| Part of a series on | ||||
| Network science | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network types | ||||
| Graphs | ||||
|
||||
| Models | ||||
|
||||
| ||||
|
||||
Hierarchical network models are iterative algorithms for creating networks which are able to reproduce the unique properties of the scale-free topology and the high clustering of the nodes at the same time. These characteristics are widely observed in nature, from biology to language to some social networks.
Concept
The hierarchical network model is part of the scale-free model family sharing their main property of having proportionally more hubs among the nodes than by random generation; however, it significantly differs from the other similar models (Barabási–Albert, Watts–Strogatz) in the distribution of the nodes' clustering coefficients: as other models would predict a constant clustering coefficient as a function of the degree of the node, in hierarchical models nodes with more links are expected to have a lower clustering coefficient. Moreover, while the Barabási-Albert model predicts a decreasing average clustering coefficient as the number of nodes increases, in the case of the hierarchical models there is no relationship between the size of the network and its average clustering coefficient.
The development of hierarchical network models was mainly motivated by the failure of the other scale-free models in incorporating the scale-free topology and high clustering into one single model. Since several real-life networks (metabolic networks, the protein interaction network, the World Wide Web or some social networks) exhibit such properties, different hierarchical topologies were introduced in order to account for these various characteristics.
Algorithm
Hierarchical network models are usually derived in an iterative way by replicating the initial cluster of the network according to a certain rule. For instance, consider an initial network of five fully interconnected nodes (N=5). As a next step, create four replicas of this cluster and connect the peripheral nodes of each replica to the central node of the original cluster (N=25). This step can be repeated indefinitely, thereby for any k steps the number of nodes in the system can be derived by N=5k+1.[1]
Of course there have been several different ways for creating hierarchical systems proposed in the literature. These systems generally differ in the structure of the initial cluster as well as in the degree of expansion which is often referred to as the replication factor of the model.[2][3]
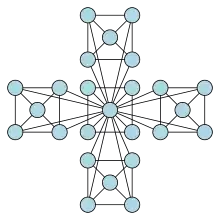
Properties
Degree distribution
Being part of the scale-free model family, the degree distribution of the hierarchical network model follows the power law meaning that a randomly selected node in the network has k edges with a probability
where c is a constant and γ is the degree exponent. In most real world networks exhibiting scale-free properties γ lies in the interval [2,3].[4]
As a specific result for hierarchical models it has been shown that the degree exponent of the distribution function can be calculated as
where M represents the replication factor of the model.[5]
Clustering coefficient
In contrast to the other scale-free models (Erdős–Rényi, Barabási–Albert, Watts–Strogatz) where the clustering coefficient is independent of the degree of a specific node, in hierarchical networks the clustering coefficient can be expressed as a function of the degree in the following way:
It has been analytically shown that in deterministic scale-free networks the exponent β takes the value of 1.[2]
Examples
Actor network
Based on the actor database available at www.IMDb.com the network is defined by Hollywood actors who are connected to each other if they both appeared in the same movie, resulting in a data set of 392,340 nodes and 15,347,957 edges. As earlier studies have shown, this network exhibits scale-free properties at least for high values of k. Moreover, the clustering coefficients seem to follow the required scaling law with the parameter -1 providing evidence for the hierarchical topology of the network. Intuitively, one-performance actors have by definition a clustering coefficient of one while actors starring in several movies are highly unlikely to work with the same crew which in general results in a decreasing clustering coefficient as the number of co-stars grows.[1]
Language network
Words can be regarded as network if one specifies the linkage criteria between them. Defining links as appearance as a synonym in the Merriam-Webster dictionary a semantic web of 182,853 nodes with 317,658 edges was constructed. As it turned out, the obtained network of words indeed follows a power law in its degree distribution while the distribution of the clustering coefficient indicates that the underlying web follows a hierarchical structure with γ=3.25 and β=1.[1]
Network of webpages
By mapping the www.nd.edu domain a network of 325,729 nodes and 1,497,135 edges was obtained whose degree distribution followed a power law with γout=2.45 and γin=2.1 for the out- and in-degrees, respectively. The evidence for the scaling law distribution of the clustering coefficients is significantly weaker than in the previous cases although there is a clearly visible declining pattern in the distribution of C(k) indicating that the more links a domain has the less interconnected the linked/linking web pages are.[1][6]
Domain network
The domain network, i.e. the internet at the autonomous system (AS) level where the administrative domains are said to be connected in case there is a router which connects them, was found to comprise 65,520 nodes and 24,412 links between them and exhibit the properties of a scale-free network. The sample distribution of the clustering coefficients was fitted by the scaling function C(k)~k−0.75 whose exponent is (in absolute terms) somewhat smaller than the theoretical parameter for deterministic scale-free networks.[1][7]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Ravasz, E. B.; Barabási, A. L. S. (2003). "Hierarchical organization in complex networks". Physical Review E. 67 (2): 026112. arXiv:cond-mat/0206130. Bibcode:2003PhRvE..67b6112R. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.67.026112. PMID 12636753.
- 1 2 Dorogovtsev, S.; Goltsev, A.; Mendes, J. (2002). "Pseudofractal scale-free web". Physical Review E. 65 (6): 066122. arXiv:cond-mat/0112143. Bibcode:2002PhRvE..65f6122D. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.65.066122. PMID 12188798.
- ↑ Barabási, A. L. S.; Ravasz, E. B.; Vicsek, T. S. (2001). "Deterministic scale-free networks". Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications. 299 (3–4): 559. arXiv:cond-mat/0107419. Bibcode:2001PhyA..299..559B. doi:10.1016/S0378-4371(01)00369-7.
- ↑ Barabási, A.; Albert, R. (1999). "Emergence of Scaling in Random Networks". Science. 286 (5439): 509–512. arXiv:cond-mat/9910332. Bibcode:1999Sci...286..509B. doi:10.1126/science.286.5439.509. PMID 10521342.
- ↑ Noh, J. (2003). "Exact scaling properties of a hierarchical network model". Physical Review E. 67 (4). arXiv:cond-mat/0211399. Bibcode:2003PhRvE..67d5103N. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.67.045103.
- ↑ Barabási, A. L. S.; Albert, R. K.; Jeong, H. (1999). "Internet: Diameter of the World-Wide Web". Nature. 401 (6749): 130. arXiv:cond-mat/9907038. Bibcode:1999Natur.401..130A. doi:10.1038/43601.
- ↑ Vázquez, A.; Pastor-Satorras, R.; Vespignani, A. (2002). "Large-scale topological and dynamical properties of the Internet". Physical Review E. 65 (6): 066130. arXiv:cond-mat/0112400. Bibcode:2002PhRvE..65f6130V. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.65.066130. PMID 12188806.
