 | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | HMS Temeraire |
| Builder | Chatham Dockyard |
| Laid down | 18 August 1873 |
| Launched | 9 May 1876 |
| Completed | 31 August 1877 |
| Fate | Broken up, 26 May 1921 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type | Battleship |
| Displacement | 8,540 long tons (8,677 t) |
| Length | 285 ft (87 m) |
| Beam | 62 ft (19 m) |
| Draught | 27 ft 6 in (8.38 m) |
| Propulsion |
|
| Sail plan | Brig-rigged, sail area 25,000 sq ft (2,300 m2) |
| Speed | 14.65 knots (16.86 mph; 27.13 km/h) |
| Complement | 580 |
| Armament |
|
| Armour |
|
HMS Temeraire was an ironclad battleship of the Victorian Royal Navy which was unique in that she carried her main armament partly in the traditional broadside battery, and partly in barbettes on the upper deck.
Design and construction
_11-inch_gun.jpg.webp)
Propulsion
Temeraire was equipped with two Humpreys & Tennant 2-cyl. steam engines, each driving one shaft and developing a total of 7,697 hp (5,661 kW), with which she reached a top speed of 14.65 knots (16.86 mph). Steam was supplied by twelve boilers. The ship could carry a maximum of 629 t. coal. Temeraire was rigged as a two-masted barque and had a sail area of 25,000 sq ft. The ship's crew consisted of 580 officers and ratings.[1]
Armament
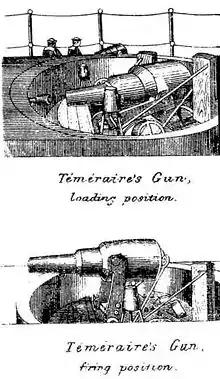
Her armament was partly conventional, being deployed on the broadside, and partly experimental; she was the first British ship to be equipped with guns in barbettes located on the midline on the upper deck. Indeed, she was the first British ship with barbettes of any kind.The armament consisted of four 11-inch muzzle-loading guns, one each on the forecastle and stern, and one each at the forward corners of the central battery to port and starboard. The 11-inch guns were installed on a Moncrieff mount, which had a mechanism for raising and lowering the gun. The mount was on a massive turntable that provided enough space for the hydraulic ramrod. The loading and lifting process, as well as the rotation of the mount, were operated by a disguised stand with four control levers. When the gun was extended and aimed at the target, it was adjusted to elevation graduated in degrees by a rod linkage on each side of the breech. A full gun crew consisted of six men, but the guns could be operated by three in an emergency. In addition, four 10in muzzle-loading guns were located in the rear of the central battery, two on each broadside. To protect against attack by boats armed with torpedoes, the ship received four 20-pounder breech-loading guns. Temeraire was also fitted with two launchers for spar torpedoes. In 1884, the 20-pounders were replaced by four 25-pounder breech-loading guns, and four 3-pounder Hotchkiss and ten 3-pounder Nordenfelt QF guns were also added to the ship.[2][1]
Armour
The armoured belt extended along the entire length of the ship. It was 11in thick amidships and had a total height of 18.8ft, of which 10ft was above and 8.9ft below the waterline. Towards the bow and stern it tapered to 5in and 5.5in respectively. The central battery was protected by 8in sides and 5in transverse bulkheads. The oval barbettes were protected by 10in forward and 8in aft. This shape was necessary to make room not only for the guns to be lowered, but also for a hydraulic ramrod, which was opposite the gun muzzle and almost as long as the barrel itself. The wider end was open at the top to allow the gun to rise and fire, and the narrower end with the ramrod was covered with iron plates. Its distinctive feature was a complete and continuous armour by a parapet that rose 36in above the deck surrounding it, protecting the gun crew and the gun itself when loaded or not in use.[2][1]
Service history
The Temeraire named after the French ship of the line Téméraire captured in 1759, was laid down at Chatham on 18 August 1873, launched on 9 May, and commissioned in 1877 for service in the Mediterranean fleet under Captain Michael Culme-Seymour.[3] She remained there for the next fourteen years except for the winter of 1887-88 when she was part of the Channel Squadron. Upon her arrival in Besika Bay, she became Admiral Hornby's flagship. In 1878 she was ordered to the Dardanelles to observe the progress of the Russo-Turkish War. She remained near Istanbul (then Constantinople) until 1879 to represent a strong British position during the protracted international negotiations that led to the Congress of Berlin.
She then took part in the reconquest of Ottoman-occupied Cyprus. In 1881 she was paid off in Malta and given a new command. At the outbreak of the Anglo-Egyptian War in 1882, she was recommissioned and took part in the attack on the defensive positions on the coast of Alexandria. In 1884, she was again decommissioned and recommissioned the same year for service in the Mediterranean under Compton Edward Domvile. In 1887 she returned home and was paid off at Portsmouth. After being recommissioned for service in the Channel Squadron, she visited Vigo, Genoa, and Lisbon. She then returned home, but the growing threat from the French fleet at Toulon made it necessary to increase British forces in the Mediterranean as well. Therefore, Temeraire was reassigned to the Mediterranean Fleet under the command of James Drummond.[4]
During this time, an incident occurred that resulted in a near disaster with HMS Orion. The squadron was in close formation, at sea with Temeraire as the last ship in the starboard column and Orion as the next-to-last ship in the port column, which, with two hawsers between the columns, resulted in her being four points off port bow of the former in short manoeuvring distance. Both ships were signalled to change position. According to the instructions of the signal book used at the time, such movements had to comply with the traffic rules by moving from port to port. But due to the prevailing situation, the Orion's engines had to be stopped when turning to starboard. When the flagship's signal sounded, the Orion's watch officer kept his engines running, leaving little room to avoid a collision at full speed. Fortunately, the officer on watch of the Temraire had recognized the impending danger and immediately gave the order to head for Orion instead of turning away from it. When Orion's ram struck the Temeraire next to the engine room and below the armour belt, Temeraire's stern was already swinging away from it, which tore through the ship's outer skin and flooded a wing compartment.[5]
When Gerard Noel took command on 26 October 1889,[4] Termeraire was the last ship to carry sails on its masts. All other ships were already turret ships at that time. From 1890 she cruised in the Levant and visited Souda Bay in Crete. After wintering in Thessaloniki, Temeraire was ordered to return home in the spring of 1891, where she was paid off in Plymouth and assigned to the reserve. Plans for a possible modernization were developed but ultimately discarded due to excessive cost. In 1904 she was renamed Indus II and in 1915 Akbar. She was finally sold to the Netherlands for scrapping in May 1921.[5]
References
Publications
- Ballard, G. A., Admiral (1980). The Black Battlefleet. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-924-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Brown, David K. (1997). Warrior to Dreadnought: Warship Development 1860–1905. London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 1-86176-022-1.
- Colledge, J. J.; Warlow, Ben (2006) [1969]. Ships of the Royal Navy: The Complete Record of all Fighting Ships of the Royal Navy (Rev. ed.). London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-281-8.
- Dittmar F. J. & Colledge J. J., British Warships 1914-1919, (Ian Allan, London,1972) ISBN 0-7110-0380-7
- Dodson, Aidan (2015), "The Incredible Hulks: The Fisgard Training Establishment and Its Ships", Warship 2015, London: Conway, pp. 29–43, ISBN 978-1-84486-276-4
- Oscar Parkes British Battleships ISBN 0-85052-604-3
- Roberts, John (1979). "Great Britain and Empire Forces". In Chesneau, Roger & Kolesnik, Eugene M. (eds.). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1860-1905. Greenwich, UK: Conway Maritime Press. ISBN 0-8317-0302-4.
- Winfield, R.; Lyon, D. (2004). The Sail and Steam Navy List: All the Ships of the Royal Navy 1815–1889. London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-032-6.