.png.webp) LRO image of Hipparchus | |
| Coordinates | 5°30′S 4°48′E / 5.5°S 4.8°E |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 150 km |
| Depth | 3.3 km |
| Colongitude | 354° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Hipparchus |
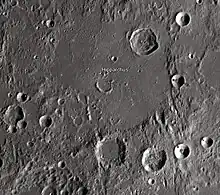
Hipparchus is the degraded remnant of a lunar impact crater. It was named after the Greek astronomer, geographer and mathematician Hipparchus.[1] It is located to the southeast of Sinus Medii, near the center of the visible Moon. To the south is the prominent crater Albategnius, and to the southwest lies Ptolemaeus, a feature of comparable dimensions to Hipparchus. Horrocks lies entirely within the northeast rim of the crater. Halley is attached to the south rim, and Hind lies to the southeast. To the north-northeast is the bowl-shaped Pickering, and the flooded Saunder is located off the northeast rim. High-resolution images of Hipparchus were obtained by Lunar Orbiter 5 in 1967.
Description

This feature is an ancient crater that has been subject to considerable modification due to subsequent impacts. The western rim of Hipparchus has been all but worn away from impact erosion, and only low hills and rises in the surface remain to outline the feature. The wall to the east is somewhat more intact, but it too is heavily worn. A pair of deep clefts lie in the western wall. These parallel a sets of scars running through the south-central highlands. The crater floor has been partially resurfaced by basaltic lava flow. The southwest part of the floor, however, is slightly raised and much more rugged than the remainder. A few small rises and the raised partial rim of a flooded crater are all that remain of a central massif. Gaps in the northwest rim of Hipparchus form valleys that connect with the mare to the northwest. A rille named Rima Réaumur runs from this site to the outer wall of Réaumur.
Satellite craters

By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Hipparchus.
| Hipparchus | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| B | 6.9° S | 1.7° E | 5 km |
| C | 7.3° S | 8.2° E | 17 km |
| D | 4.5° S | 2.1° E | 5 km |
| E | 4.2° S | 2.3° E | 5 km |
| F | 4.2° S | 2.5° E | 9 km |
| G | 5.0° S | 7.4° E | 15 km |
| H | 5.4° S | 2.3° E | 5 km |
| J | 7.6° S | 3.2° E | 14 km |
| K | 6.9° S | 2.2° E | 12 km |
| L | 6.8° S | 9.0° E | 13 km |
| N | 4.8° S | 5.0° E | 6 km |
| P | 4.7° S | 2.8° E | 5 km |
| Q | 8.5° S | 2.9° E | 8 km |
| T | 7.1° S | 3.6° E | 8 km |
| U | 6.7° S | 3.6° E | 8 km |
| W | 5.0° S | 7.8° E | 5 km |
| X | 5.7° S | 4.9° E | 17 km |
| Z | 8.5° S | 9.1° E | 6 km |
Hooke's Observations

In October 1664, Robert Hooke used a 36-foot telescope to make a detailed drawing of the single crater Hipparchus and surrounding terrain, which he published as a plate in his Micrographia (1665).[2][3] His drawing contained an abundance of detail, and can be considered the first high-definition illustration of an individual lunar feature. Hooke argued that its features were not fixed, but were a product of ongoing physical forces. He suggested two possible models to explain lunar crater formation: projectile bombardment from space and subterranean lunar vulcanism. Less accurately, he speculated that the crater might contain "verdant pastures" and "Vegetables analogous to our Grass, Shrubs, and Trees”.[2]
Hipparchus in fiction
In the original version of the 1954 Tintin book Explorers on the Moon (On a marché sur la lune), the crew lands on Hipparchus.[4]
See also
- Asteroid 4000 Hipparchus
References
- ↑ "Hipparchus (lunar crater)". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Research Program.
- 1 2 Chapman, Allan (22 September 2015). "'Micrographia' on the Moon". Astronomy & Geophysics. 56 (5): 5.23–5.29. doi:10.1093/astrogeo/atv169.
- ↑ Hooke, Robert (1665). Micrographia : or, Some physiological descriptions of minute bodies made by magnifying glasses. With observations and inquiries thereupon. London: Allestry, J. & Martyn, J. p. 242, Plate 38. Retrieved 17 July 2019.
- ↑ éd. Casterman, coll. Tintin, 1954 (French)
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.
- Blue, Jennifer (July 25, 2007). "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature". USGS. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763. S2CID 122125855.
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.
External links
- Lunar Orbiter 5 frames of the interior of Hipparchus: 5098, 5099, 5100, 5101
- LTO-77B3 Hipparchus — L&PI topographic map
Related articles
- Wood, Chuck (January 31, 2004). "Hooke & Hipparchus". Lunar Photo of the Day.
- Wood, Chuck (February 4, 2006). "On Approach for Landing". Lunar Photo of the Day.
- Wood, Chuck (October 17, 2006). "A Hole in the Middle". Lunar Photo of the Day.
- Wood, Chuck (May 27, 2007). "Drawing". Lunar Photo of the Day.
- Wood, Chuck (April 24, 2009). "Double Crossed". Lunar Photo of the Day.