| Isthomosacanthidae | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Acanthocephala |
| Class: | Palaeacanthocephala |
| Order: | Polymorphida |
| Family: | Isthomosacanthidae Smales, 2012 |
Isthomosacanthidae is a family of parasitic spiny-headed (or thorny-headed) worms.[1]
Species
Isthomosacanthidae contains the following genera and species:[lower-alpha 1]
Golvanorhynchus Noronha, Fabio & Pinto, 1978
- Golvanorhynchus golvani Noronha, Fabio & Magalhaes, 1978
G. golvani was found parasitizing the Atlantic chub mackerel (Scomber colias).[2]
Gorgorhynchoides Cable and Linderoth, 1963
- Gorgorhynchoides bullocki Cable and Mafarachisi, 1970
- Gorgorhynchoides cablei (Gupta and Fatma, 1987)
- Gorgorhynchoides cribbi Smales, 2014
- Gorgorhynchoides elongatus Cable and Linderoth, 1963
- Gorgorhynchoides epinepheli Wang, 1986
- Gorgorhynchoides gnathanodontos Smales, 2014
- Gorgorhynchoides golvani (Chandra, Hanumantha-Rao and Shyamasundari, 1984)
- Gorgorhynchoides indicus Bhattacharya and Banerjee, 2003
- Gorgorhynchoides lintoni Cable and Mafarachisi, 1970
- Gorgorhynchoides orientalis (Wang, 1966)
- Gorgorhynchoides queenslandensis Smales, 2014
- Gorgorhynchoides valiyathurae (Nadakal, John and Jacob, 1990)
Serrasentis Van Cleave, 1923
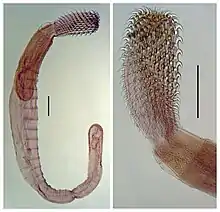
A juvenile male Serrasentis sagittifer with a detail of the proboscis and neck. Bars are 0.4 mm.[3]
- Serrasentis engraulisi Gupta & Gupta, 1980
- Serrasentis fotedari Gupta & Fatma, 1980
- Serrasentis golvani Gupta & Kumar, 1987
- Serrasentis lamelliger (Diesing, 1854)
- Serrasentis manazo Bilqees & Khan, 2005
- Serrasentis mujibi Bilqees, 1972
- Serrasentis nadakali George & Nadakal, 1978
- Serrasentis niger Kahatoon and Bilqees, 2007
- Serrasentis psenesi Gupta & Gupta, 1980
- Serrasentis sagittifer (Linton, 1889)
- Serrasentis sauridae Surekha and Vijayalakshmi, 2006
- Serrasentis sciaenus Bilqees, 1972
- Serrasentis sidaroszakaio Tadros, Iskandar & Wassef, 1979
Hosts
Isthomosacanthidae species parasitize fish hosts.
- Hosts for Diplosentidae species
 Golvanorhynchus golvani was found parasitizing the Atlantic chub mackerel
Golvanorhynchus golvani was found parasitizing the Atlantic chub mackerel
Notes
- ↑ A binomial authority in parentheses indicates that the species was originally described in a genus other than the present genus.
References
- ↑ Huston, D. C., Cribb, T. H., & Smales, L. R. (2020). Molecular characterisation of acanthocephalans from Australian marine teleosts: proposal of a new family, synonymy of another and transfer of taxa between orders. Systematic Parasitology, 1-23.
- ↑ Pichelin, S. & Cribb, T. (2001). The status of the Diplosentidae (Acanthocephala: Palaeacanthocephala) and a new family of acanthocephalans from Australian wrasses (Pisces: Labridae). Folia Parasitologica, 48(4), 289–303.
- ↑ Fonseca, Michelle Cristie Gonçalves da, Knoff, Marcelo, Felizardo, Nilza Nunes, Torres, Eduardo José Lopes, Di Azevedo, Maria Isabel Nogueira, Gomes, Delir Corrêa, Clemente, Sérgio Carmona de São, & Iñiguez, Alena Mayo. (2019). Acanthocephalan parasites of the flounder species Paralichthys isosceles, Paralichthys patagonicus and Xystreurys rasile from Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Parasitologia Veterinária, 28(3), 346-359. Epub June 13, 2019.https://dx.doi.org/10.1590/s1984-29612019031
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.