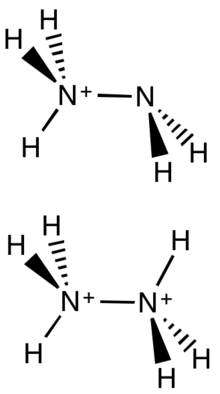
 Structures of hydrazinium [N2H5]+ and hydrazinediium [N2H6]2+. | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Amidoammonium Azanous azinide Ammonia dimer Azane dimer | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| 183 | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Hydrazinium is the cation with the formula [N2H5]+. This cation has a methylamine-like structure ([H2N−NH3]+). It can be derived from hydrazine by protonation (treatment with a strong acid). Hydrazinium is a weak acid with pKa = 8.1.
Salts of hydrazinium are common reagents in chemistry and are often used in certain industrial processes.[1] Notable examples are hydrazinium hydrogensulfate, N2H6SO4 or [N2H5]+[HSO4]−, and hydrazinium azide, N5H5 or [N2H5]+[N3]−. In the common names of such salts, the cation is often called "hydrazine", as in "hydrazine sulfate" for hydrazinium hydrogensulfate.
The terms "hydrazinium" and "hydrazine" may also be used for the doubly protonated cation [N2H6]2+, more properly called hydrazinediium or hydrazinium(2+). This cation has an ethane-like structure ([H3N−NH3]2+). Salts of this cation include hydrazinediium sulfate [N2H6]2+[SO4]2−[2] and hydrazinediium bis(6-carboxypyridazine-3-carboxylate), [N2H6]2+([C6H3N2O4]−)2.[3]
See also
- Ammonium, [NH4]+
References
- ↑ Jean-Pierre Schirmann, Paul Bourdauducq "Hydrazine" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2002. doi:10.1002/14356007.a13_177.
- ↑ Klapötke, T.; Peter S. White; Inis C. Tornieporth-Oetting (1996). "Reaction of hydrazinium azide with sulfuric acid: the X-ray structure of [N
2H
6][SO
4]". Polyhedron. 15 (15): 2579–2582. doi:10.1016/0277-5387(95)00527-7. - ↑ W. Starosta and J. Leciejewicz (2008), "Hydrazinediium bis(6-carboxypyridazine-3-carboxylate) dihydrate". Acta Crystallographica, volume E64, article o461. doi:10.1107/S1600536808001037