The iPhone is a line of smartphones designed and marketed by Apple Inc. that uses Apple's iOS mobile operating system. The first-generation iPhone was announced by former Apple CEO Steve Jobs on January 9, 2007. Since then, Apple has annually released new iPhone models and iOS updates. iPhone naming has followed various patterns throughout its history.
Nomenclature
Current naming style
iPhones are named with "iPhone" followed by a number, which denotes the iPhone generation, and sometimes a suffix (such as C, S, Plus, Pro, Pro Max). The current naming pattern is that "Plus" or "Max" indicates a physical larger iPhone model of the same generation (iPhone XS Max, 11 Pro Max, 12 Pro Max, 13 Pro Max, 14 Plus, 14 Pro Max, 15 Plus, 15 Pro Max). "Pro" indicates the higher end model (iPhone 11 Pro, 12 Pro, 13 Pro, 14 Pro, 15 Pro). Currently, models with just a number (i.e. without a suffix) indicate the lower-priced iPhones (iPhone 11, 12, 13, 14, 15). The "SE" used in the iPhone SE line stands for "Special Edition".[1][2]
Previous naming style
"S" used to denote a slight upgrade (iPhone 3GS, 4S, 5S, 6S & 6S Plus, XS & XS Max), but it has since been dropped; iPhone XS and XS Max were the last models to feature the "S" (iPhone 12, 12 Pro, 12 Pro Max instead of iPhone 11, 11 Pro, 11 Pro Max). "C" used to denote the lower-priced iPhones (iPhone 5C). iPhone X (pronounced "10"), iPhone XR (pronounced "10R") and iPhone XS and XS Max (pronounced "10S") are currently the only iPhones to have been branded with roman numerals (X).
iPhones
42 different iPhone models have been produced:
|
Timeline
| Timeline of iPhone models |
|---|
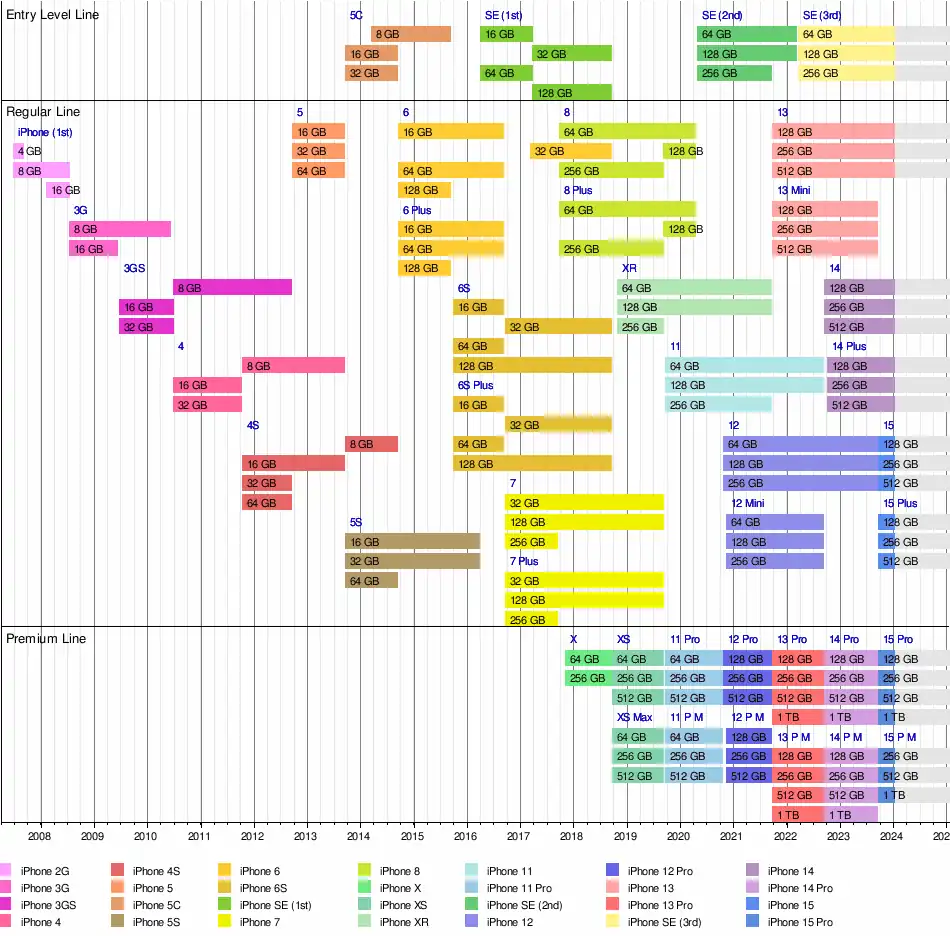 |
Models never made
No models called the iPhone 2, iPhone 7S, iPhone 8S, iPhone 9, iPhone 11S, iPhone 12S, iPhone 13S and iPhone 14S were ever produced; however, iPhone 9 was the rumored name for the iPhone SE (2020).[4][5]
The 1st-generation iPhone was colloquially known, retronymically, as the iPhone 2G, as the 2nd generation iPhone was the iPhone 3G. The iPhone 4 did not support 4G; the iPhone 5 was the first with LTE support,[6] while the iPhone 12 and 12 Pro were the first with 5G support.[7][8]
References
- ↑ Langly, Hugh (22 March 2016). "What the iPhone SE stands for – and what we think it should stand for". TechRadar.com. Retrieved 23 June 2022.
- ↑ "Apple iPhone SE: Wofür steht eigentlich das SE? - WELT". Die Welt (in German). 1 June 2017. Retrieved 26 May 2023.
- ↑ Apple Inc. (2007–2023). iPhone News - Newsroom Archive. Retrieved September 12, 2023.
- ↑ "Why was there no iPhone 9? Plus, what happened to the iPhone 10". pocket-lint.com. 15 April 2020. Retrieved 12 August 2020.
- ↑ "Will Apple Ever Release an iPhone 9? Here's What We Know". gadgetadvisor.com. 3 June 2019. Retrieved 13 August 2020.
- ↑ "Apple Introduces iPhone 5". Apple Newsroom. 12 September 2012. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ↑ "Apple announces iPhone 12 and iPhone 12 mini: A new era for iPhone with 5G". Apple Newsroom. 13 October 2020. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ↑ "Apple introduces iPhone 12 Pro and iPhone 12 Pro Max with 5G". Apple Newsroom. 13 October 2023. Retrieved 16 October 2023.