| IL1RAPL2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | IL1RAPL2, IL-1R9, IL1R9, IL1RAPL-2, TIGIRR-1, interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein like 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 300277 MGI: 1913106 HomoloGene: 9681 GeneCards: IL1RAPL2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
X-linked interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein-like 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL1RAPL2 gene.[5][6]
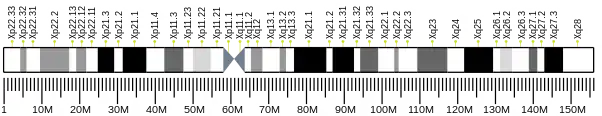
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the interleukin 1 receptor family. This protein is similar to the interleukin 1 accessory proteins, and is most closely related to interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein-like 1 (IL1RAPL1). This gene and IL1RAPL1 are located at a region on chromosome X that is associated with X-linked non-syndromic mental retardation.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000189108 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000059203 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Jin H, Gardner RJ, Viswesvaraiah R, Muntoni F, Roberts RG (May 2000). "Two novel members of the interleukin-1 receptor gene family, one deleted in Xp22.1-Xp21.3 mental retardation". Eur J Hum Genet. 8 (2): 87–94. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200415. PMID 10757639. S2CID 22262168.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: IL1RAPL2 interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein-like 2".
Further reading
- Grundtman C, Salomonsson S, Dorph C, et al. (2007). "Immunolocalization of interleukin-1 receptors in the sarcolemma and nuclei of skeletal muscle in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies". Arthritis Rheum. 56 (2): 674–87. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.489.4969. doi:10.1002/art.22388. PMID 17265504.
- Libra M, Mangano K, Anzaldi M, et al. (2006). "Analysis of interleukin (IL)-1beta IL-1 receptor antagonist, soluble IL-1 receptor type II and IL-1 accessory protein in HCV-associated lymphoproliferative disorders". Oncol. Rep. 15 (5): 1305–8. doi:10.3892/or.15.5.1305. PMID 16596202.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ferrante MI, Ghiani M, Bulfone A, Franco B (2001). "IL1RAPL2 maps to Xq22 and is specifically expressed in the central nervous system". Gene. 275 (2): 217–21. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00659-X. PMID 11587848.
- Sana TR, Debets R, Timans JC, et al. (2001). "Computational identification, cloning, and characterization of IL-1R9, a novel interleukin-1 receptor-like gene encoded over an unusually large interval of human chromosome Xq22.2-q22.3". Genomics. 69 (2): 252–62. doi:10.1006/geno.2000.6328. PMID 11031108.
- Born TL, Smith DE, Garka KE, et al. (2000). "Identification and characterization of two members of a novel class of the interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) family. Delineation of a new class of IL-1R-related proteins based on signaling". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (39): 29946–54. doi:10.1074/jbc.M004077200. PMID 10882729.
- Nagaoka H, Ozawa K, Matsuda F, et al. (1994). "Recent translocation of variable and diversity segments of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain from chromosome 14 to chromosomes 15 and 16". Genomics. 22 (1): 189–97. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1360. PMID 7959766.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.