| Interpeduncular fossa | |
|---|---|
 Base of brain | |
 Section through superior colliculus showing path of oculomotor nerve (interpeduncular fossa not labeled, but visible at bottom center) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fossa interpeduncularis |
| NeuroNames | 489 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The interpeduncular fossa is a deep depression[1] of the ventral surface of the midbrain[2]: 456 between the two crura cerebri.[2]: 456 [3]
It has been found in humans and macaques, but not in rats or mice, showing that this is a relatively new evolutionary region.[4]
Anatomy
The interpeduncular fossa is a somewhat rhomboid-shaped area of the base of the brain.[5]
Features
The lateral wall of the interpeduncular fossa bears a groove - the oculomotor sulcus - from which[6] rootlets of the oculomotor nerve emerge from the substance of the brainstem[6][2]: 456 and aggregate into a single fascicle.[2]: 456
Anatomical relations
The ventral tegmental area lies at the depth of the interpeduncular fossa.[2]: 459
Boundaries
The interpeduncular fossa is in front by the optic chiasma, behind by the antero-superior surface of the pons, antero-laterally by the converging optic tracts, and postero-laterally by the diverging cerebral peduncles.[5]
The floor of interpeduncular fossa, from behind forward, are the posterior perforated substance,[1] corpora mamillaria, tuber cinereum, infundibulum, and pituitary gland.
Contents
Contents of interpeduncular fossa include oculomotor nerve, and circle of Willis.
The basal veins pass alongside the interpeduncular fossa before joining the great cerebral vein.[2]: 422
Clinical significance
The most common locations for neurocutaneous melanosis have occurred along the interpeduncular fossa, ventral brainstem, upper cervical cord, and ventral lumbosacral cord.[7]
See also
Additional images
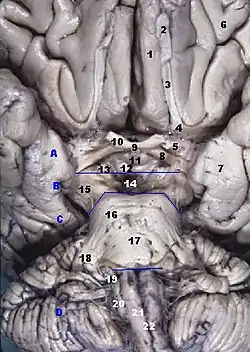 Human brainstem anterior view
Human brainstem anterior view Interpeduncular fossa. Cerebrum. Deep dissection. Inferior dissection.
Interpeduncular fossa. Cerebrum. Deep dissection. Inferior dissection.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 816 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 816 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- 1 2 "fossa interpeduncularis". TheFreeDictionary.com. Retrieved 2022-08-08.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Gray's anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Susan Standring (42nd ed.). [New York]. 2021. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: others (link) - ↑ Basinger, Hayden; Hogg, Jeffery P. (2022), "Neuroanatomy, Brainstem", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 31335017, retrieved 2022-08-08
- ↑ "BrainInfo". braininfo.rprc.washington.edu. Retrieved 2019-04-03.
- 1 2 "Interpeduncular fossa". IMAIOS. Retrieved 2019-04-03.
- 1 2 "sulcus of the oculomotor nerve". TheFreeDictionary.com. Retrieved 2022-08-08.
- ↑ Islam, Monica P. (2015). "Neurocutaneous melanosis". Neurocutaneous Syndromes. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Vol. 132. pp. 111–7. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-62702-5.00007-X. ISBN 978-0-444-62702-5. PMID 26564074.