| Hongshui River | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) | |
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | China |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Nanpan River |
| 2nd source | |
| • location | Beipan River |
| Mouth | |
• location | Qian River near Laibin |
| Length | 669.6 km (416.1 mi) |
| Basin size | 141,674 km2 (54,701 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 2,049 m3/s (72,400 cu ft/s)[1] |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Meng, Caodu, Qingshui, Diao |
| • right | Buliu |
| Hongshui River | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 紅水河 | ||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 红水河 | ||||||||
| Literal meaning | Redwater River | ||||||||
| |||||||||
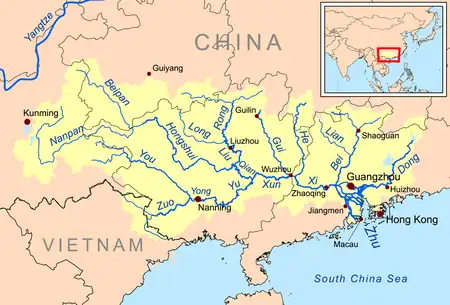
The Hongshui River is a major river in the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region in Southern China. It is one of the main rivers in the basin of the Xi River, which in its turn is one of the main tributaries of the Pearl River. Because it flows through the red rock series area, the river is reddish brown, hence the name Hongshui River (lit. 'red water river').
Conventionally, the Hongshui River is formed by the merging of the Beipan and Nanpan Rivers (Beipanjiang and Nanpanjiang, i.e., the Northern and Southern Pan Rivers) at the Guizhou-Guangxi border. From there, it flows in the general southeastern direction. In Laibin Prefecture in central Guangxi the Hongshui merges with the Liu River that comes from the north, forming the Qian River, which continues to the east toward, eventually, the Xi River.
The Hongshui has 10 large dams on it, that provide electric power and flood control.[2]
According to the Beijing Review the Hongshui River had 300 shoals that interfered with navigating the river with cargo vessels.[3] Several of the dams are equipped with ship lifts capable of lifting vessels of 300 tons displacement.
| name | cascade | date started | Megawatts | height | vessel capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dahua Dam | - | 1975 | 600 MW | 83.28m | |
| Yantan Dam | 5th | 1984 | 1210 MW | 110m | 250-ton ship lift[4][5] |
| Bailongtan Dam | - | 192 MW | - | 250-ton lock | |
| Pingban Dam | 3rd | ||||
| Xijing Dam | 1st | 1958 | - | - | 1000-ton lock |
| Longtan Dam | = | 2009 | 4,900 MW | 192m | 300-ton ship lift |
References
- ↑ Delineation of the Pearl River Basin (PRB), nine hydrological stations, and the primary hydraulic projects. Symbols ①~⑧ with triangles indicate the Tianshengqiao (I & II), Longtan, Baise, Xijin, Datengxia (under construction), Feilaixia, Xinfengjiang, and Fengshuba reservoirs, respectively – via ResearchGate.
- ↑ "Hydroelectric Projects". Guangxi Electric Power Industry Investigation Design and Research Institute. Archived from the original on 2005-07-28. Retrieved 2009-10-14.
- ↑ Lan Xinzhen (2008-10-30). "Harnessing the Hongshuihe". Beijing Review. Archived from the original on 2016-09-19.
- ↑ Zhu Shihong; Niu Xingqiang; Yang Chun. "PROTOTYPE OBSERVATION STUDY OF YANTAN VERTICAL SHIP LIFT". Yangitze River Scientific Research Institute. Archived from the original on 2011-07-17. Retrieved 2009-10-14.
- ↑ "Yantan Hydroelectric Project". World Bank. 1986-05-05. Retrieved 2009-10-14.
23°47′56″N 109°31′54″E / 23.79889°N 109.53167°E