Fédération internationale de hockey sur glace Internationale Eishockey-Föderation | |
 | |
| Abbreviation | IIHF |
|---|---|
| Formation | 15 May 1908 |
| Founded at | Paris, France |
| Type | Sports federation |
| Legal status | Governing body of ice hockey |
| Purpose | Sport governance |
| Headquarters | Zurich, Switzerland |
Region served | Worldwide |
Membership | 82 members |
Official languages | English, French, German |
| Luc Tardif | |
| Website | IIHF.com |
The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF; French: Fédération internationale de hockey sur glace; German: Internationale Eishockey-Föderation) is a worldwide governing body for ice hockey.[1] It is based in Zurich, Switzerland, and has 83 member countries.
The IIHF maintains the IIHF World Ranking based on international ice hockey tournaments. Rules of play for IIHF events differ from hockey in North America and the rules of the National Hockey League (NHL). Decisions of the IIHF can be appealed through the Court of Arbitration for Sport in Lausanne, Switzerland. The IIHF maintains its own hall of fame for international ice hockey. The IIHF Hall of Fame was founded in 1997, and has been located within the Hockey Hall of Fame since 1998.
Previously, the IIHF also managed the development of inline hockey; however, in June 2019, the IIHF announced that they would no longer govern inline hockey or organize the Inline Hockey World Championships.[2]
Functions

The main functions of the IIHF are to govern, develop and organize hockey throughout the world. Another duty is to promote friendly relations among the member national associations and to operate in an organized manner for the good order of the sport.[3] The federation may take the necessary measures in order to conduct itself and its affairs in accordance with its statutes, bylaws and regulations as well as in holding a clear jurisdiction with regards to ice hockey at the international level. The IIHF is the body responsible with arranging the sponsorships, license rights, advertising and merchandising in connection with all IIHF competitions.
Another purpose of the federation is to provide aid in the young players' development and in the development of coaches and game officials. On the other hand, all the events of IIHF are organized by the federation along with establishing and maintaining contact with any other sport federations or sport groups. The IIHF is responsible for processing the international players' transfers. It is also the body that presides over ice hockey at the Olympic Games as well as over all levels of the IIHF World Championships.[4] The federation works in collaboration with local committees when organizing its 25 World Championships, at five different categories.
Even though the IIHF runs the world championships, it is also responsible for the organization of several European club competitions such as the Champions Hockey League or the Continental Cup.
The federation is governed by the legislative body of the IIHF which is the General Congress along with the executive body, which is the Council. The Congress is entitled to make decisions with regard to the game's rules, the statutes and bylaws in the name of the federation. It is also the body that elects the president and the council or otherwise known as board.[5] The president of the IIHF is basically the representative of the federation. He represents the federation's interests in all external matters and he is also responsible that the decisions are made according to the federation's statutes and regulations. The president is assisted by the General Secretary, who is also the highest ranked employee of the IIHF.
History
The International Ice Hockey Federation was founded on 15 May 1908 at 34 Rue de Provence in Paris, France, as Ligue Internationale de Hockey sur Glace (LIHG).[6] The 1920 Olympics were the first to integrate hockey into their program.

The 1928 Winter Olympics, which also served as the World and European Championship for the year, saw a record 11 countries participate.[7] The 1936 Winter Olympics set a new record with 15 participants.
The Hungarian Revolution of 1956 which had caused Hungary to be occupied by the Soviet Army, led to a boycott of the 1957 World Championships, which were being staged in Moscow. Canada and the United States led the boycott, and were joined by Norway, West Germany, Italy, and Switzerland.[8]
The 1962 World Championship, hosted by the American cities of Colorado Springs and Denver, was boycotted by the Soviet Union and Czechoslovakia, which led to a further boycott by the other Eastern Bloc countries. At issue was the boycott of the 1957 championships in Moscow by Canada and the United States, and the Americans refusal of East German passports in reaction to the building of the Berlin Wall by East Germany.[9]
For the 1965–66 season, the IIHF created the European Cup, a tournament consisting of the top club teams from around Europe. The competition was originated by Günther Sabetzki, based on the Association football European Cup (now UEFA Champions League). In 1968 the IIHF organized the European U19 Championship, a junior competition for players aged 19 and under. The age limit was later reduced to 18 in 1977.[8]
During the 1980s Canada stopped boycotting the World Championships and Olympic Games. The Canadians had boycotted these tournaments between 1970 and 1976 after the IIHF had refused to allow them to roster professional players at the World Championships from NHL teams that had not qualified for the Stanley Cup playoffs. President Sabetzki managed to find a compromise that resulted in the return of Canada to international events beginning in 1977. The pro players whose teams had been eliminated from the playoffs were allowed to compete and in exchange, Canada agreed to participate in the World Championships. They also waived their right to host any World Championships. The creation of the Canada Cup (a competition organized by the NHL in Canada every four years) was also part of the new agreement between the IIHF and North American professional hockey.[9]
The IIHF continued to grow in numbers during the 1980s and 1990s, both due to political events and the continued growth of hockey worldwide. The dissolution of the Soviet Union saw its membership transferred to Russia, and the addition of four ex-Soviet republics; Azerbaijan, Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Ukraine to the federation. In addition, the memberships of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania - all of which had initially joined the IIHF in the 1930s but were expelled following their annexation by the Soviet Union - were renewed. The breakup of Yugoslavia also resulted in an increase in membership. Croatia and Slovenia joined as new members, while the membership of the old Yugoslavia was transferred to FR Yugoslavia (which later became known as Serbia and Montenegro and still later dissolved into the independent republics of Serbia and Montenegro). When Czechoslovakia broke up, its membership rights were transferred to the Czech Republic, and Slovakia was admitted as a new member. The influx of new members resulted in the IIHF increasing the size of the Group A tournament. It expanded from 8 teams to 12 in 1992 and from 12 to 16 in 1998.[10]
The IIHF celebrated its 100th anniversary in 2008. As part of the celebrations, the 2008 World Championship was held in Canada for the first time (the tournament was co-hosted by the cities of Halifax and Quebec City).[11] To commemorate the anniversary, the IIHF Centennial All-Star Team was chosen by votes.
The number of members grew in the 21st century: Chile (2000), Bosnia and Herzegovina (2001), Liechtenstein (2001), North Macedonia (2001), the United Arab Emirates (2001), Macau (2005), Malaysia (2006), Moldova (2008; presumably expelled from IIHF membership in 2023), Georgia (2009), Kuwait (2009; had originally joined in 1985, but was expelled in 1992), Morocco (2010), Kyrgyzstan (2011), Jamaica (2012), Qatar (2012), Oman (2014), Turkmenistan (2015), Indonesia (2016), Nepal (2016), the Philippines (2016), Algeria (2019), Colombia (2019), Iran (2019), Lebanon (2019), Uzbekistan (2019), Tunisia (2021), and Puerto Rico (2022).[10]
The IIHF received international criticism for holding the 2014 Men's Ice Hockey World Championships in Belarus because of the poor human rights record of the country. Several human rights organisations launched the "Don't play with the dictator!" boycott campaign[12] and there were appeals from the US Congress, the German Parliament, and the European Parliament.[13] The IIHF again received criticism for planning to partly hold the 2021 Men's Ice Hockey World Championships in Belarus.[14][15] In January 2021, the IIHF withdrew the 2021 World Championship from Minsk due to safety and security issues during the political unrest, besides the COVID-19 pandemic and decided to solely hold the tournament in Riga, Latvia.[16]
On 23 May 2021, civilian Ryanair Flight 4978, which was enroute from Athens to Vilnius, was forced to land in Minsk and a passenger of that flight was detained. In protest, Latvian officials replaced the Belarusian state flag in Riga with the former flag associated with the Belarusian opposition groups, including at the 2021 IIHF World Championship display of flags. This was by order of Mayor of Riga Mārtiņš Staķis and Minister of Foreign Affairs of Latvia Edgars Rinkēvičs. The IIHF issued a statement protesting the replacement of the flag, and IIHF president René Fasel asked the mayor to remove the IIHF name, its flag and its symbols from such sites, or to restore the flag, insisting that the IIHF is an "apolitical sports organization".[17] In response, Staķis said he would remove the IIHF flags.[18][19]
On 28 February 2022, the IIHF suspended the memberships of the Russian and Belarusian ice hockey federations until further notice due to the countries' invasion of Ukraine.[20] Still, non-Russian players in Russian clubs are according to IIHF rules bound by their contracts, and can not leave their clubs and Russia until their contracts expire or is terminated by their club. If players leave anyway they can be sued and would be blocked from playing for other clubs.[21]
On 22 March 2023, the IIHF excluded Russian and Belarusian national and club teams from IIHF competitions during the 2023–24 season, based on safety considerations.[22]
IIHF Hall of Fame

Prior to the establishment of the IIHF Hall of Fame, the IIHF displayed a collection of historical artifacts from World Championships and the Olympic Games in temporary exhibits. From 1992 to 1997, the IIHF loaned its exhibits to the International Hockey Hall of Fame in Kingston, Ontario, Canada.[23]
The first step taken by the IIHF to create its own hall of fame was a proposal made in 1996, which was later ratified at the 1997 IIHF summer congress to host the museum in Zürich.[23] The approval came exactly 89 years from the foundation of the IIHF, with the purpose of honoring former international ice hockey players, builders (administrators) and officials.[24] The annual induction ceremony takes place on the medal presentation day of the Ice Hockey World Championships.[23][24] The IIHF agreed with the National Hockey League to transfer its exhibits to the Hockey Hall of Fame in Toronto, Canada, as of 29 July 1998.[23]
Tournaments
Men's
| Tournament | Year | Champions | Runners-up | Third place | Fourth place |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winter Olympics | |||||
| IIHF World Championship | |||||
| U-20 IIHF World Championship | |||||
| U-18 IIHF World Championship |
Women's
| Tournament | Year | Champions | Runners-up | Third place | Fourth place |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winter Olympics | |||||
| IIHF Women's World Championship | |||||
| U-18 IIHF Women's World Championship |
Club
| Tournament | Year | Champions | Runners-up | Third place | Fourth place |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Champions Hockey League | 2022–23 | ||||
| IIHF Continental Cup | 2023–24 | ||||
Executives and personnel
The IIHF employs twenty staff members at the headquarters in Zurich.[28]
Presidents
| Name | Years |
|---|---|
| 1908–1912 | |
| 1912–1914 | |
| 1914 | |
| 1914 | |
| 1914–1920 | |
| 1920–1922 | |
| 1922–1947 | |
| 1947–1948 | |
| 1948–1951 | |
| 1951–1954 | |
| 1954–1957 | |
| 1957–1960 | |
| 1960–1963 | |
| 1963–1966 | |
| 1966–1969 | |
| 1969–1975 | |
| 1975–1994 | |
| 1994–2021 | |
| 2021–present |
Chief Medical Officers
- Wolf-Dieter Montag, Germany (1975 to 1998)[29]
- Mark Aubry, Canada (1998 to present)[30][31]
Members
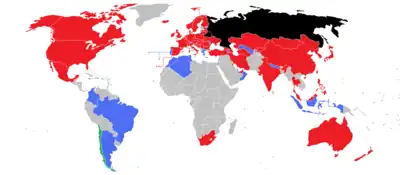
As of 2022, the IIHF has 82 members.[32]
The federation has 60 full members, including two suspended members: Australia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Belarus (suspended), Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Canada, China, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Great Britain, Hong Kong, Hungary, Iceland, India, Iran, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Kazakhstan, Korea, Kuwait, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malaysia, Mexico, Mongolia, Netherlands, New Zealand, North Korea, Norway, the Philippines, Poland, Qatar, Romania, Russia (suspended), Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, South Africa, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, Thailand, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, the United Arab Emirates, and the United States. Full members have a national body dedicated to the sport, and participate annually in the international championships. Only full members have voting rights.
In addition, there are 21 associate members who either do not have a national body dedicated to the sport, or do not regularly participate in the international championships. They are Algeria, Andorra, Argentina, Armenia, Brazil, Colombia, Greece, Indonesia, Jamaica, Lebanon, Liechtenstein, Macau, Morocco, Nepal, North Macedonia, Oman, Portugal, Puerto Rico, Singapore, Tunisia, and Uzbekistan.
The IIHF recognizes Chile as an affiliated member that only participates in inline championships.
By division
Men
The following are countries who will compete in the 2024 Men's Ice Hockey World Championships, divided by tier:[33]
| Division | IIHF Members |
|---|---|
| Top | |
| I | |
| II | |
| III | |
| IV |
Men U20
The following are countries who are competing in the 2024 World Junior Ice Hockey Championships, divided by tier:[34]
| Division | IIHF Members |
|---|---|
| Top | |
| I | |
| II | |
| III |
Women
The following are countries who are competing in the 2024 Women's Ice Hockey World Championships, divided by tier:[35]
| Division | IIHF Members |
|---|---|
| Top | |
| I | |
| II | |
| III |
Registered players
Based on the number of registered ice hockey players, including male, female and junior, provided by the respective countries' federations. This list includes 71 out of 82 IIHF member countries with more than 100 registered players as of October 2022.[32][36]
| Country | Registered players | % of registered players | % of population |
|---|---|---|---|
| 551,006 | 35.44% | 0.166% | |
| 513,674 | 33.04% | 1.361% | |
| 103,101 | 6.63% | 0.071% | |
| 66,687 | 4.29% | 1.204% | |
| 61,547 | 3.96% | 0.609% | |
| 34,341 | 2.21% | 0.321% | |
| 29,360 | 1.89% | 0.339% | |
| 21,090 | 1.36% | 0.025% | |
| 18,686 | 1.20% | 0.029% | |
| 16,219 | 1.04% | 0.013% | |
| 13,388 | 0.86% | 0.001% | |
| 13,327 | 0.86% | 0.020% | |
| 11,447 | 0.74% | 0.210% | |
| 8,943 | 0.58% | 0.093% | |
| 8,618 | 0.55% | 0.159% | |
| 7,898 | 0.51% | 0.419% | |
| 7,232 | 0.47% | 0.080% | |
| 7,053 | 0.45% | 0.075% | |
| 6,150 | 0.40% | 0.024% | |
| 5,341 | 0.34% | 0.012% | |
| 5,147 | 0.33% | 0.089% | |
| 5,136 | 0.33% | 0.008% | |
| 4,320 | 0.28% | 0.023% | |
| 3,950 | 0.25% | 0.010% | |
| 3,515 | 0.23% | 0.021% | |
| 3,044 | 0.20% | 0.006% | |
| 2,702 | 0.17% | 0.041% | |
| 2,213 | 0.14% | 0.012% | |
| 2,035 | 0.13% | 0.042% | |
| 1,793 | 0.12% | 0.015% | |
| 1,700 | 0.11% | 0.007% | |
| 1,502 | 0.10% | 0.000% | |
| 1,486 | 0.10% | 0.002% | |
| 1,340 | 0.09% | 0.049% | |
| 1,232 | 0.08% | 0.001% | |
| 1,072 | 0.07% | 0.052% | |
| 995 | 0.06% | 0.075% | |
| 980 | 0.06% | 0.002% | |
| 945 | 0.06% | 0.014% | |
| 893 | 0.06% | 0.002% | |
| 868 | 0.06% | 0.004% | |
| 828 | 0.05% | 0.025% | |
| 752 | 0.05% | 0.220% | |
| 695 | 0.04% | 0.007% | |
| 668 | 0.04% | 0.008% | |
| 624 | 0.04% | 0.001% | |
| 598 | 0.04% | 0.015% | |
| 576 | 0.04% | 0.008% | |
| 520 | 0.03% | 0.013% | |
| 508 | 0.03% | 0.006% | |
| 492 | 0.03% | 0.079% | |
| 480 | 0.03% | 0.001% | |
| 421 | 0.03% | 0.001% | |
| 402 | 0.03% | 0.009% | |
| 350 | 0.02% | 0.007% | |
| 347 | 0.02% | 0.006% | |
| 269 | 0.02% | 0.003% | |
| 250 | 0.02% | 0.001% | |
| 242 | 0.02% | 0.007% | |
| 233 | 0.01% | 0.000% | |
| 225 | 0.01% | 0.001% | |
| 220 | 0.01% | 0.004% | |
| 208 | 0.01% | 0.003% | |
| 205 | 0.01% | 0.007% | |
| 187 | 0.01% | 0.006% | |
| 185 | 0.01% | 0.000% | |
| 165 | 0.01% | 0.006% | |
| 139 | 0.01% | 0.000% | |
| 121 | 0.01% | 0.019% | |
| 110 | 0.01% | 0.000% | |
| 110 | 0.01% | 0.000% |
IIHF World Ranking
The IIHF World Ranking is a tool to reflect the long-term quality of the countries' national team program.[37] The IIHF World Ranking is released following each IIHF Ice Hockey World Championship and the Olympic Ice Hockey Tournament.
References
- ↑ "IIHF - Who we are". International Ice Hockey Federation.
- ↑ "Statutes, Regulations amended". International Ice Hockey Federation. 24 June 2019. Retrieved 24 June 2019.
- ↑ International Ice Hockey Federation. "IIHF Mission" 8 May 2019.
- ↑ International Hockey online portal. "International hockey and the olympics" Archived 10 April 2010 at the Wayback Machine 18 February 2010.
- ↑ International Ice Hockey Federation. "IIHF Statutes and Bylaws" 8 May 2019.
- ↑ It all Started in Paris, 1908 International Ice Hockey Federation. Retrieved on 7 May 2019
- ↑ "IIHF 1914-1933". iihf.com. IIHF. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- 1 2 "IIHF 1957-1974". iihf.com. IIHF. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- 1 2 "IIHF 1975-1989". iihf.com. IIHF. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- 1 2 "IIHF 1990-today". iihf.com. IIHF. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ↑ "IIHF Timeline". iihf.com. IIHF. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ↑ "International Campaign: Don't play with the dictator!". 17 April 2012.
- ↑ Davide Tuniz (15 March 2012). "European Parliament calls to move the 2014 World Championship from Belarus".
- ↑ "Ice hockey-IIHF president to meet Belarus' Lukashenko to discuss 2021 world championship – RIA". Reuters. 29 December 2020. Retrieved 11 January 2021.
- ↑ "Ice Hockey: Belarus must meet 'specific requirements' to host World Championship". Deutsche Welle. 14 January 2021. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ↑ "IIHF to move 2021 World Championship". International Ice Hockey Federation. 18 January 2021. Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- ↑ "Latvia and hockey body spar over Belarus opposition flag". France 24. 25 May 2021.
- ↑ "Ice Hockey Federation boss Fasel unhappy with Belarus flag switch". lsm.lv. 25 May 2021. Retrieved 25 May 2021.
- ↑ "Latvia removes ice hockey body's banner in row over Belarus flag swap". Reuters. 25 May 2021. Retrieved 25 May 2021.
- ↑ "IIHF - IIHF Council takes definitive action over Russia, Belarus". IIHF.com. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ↑ IIHF won’t be able to cancel KHL Legionnaires’ contracts until 2023
- ↑ "Update on Russia and Belarus", IIHF, 22 March 2023
- 1 2 3 4 "IIHF Hall of Fame". Hockey Archives (in Russian). Retrieved 12 March 2019.
- 1 2 "IIHF Hall of Fame". International Ice Hockey Federation. Retrieved 12 March 2019.
- 1 2 "IIHF - Tournaments". IIHF. Retrieved 4 January 2022.
- ↑ Competed as the
 Russian Olympic Committee due to sanctions from the Russian doping scandal
Russian Olympic Committee due to sanctions from the Russian doping scandal - ↑ "IIHF - Tournaments (Club)". IIHF. Retrieved 4 January 2022.
- ↑ "IIHF Staff". International Ice Hockey Federation. Retrieved 26 January 2021.
- ↑ "Wolf-Dieter Montag – Curriculum Vitae" (PDF). Gesellschaft für Orthopädisch-Traumatologische Sportmedizin (in German). 19 November 2014. p. 2. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 November 2018.
- ↑ "Paul Loicq Award: Dr Mark Aubry (CAN)". IIHF. 2014. Retrieved 31 July 2018.
- ↑ "Dr. Mark Aubry – 2006 Dr. Tom Pashby Sports Safety Award". Dr. Pashby Sports Safety Fund. 18 November 2006. Retrieved 1 August 2018.
- 1 2 "IIHF Member National Associations". International Ice Hockey Federation. 29 September 2022.
- ↑ "2024 IIHF Men's World Championships Divisions". IIHF. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ↑ "2024 IIHF World Junior Championships Divisions". IIHF. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ↑ "2024 IIHF Women's World Championships Divisions". IIHF. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ↑ "Countries in the world by population (2022)". Worldometer. Retrieved 6 October 2022.
- ↑ "IIHF World Ranking". iihf.com. IIHF. Retrieved 4 October 2022.
Sources
- Podnieks, Andrew; Szemberg, Szymon (2007). World of hockey : celebrating a century of the IIHF. Fenn Publishing. ISBN 9781551683072.
External links
![]() Media related to International Ice Hockey Federation at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to International Ice Hockey Federation at Wikimedia Commons