 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Pasaden,[1][2] Oldagen (in Argentina)[3][4] |
| Other names | HFZ[5] |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
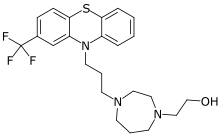
| Formula | C23H28F3N3OS |
| Molar mass | 451.55 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Boiling point | 230–240 °C (446–464 °F) [7] |
| |
| |
Homofenazine is an antipsychotic drug of the phenothiazines class.[5] It was synthesized by Wilhelm Schuler and colleagues at Degussa.[8][9] In 1966, it was released in Belgium under the brand name Pasaden.[1] At some point, it was quietly discontinued and is no longer marketed.
Synthesis
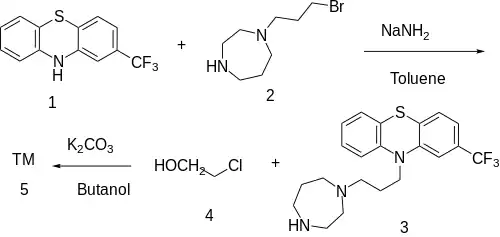
The alkylation between 2-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenothiazine [92-30-8] (1) and 1-(3-bromopropyl)-1,4-diazepane (2) led to 10-[3-(1,4-diazepan-1-yl)propyl]-2-(trifluoromethyl)phenothiazine, CID:110174391 (3). Further alkylation with 2-Chloroethanol [107-07-3] (4) completed the synthesis of homofenazine (5).
References
- 1 2 Schlesser JL (1990). 1991 Drugs available abroad: a guide to therapeutic drugs available and approved outside the U.S. Detroit : Gale Research. p. 107. ISBN 978-0-8103-7177-4. OCLC 1348900780.
- ↑ "Substâncias e remédios sob controle" [Substances and drugs under control] (PDF). Jornal do Brasil (in Brazilian Portuguese). 1986-11-05. p. 14. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2023-08-08. Retrieved 2023-08-08.
- ↑ Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory (17 ed.). Taylor & Francis. 2000. p. 1499. ISBN 9783887630751.
- ↑ Sitting, Marshall (1988). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia (Vols 1&2, 2nd Ed) (2 ed.). Westwood, NJ: Noyes Publications. p. 769. ISBN 0-8155-1144-2. LCCN 87-31547. OCLC 52233518.
- 1 2 Martindale: the complete drug reference. London; Chicago: Pharmaceutical Press. 2007. p. 899. ISBN 978-0-85369-687-2. OCLC 1176310249.
- ↑ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-03.
- ↑ Elks J, Ganellin CR, eds. (1990). Dictionary of Drugs. Boston, MA: Springer US. p. 635. doi:10.1007/978-1-4757-2085-3. ISBN 978-1-4757-2087-7.
- ↑ The Merck index : an encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs, and biologicals. Whitehouse Station, NJ : Merck. 1996. p. 810. ISBN 978-0-911910-12-4. OCLC 1285743402.
- ↑ US patent 3040043, Schuler et al., "3-trifluoromethyl-10-[3'-(4"-(2"'-hydroxy ethyl)-homopiperazino)-propyl]-phenothiazine and 3-trifluoromethyl-10-[3'-(4"-(2"'-acetoxyethyl)-homopiperazino)-propyl]-phenothiazine", published 1962-06-19, issued 1962-06-19, assigned to Degussa.
- ↑ Schuler Wilhelm Alfons, Beschke Helmut, Schlichtegroll Ansgar Von, U.S. Patent 3,040,043 (1962 to Degussa).
- ↑ Helmut Beschke, Schuler Dr Wilhelm Alfons, DE1445648A1 (1968 to Degussa).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.