 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hexanedihydrazide | |
| Other names
Adipic dihydrazide Adipohydrazide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | ADH |
| 973863 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.727 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Adipic+dihydrazide |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H14N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 174.20 g/mol |
| Melting point | 176 to 185 °C (349 to 365 °F; 449 to 458 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Material Safety Data Sheet |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
hexanedioic acid hexanedihydrazide hexanedioyl dichloride hexanedinitrile hexanediamide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
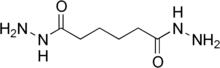
Adipic acid dihydrazide (ADH) is a chemical used for cross-linking water-based emulsions. It can also be used as a hardener for certain epoxy resins.[2] ADH is a symmetrical molecule with a C4 backbone, and the reactive group is C=ONHNH2. Dihydrazides are made by the reaction of an organic acid with hydrazine. Other dihydrazides with different backbones are also common, including isophthalic dihydrazide (IDH) and sebacic dihydrazide (SDH).
References
- ↑ Physical Properties of ADH
- ↑ Adipic acid dihydrazide - Adipic dihydrazide - ADH Archived April 18, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
External links
- Preparation of Enzyme Conjugate through Adipic Acid Dihydrazide as Linker
- Ďurana, R; Bystrický, S (2002). "Preparation and characterization of adipic acid dihydrazide derivatives of yeast mannans". Carbohydrate Polymers. 50 (2): 177. doi:10.1016/S0144-8617(02)00020-6.
- Technical Article About the Chemistry and Use of Dihydrazides in Thermosets, Including ADH
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.