups:
HLA-DR4 - DRB1*04
HLA-DR7 - DRB1*07
HLA-DR9 - DRB1*09
References
- ↑ Gorski J, Rollini P, Mach B (1987). "Structural comparison of the genes of two HLA-DR supertypic groups: the loci encoding DRw52 and DRw53 are not truly allelic". Immunogenetics. 25 (6): 397–402. doi:10.1007/BF00396106. PMID 3596674. S2CID 25853147.
- ↑ Gyllensten U, Sundvall M, Ezcurra I, Erlich HA (1991). "Genetic diversity at class II DRB loci of the primate MHC". J. Immunol. 146 (12): 4368–76. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.146.12.4368. PMID 2040804.
- ↑ Stunz LL, Karr RW, Anderson RA (1989). "HLA-DRB1 and -DRB4 genes are differentially regulated at the transcriptional level". J. Immunol. 143 (9): 3081–6. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.143.9.3081. PMID 2809218.
- ↑ Leen MP, Gorski J (1996). "Differential expression of isomorphic HLA-DR beta genes is not a sole function of transcription". Hum. Immunol. 50 (2): 111–20. doi:10.1016/0198-8859(96)00154-1. PMID 8891734.
- ↑ derived from IMGT/HLA
- ↑ Lepage V, Douay C, Mallet C, et al. (1988). "Erythema multiforme is associated to HLA-Aw33 and DRw53". Tissue Antigens. 32 (3): 170–5. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0039.1988.tb01654.x. PMID 3217933.
- ↑ Kobayashi K, Atoh M, Yagita A, et al. (1990). "Crohn's disease in the Japanese is associated with the HLA-DRw53". Exp. Clin. Immunogenet. 7 (2): 101–8. PMID 2322470.
- ↑ Morita K, Moriuchi J, Inoko H, Tsuji K, Arimori S (1991). "HLA class II antigens and DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism in myasthenia gravis in Japan". Ann. Neurol. 29 (2): 168–74. doi:10.1002/ana.410290209. PMID 1672809. S2CID 45699820.
- ↑ Morling N, Andersen V, Fugger L, et al. (1991). "Immunogenetics of rheumatoid arthritis and primary Sjögren's syndrome: DNA polymorphism of HLA class II genes". Dis. Markers. 9 (5): 289–96. PMID 1686751.
- ↑ Terauchi M, Yanagawa T, Ishikawa N, Ito K, Fukazawa T, Maruyama H, Saruta T (2003). "Interactions of HLA-DRB4 and CTLA-4 genes influence thyroid function in Hashimoto's thyroiditis in Japanese population". J Endocrinol Invest. 26 (12): 1208–12. doi:10.1007/bf03349159. PMID 15055474. S2CID 2344535.
- ↑ Zamani M, Spaepen M, Sghar S, Huang C, Westerhof W, Nieuweboer-Krobotova L, Cassiman J (2001). "Linkage and association of HLA class II genes with vitiligo in a Dutch population". Br J Dermatol. 145 (1): 90–4. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04288.x. PMID 11453913. S2CID 25942367.
- ↑ Shimoda S, Nakamura M, Ishibashi H, Hayashida K, Niho Y (1995). "HLA DRB4 0101-restricted immunodominant T cell autoepitope of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in primary biliary cirrhosis: evidence of molecular mimicry in human autoimmune diseases". J Exp Med. 181 (5): 1835–45. doi:10.1084/jem.181.5.1835. PMC 2191998. PMID 7536796.
- ↑ Corzo D, Yunis J, Salazar M, Lieberman J, Howard A, Awdeh Z, Alper C, Yunis E (1995). "The major histocompatibility complex region marked by HSP70-1 and HSP70-2 variants is associated with clozapine-induced agranulocytosis in two different ethnic groups". Blood. 86 (10): 3835–40. doi:10.1182/blood.V86.10.3835.bloodjournal86103835. PMID 7579351.
- ↑ Kobayashi H, Kokubo T, Takahashi M, Sato K, Miyokawa N, Kimura S, Kinouchi R, Katagiri M (1998). "Tyrosinase epitope recognized by an HLA-DR-restricted T-cell line from a Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease patient". Immunogenetics. 47 (5): 398–403. doi:10.1007/s002510050375. PMID 9510558. S2CID 1592923.