| Malabsorption | |
|---|---|
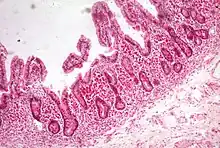 | |
| Whipple's disease: Alcian blue with apparently eosin counterstain enlarged villus with many macrophages | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
| Complications | Malnutrition; anaemia; steatorrhoea; diarrhoea |
| Causes | Coeliac disease; short bowel syndrome; lactase deficiency; exocrine pancreatic insufficiency; small intestinal bacterial overgrowth; Whipple's disease; genetic diseases; certain medications[1] |
| Treatment | Depends on cause |
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a variety of anaemias.[1]
Normally the human gastrointestinal tract digests and absorbs dietary nutrients with remarkable efficiency. A typical Western diet ingested by an adult in one day includes approximately 100 g of fat, 400 g of carbohydrate, 100 g of protein, 2 L of fluid, and the required sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium, vitamins, and other elements. Salivary, gastric, intestinal, hepatic, and pancreatic secretions add an additional 7–8 L of protein-, lipid-, and electrolyte-containing fluid to intestinal contents. This massive load is reduced by the small and large intestines to less than 200 g of stool that contains less than 8 g of fat, 1–2 g of nitrogen, and less than 20 mmol each of Na+, K+, Cl–, HCO3–, Ca2+, or Mg2+.
If there is impairment of any of the many steps involved in the complex process of nutrient digestion and absorption, intestinal malabsorption may ensue. If the abnormality involves a single step in the absorptive process, as in primary lactase deficiency, or if the disease process is limited to the very proximal small intestine, then selective malabsorption of only a single nutrient may occur. However, generalized malabsorption of multiple dietary nutrients develops when the disease process is extensive, thus disturbing several digestive and absorptive processes, as occurs in coeliac disease with extensive involvement of the small intestine.[1]
Signs and symptoms
Gastrointestinal manifestations
Depending on the nature of the disease process causing malabsorption and its extent, gastrointestinal symptoms may range from severe to subtle or may even be totally absent. Diarrhea, weight loss, flatulence, abdominal bloating, abdominal cramps, and pain may be present. Although diarrhea is a common complaint, the character and frequency of stools may vary considerably ranging from over 10 watery stools per day to less than one voluminous putty-like stool, the latter causing some patients to complain of constipation. On the other hand, stool mass is invariably increased in patients with steatorrhea and generalized malabsorption above the normal with 150–200 g/day. Not only do unabsorbed nutrients contribute to stool mass but mucosal fluid and electrolyte secretion is also increased in diseases associated with mucosal inflammation such as coeliac disease. In addition, unabsorbed fatty acids, converted to hydroxy-fatty acids by colonic flora, as well as unabsorbed bile acids both impair absorption and induce secretion of water and electrolytes by the colon adding to stool mass. Weight loss is common among patients with significant intestinal malabsorption but must be evaluated in the context of caloric intake. Some patients compensate for fecal wastage of unabsorbed nutrients by significantly increasing their oral intake. Eliciting a careful dietary history from patients with suspected malabsorption is therefore crucial. Excessive flatus and abdominal bloating may reflect excessive gas production due to fermentation of unabsorbed carbohydrate, especially among patients with a primary or secondary disaccharidase deficiency, such as lactose intolerance or sucrose intolerance. Malabsorption of dietary nutrients and excessive fluid secretion by inflamed small intestine also contribute to abdominal distention and bloating. Prevalence, severity, and character of abdominal pain vary considerably among the various disease processes associated with intestinal malabsorption. For example, pain is common in patients with chronic pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer and Crohn's disease, but it is absent in many patients with coeliac disease or postgastrectomy malabsorption.[1]
Extraintestinal manifestations
Substantial numbers of patients with intestinal malabsorption present initially with symptoms or laboratory abnormalities that point to other organ systems in the absence of or overshadowing symptoms referable to the gastrointestinal tract. For example, there is increasing epidemiologic evidence that more patients with coeliac disease present with anemia and osteopenia in the absence of significant classic gastrointestinal symptoms. Microcytic, macrocytic, or dimorphic anemia may reflect impaired iron, folate, or vitamin B12 absorption. Purpura, subconjunctival hemorrhage, or even frank bleeding may reflect hypoprothrombinemia secondary to vitamin K malabsorption. Osteopenia is common, especially in the presence of steatorrhea. Impaired calcium and vitamin D absorption and chelation of calcium by unabsorbed fatty acids resulting in fecal loss of calcium may all contribute. If calcium deficiency is prolonged, secondary hyperparathyroidism may develop. Prolonged malnutrition may induce amenorrhea, infertility, and impotence. Edema and even ascites may reflect hypoproteinemia associated with protein losing enteropathy caused by lymphatic obstruction or extensive mucosal inflammation. Dermatitis and peripheral neuropathy may be caused by malabsorption of specific vitamins or micronutrients and essential fatty acids.[2]
Presentation
Symptoms can manifest in a variety of ways and features might give a clue to the underlying condition. Symptoms can be intestinal or extra-intestinal - the former predominates in severe malabsorption.
- Diarrhoea, often steatorrhoea, is the most common feature. Watery, diurnal and nocturnal, bulky, frequent stools are the clinical hallmark of overt malabsorption. It is due to impaired water, carbohydrate and electrolyte absorption or irritation from unabsorbed fatty acid. The latter also results in bloating, flatulence and abdominal discomfort. Cramping pain usually suggests obstructive intestinal segment e.g. in Crohn's disease, especially if it persists after defecation.[3]
- Weight loss can be significant despite increased oral intake of nutrients.[4]
- Growth retardation, failure to thrive, delayed puberty in children
- Swelling or oedema from loss of protein
- Anaemias, commonly from vitamin B12, folic acid and iron deficiency presenting as fatigue and weakness, and the first of which can give rise to neuropsychiatric symptoms such as abnormal sensations, difficulty walking, and decreased mental abilities.
- Muscle cramp from decreased vitamin D, calcium absorption. Also lead to osteomalacia and osteoporosis
- Bleeding tendencies from vitamin K and other coagulation factor deficiencies.
Causes
Due to infective agents
|
Due to structural defects[5]
|
| Due to surgical structural changes |
Due to mucosal abnormality
|
Due to enzyme deficiencies
|
Due to digestive failure
|
Due to other systemic diseases affecting GI tract
|
Other Possible Causes
|
Pathophysiology
The main purpose of the gastrointestinal tract is to digest and absorb nutrients (fat, carbohydrate, protein, micronutrients (vitamins and trace minerals), water, and electrolytes. Digestion involves both mechanical and enzymatic breakdown of food. Mechanical processes include chewing, gastric churning, and the to-and-fro mixing in the small intestine. Enzymatic hydrolysis is initiated by intraluminal processes requiring gastric, pancreatic, and biliary secretions. The final products of digestion are absorbed through the intestinal epithelial cells.
Malabsorption constitutes the pathological interference with the normal physiological sequence of digestion (intraluminal process), absorption (mucosal process) and transport (postmucosal events) of nutrients.[3]
Intestinal malabsorption can be due to:[7]
- Congenital or acquired reduction in absorptive surface
- Defects of ion transport
- Defects of specific hydrolysis
- Impaired enterohepatic circulation
- Mucosal damage (enteropathy)
- Pancreatic insufficiency
Diagnosis
There is no single, specific test for malabsorption. As for most medical conditions, investigation is guided by symptoms and signs. A range of different conditions can produce malabsorption and it is necessary to look for each of these specifically. Many tests have been advocated, and some, such as tests for pancreatic function are complex, vary between centers and have not been widely adopted. However, better tests have become available with greater ease of use, better sensitivity and specificity for the causative conditions. Tests are also needed to detect the systemic effects of deficiency of the malabsorbed nutrients (such as anaemia with vitamin B12 malabsorption).
Classification
Some prefer to classify malabsorption clinically into three basic categories:[8]
- selective, as seen in lactose malabsorption.
- partial, as observed in abetalipoproteinaemia.
- total, as in exceptional cases of coeliac disease.[9]
Blood tests
- Routine blood tests may reveal anaemia, high CRP or low albumin; which shows a high correlation for the presence of an organic disease.[10][11] In this setting, microcytic anaemia usually implies iron deficiency and macrocytosis can be caused by impaired folic acid or B12 absorption or both. Low cholesterol or triglyceride may give a clue toward fat malabsorption.[12] Low calcium and phosphate may give a clue toward osteomalacia from low vitamin D.[12]
- Specific vitamins like vitamin D or micronutrient like zinc levels can be checked. Fat soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K) are affected in fat malabsorption. Prolonged prothrombin time can be caused by vitamin K deficiency.
- Serological studies. Specific tests are carried out to determine the underlying cause.
Stool studies
- Microscopy is particularly useful in diarrhoea, may show protozoa like Giardia, ova, cyst and other infective agents.
- Fecal fat study to diagnose steatorrhoea is rarely performed nowadays.
- Low fecal pancreatic elastase is indicative of pancreatic insufficiency. Chymotrypsin and pancreolauryl can be assessed as well[12]
Radiological studies
- Barium follow through is useful in delineating small intestinal anatomy. Barium enema may be undertaken to see colonic or ileal lesions.
- CT abdomen is useful in ruling out structural abnormality, done in pancreatic protocol when visualising pancreas.
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) to complement or as an alternative to ERCP.
Interventional studies

- OGD to detect duodenal pathology and obtain D2 biopsy (for coeliac disease, tropical sprue, Whipple's disease, abetalipoproteinaemia etc.)
- Enteroscopy for enteropathy and jejunal aspirate and culture for bacterial overgrowth
- Capsule Endoscopy is able to visualise the whole small intestine and is occasionally useful.
- Colonoscopy is necessary in colonic and ileal disease.
- ERCP will show pancreatic and biliary structural abnormalities.
Other investigations
- 75SeHCAT test to diagnose bile acid malabsorption in ileal disease or primary bile acid diarrhea.
- Glucose hydrogen breath test for bacterial overgrowth
- Lactose hydrogen breath test for lactose intolerance
- Sugar probes or 51Cr-EDTA to determine intestinal permeability.[3]
Obsolete tests no longer used clinically
- D-xylose absorption test for mucosal disease or bacterial overgrowth. Normal in pancreatic insufficiency.
- Bile salt breath test (14C-glycocholate) to determine bile salt malabsorption.
- Schilling test to establish cause of B12 deficiency.
Management
Treatment is directed largely towards management of underlying cause:[1]
- Replacement of nutrients, electrolytes and fluid may be necessary. In severe deficiency, hospital admission may be required for nutritional support and detailed advice from dietitians. Use of enteral nutrition by naso-gastric or other feeding tubes may be able to provide sufficient nutritional supplementation. Tube placement may also be done by percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy, or surgical jejunostomy. In patients whose intestinal absorptive surface is severely limited from disease or surgery, long term total parenteral nutrition may be needed.
- Pancreatic enzymes are supplemented orally in pancreatic insufficiency.
- Dietary modification is important in some conditions:
- Gluten-free diet in coeliac disease.
- Lactose avoidance in lactose intolerance.
- Antibiotic therapy to treat Small Bowel Bacterial overgrowth.
- Cholestyramine or other bile acid sequestrants will help with reducing diarrhoea in bile acid malabsorption.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Malabsorption Syndrome". MedlinePlus. Retrieved 29 April 2018.
- ↑ Fine, KD; Schiller, LR (1999). "technical review on the evaluation and management of chronic diarrhea". Gastroenterology. 116 (6): 1464–1486. doi:10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70513-5. PMID 10348832. S2CID 12239612.
- 1 2 3 Bai J (1998). "Malabsorption syndromes". Digestion. 59 (5): 530–46. doi:10.1159/000007529. PMID 9705537. S2CID 46786949.
- ↑ health a to z"Malabsorption syndrome". Archived from the original on 2007-05-22. Retrieved 2007-05-10.
- ↑ Losowsky, M.S. (1974). Malabsorption in clinical practice. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-01007-2.
- ↑ Heidelbaugh, Joel J. (June 2013). "Proton pump inhibitors and risk of vitamin and mineral deficiency: evidence and clinical implications". Therapeutic Advances in Drug Safety. 4 (3): 125–133. doi:10.1177/2042098613482484. ISSN 2042-0986. PMC 4110863. PMID 25083257.
- ↑ Walker-Smith J, Barnard J, Bhutta Z, Heubi J, Reeves Z, Schmitz J (2002). "Chronic diarrhea and malabsorption (including short gut syndrome): Working Group Report of the First World Congress of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition". J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 35 Suppl 2: S98–105. doi:10.1097/00005176-200208002-00006. PMID 12192177. S2CID 10373517.
- ↑ Gasbarrini G, Frisono M: Critical evaluation of malabsorption tests; in Dobrilla G, Bertaccini G (1986). Langman G (ed.). Problems and Controversies in Gastroenterology. New York: Raven Pr. pp. 123–130. ISBN 88-85037-75-5.
- ↑ Newnham ED (2017). "Coeliac disease in the 21st century: paradigm shifts in the modern age". J Gastroenterol Hepatol (Review). 32 Suppl 1: 82–85. doi:10.1111/jgh.13704. PMID 28244672.
- ↑ Bertomeu A, Ros E, Barragán V, Sachje L, Navarro S (1991). "Chronic diarrhea with normal stool and colonic examinations: organic or functional?". J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 13 (5): 531–6. doi:10.1097/00004836-199110000-00011. PMID 1744388.
- ↑ Read N, Krejs G, Read M, Santa Ana C, Morawski S, Fordtran J (1980). "Chronic diarrhea of unknown origin". Gastroenterology. 78 (2): 264–71. doi:10.1016/0016-5085(80)90575-2. PMID 7350049.
- 1 2 3 Thomas P, Forbes A, Green J, Howdle P, Long R, Playford R, Sheridan M, Stevens R, Valori R, Walters J, Addison G, Hill P, Brydon G (2003). "Guidelines for the investigation of chronic diarrhoea, 2nd edition". Gut. 52 Suppl 5 (90005): v1–15. doi:10.1136/gut.52.suppl_5.v1. PMC 1867765. PMID 12801941.