A hydrospring or hydro-spring is a spring damped by hydraulic fluid (typically oil) being driven through holes in a piston, as the piston moves in response to a force. The spring is often made of rubber. Inside a rubber hydrospring there are hydraulic viscous damping systems which damp movement in all three directions but require very few parts. Even the slack adjustment may be integrated into the element.[1]
Hydrosprings are used mainly as shock absorbers in applications such as damped suspension in railway bogies, bulldozer blade shock absorbers and as recoil absorbers for artillery.
 A railway type rubber hydrospring[2]
A railway type rubber hydrospring[2] A railway type rubber hydrospring in compressed state
A railway type rubber hydrospring in compressed state A railway type rubber hydrospring in relaxed state
A railway type rubber hydrospring in relaxed state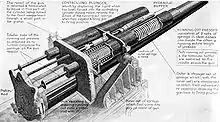 Hydro-spring recoil system of British WWI 60 pounder gun, with working explained
Hydro-spring recoil system of British WWI 60 pounder gun, with working explained
See also
References
- ↑ Hecht, Markus (2007). Wear and Energy Saving Bogie Design with Rubber Primary Springs – Principles and Experiences (pdf). IHHA Specialist Technical Session (STS). Kiruna, Sweden.
- ↑ EP patent 1369616
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.