| Umbrella squid | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Museum model of Histioteuthis bonnellii | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Cephalopoda |
| Order: | Oegopsida |
| Family: | Histioteuthidae |
| Genus: | Histioteuthis |
| Species: | H. bonnellii |
| Binomial name | |
| Histioteuthis bonnellii | |
| Synonyms | |
|
List
| |
Histioteuthis bonnellii, the umbrella squid, is a species of cock-eyed squid belonging to the family Histioteuthidae.
Distribution
This species is distributed mostly in the Atlantic Ocean. It can be found off the coast of Argentina, South Africa, and the Tasman Sea.[3] There is a population in the Mediterranean.[4] There may be several subspecies that exist in the Atlantic Ocean.[3]
Habitat
These squids can be found in mid water between 100 and 2200 m in depth. Juveniles usually inhabit the upper water column between 100 and 200 m, while larger individuals can be found between 200 and 800 m and most of mature specimens have been caught between 1000 and 2200 m in depth.[1]
Description
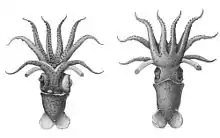
H. bonnellii is one of the larger species in its genus, usually reaching 33 cm in mantle length[5] and a total length of 119 cm.[3] Mature males can reach a mantle length of 50–330 millimetres (2.0–13.0 in).[3]
Body of these small to medium sized squids have a purplish color. Moreover they have various luminous organs, especially on the mantle, the arms and the long tentacles. The tentacles are connected by a membrane. The eyes of this animal are not symmetrical and they differ per side of the head.
Biology
Histioteuthis bonnellii is able to change color. It moves forward by pumping water into its mantle and pushing it out again through the siphon. It is a carnivore and its food consists mainly of fish, crabs, lobsters and molluscs caught with its suckers.
These cephalopods are predated by Northern bottlenose whale (Hyperoodon ampullatus), Sperm whale (Physeter macrocephalus), Blue shark (Prionace glauca), Swordfish (Xiphias gladius) and Cuvier's beaked whale (Ziphius cavirostris).[6]
Gallery
 Illustration from Die Cephalopoden
Illustration from Die Cephalopoden Histioteuthis bonnellii by Ernst Haeckel (as "Histioteuthis Rüppellii")
Histioteuthis bonnellii by Ernst Haeckel (as "Histioteuthis Rüppellii")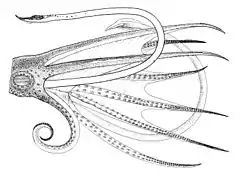
 Lower and upper parts of the beak
Lower and upper parts of the beak
Bibliography
- Clarke M.R. and N. MacLeod 1976. Cephalopods remains from the Sperm whales caught off Iceland. Journal of Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 56 : pp. 733–749
- Collins M.A., Lordan C., Flannery K., Quigley D.T.G. and F.G. Howard 1997. New records of cephalopods caught in Irish and Scottish waters. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. Cambridge University Press, New York. 77 (2) : pp. 561–564
- Santos M.B., Pierce G.J., Boyle P.R., Reid R.J., Ross H.M., Patterson I.A.P., Kinze C.C., Tougaard S., Lick R., Piatkowski U. and V, Hernández-García 1999. Stomach contents of sperm whales Physeter macrocephalus stranded in the North Sea 1990-1996. Marine Ecology Progress Series. 183 : pp. 281–294
References
- 1 2 Barratt, I.; Allcock, L. (2014). "Histioteuthis bonnellii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2014: e.T163073A968838. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2014-1.RLTS.T163073A968838.en. Retrieved 20 November 2021.
- ↑ Julian Finn (2016). "Histioteuthis bonnellii (Férussac, 1834)". World Register of Marine Species. Flanders Marine Institute. Retrieved 6 March 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 Young, R.E. & M. Vecchione 2006. Histioteuthis bonnellii (Ferussac 1834). The Tree of Life Web Project.
- ↑ Garibaldi, Fulvio; Podestà, Michela (September 2014). "Stomach contents of a sperm whale (Physeter macrocephalus) stranded in Italy (Ligurian Sea, north-western Mediterranean)". Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 94 (6): 1087–1091. doi:10.1017/S0025315413000428. ISSN 0025-3154. S2CID 86961833.
- ↑ Roper, C.F.E., M.J. Sweeney & C.E. Nauen 1984. Cephalopods of the world. Food and Agriculture Organization, Rome, Italy.
- ↑ Predators of Histioteuthis bonnellii on "CephBase "
External links
- "CephBase: Histioteuthis bonnellii". Archived from the original on 2005-08-17.
