
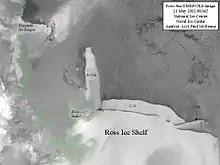
Iceberg C-19 is an iceberg that calved from the Ross Ice Shelf in May 2002 on a fissure scientists had been watching since the 1980s. After that the Ross Ice Shelf returned to the size it was in 1911, when it was mapped by Robert F. Scott’s party. It was the second-largest iceberg to calve in the region in a few years (after B-15). It had a surface area larger than 5500 km2.
During 2002 C-19 prevented sea ice from moving out of the southwestern Ross Sea region and this blockage resulted in an unusually high sea ice level during spring and summer, thus provoking a huge reduction in phytoplankton production which is at the base of the food chain.
In summer 2003 C-19 moved northward very rapidly, passed Cape Adare, and broke in two pieces: C-19A and C-19B.
In September 2005, after a two-year stay along the coast of Victoria Land (west of French station Dumont d'Urville) C-19A started drifting northward. In March 2006 its location was in the Pacific Ocean, 200 km west of Balleny Islands.
In 2008, C-19A was renamed Melting Bob by Max Dolan as a result of a contest sponsored by the Hay Festival and the Scott Polar Research Institute. As of May 2008, its surface area was approximately 5141 km2.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ Schoolboy first to 'name' iceberg, BBC, 2008-05-31, retrieved 2008-05-31
External links
- Huge Antarctic Iceberg Makes a BIG Splash on Sea Life, press release, Goddard Space Flight Center, NASA, 1 October 2003
- Antarctic iceberg C19A renamed Melting Bob by Max Dolan, 6, story of how C19A became the first iceberg to be given a proper name, May 31, 2008