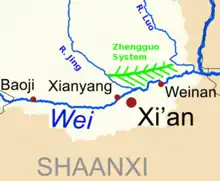
The Zhengguo Canal, Zhengguoqu or Chengkuo Canal (simplified Chinese: 郑国渠; traditional Chinese: 鄭國渠; pinyin: Zhèng Guó Qú), named after its designer, Zheng Guo, is a large canal located in Shaanxi province, China. The canal irrigates the Guanzhong plain, north of Xi'an. Together with the Dujiangyan Irrigation System and Lingqu Canal, it is one of the three biggest water conservation projects built before the Qin dynasty in ancient China.[1] The canal connects the Jing river and Luo river, northern tributaries of the Wei River.
History
Historian Sima Qian in his Records of the Grand Historian wrote of the Zhengguo Canal:
But Han heard that Qin was fond of embarking on enterprises, so with the intention of causing its energies to be dissipated and in order to prevent it from making an attack to the east, it accordingly dispatched a water engineer named Zheng Guo to give controversial advice to Qin by making it excavate a canal from the Jing River west of Mount Zhong as far as Hukou, from where it was to go east along the Northern Mountains and flow into the Luo. It would be more than 300 li long, and the intention would be to use it to irrigate the fields. When it was half completed the true purpose was realized, and Qin intended to kill Zheng Guo, but Zheng Guo said: ‘At first I was acting in order to cause dissension, but when the canal is completed it will surely be a benefit to Qin.’ Qin thought this was true, so in the end had the progress on the canal continued. When the canal did make further progress, it was used to cause the stagnant waters to flow, and irrigate the salty land over an area of more than 40,000 qing, so that the harvest totalled one zhong per mou. Thereupon the area within the passes was turned into fertile but uncultivated land, and there were no calamitous years, and thus Qin became rich and strong, and in the end unified the feudal states. Because of this it was called the Zheng Guo Canal.
The plan to drain the resources of the State of Qin back-fired as Qin successfully completed the canal, which irrigated c. 27,000 square kilometres of additional agricultural land, providing the kingdom with sufficient resources to increase the size of its already massive armies. To this day the land surrounding the Zhengguo Canal is extremely fertile.[3] The Jingshui River flows slowly and is heavy with sand, so the canal was frequently blocked. By the time of the Han dynasty, much of the canal had silted up and only a small section was still flowing. Under the supervision of engineer Bai Gong, a new canal was cut in 95 BC for irrigation. For the next 2000 years, re-cutting and moving the canal's feeder mouth upstream of the Jing River became a pattern as silt built up and river bed deepened, diminishing water flow and the efficiency of the system.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ "The Lingqu Canal, one of "The Three Great Hydraulic Engineering Projects of the Qin Dynasty" (秦代三大水利工程之一:灵渠)" (in Chinese). sina.com. July 26, 2005.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|url=(help) - ↑ Sima, Qian (2007). The First Emperor. Selections from the Historical Records. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 102. ISBN 978-0-19-922634-4.
- 1 2 Ronan, C. A.; Needham, J. (1995). The Shorter Science and Civilization in China. Vol. 5. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 200–201.