| Jaisalmer State | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kingdom 1156–1818 Princely State 1818–1947 Dynasty Bhati | |||||||||
| 1156–1947 | |||||||||
 Flag
 Coat of arms
| |||||||||
  South Asia 1525 CE ◁ | |||||||||
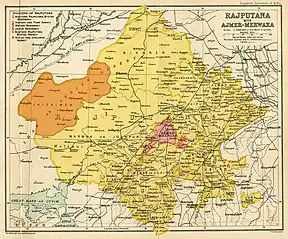
Jailsalmer State (orange) within Rajputana (yellow), 1909. | |||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
• 1931 | 41,600 km2 (16,100 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• 1931 | 76,255 | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 1156 | ||||||||
| 1947 | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Rajasthan, India | ||||||||
| Coat of arms based on The Princely Armory. Publ. by The Office of the Superintendent of Government Printing. Calcutta. 1877 | |||||||||
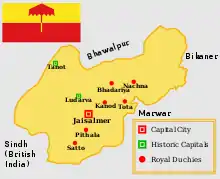


Jaisalmer State was a Bhati Rajput kingdom in the far-western part of present-day Rajasthan, India, from the mid-12th century CE until 1947. In 1156 CE, Rawal Jaisal moved his capital from Ludarva to Jaisalmer because the former was vulnerable to attacks from Turko-Afghan and Baloch tribes. The descendants of Jaisal continued to exercise absolute control over Jaisalmer until 1818 CE, when a treaty of subsidiary alliance with the British Empire made it a princely state, a British Protectorate still running its own internal affairs. Known as the Maharawal, the native ruler of the princely state was entitled to a 15-gun salute.[3]
Early history
The royal dynasty of Jaisalmer claims to be descended from the deified hero Krishna. The Bhati rulers originally ruled parts of Afghanistan; their ancestor Rawal Gaj is believed to have founded the city of Gajni. According to James Tod, this city is present-day Ghazni in Afghanistan, while Cunningham identifies it as modern-day Rawalpindi. His descendant Rawal Salivahan is believed to have founded the city of Sialkot and made it his new capital. Salivahan defeated the Saka Scythians in 78 CE at Kahror, assuming the title of Saka-ari (foe of the Sakas). Salivahan's grandson Rawal Bhati conquered several neighbouring regions. It is from him that the Bhati clan derives its name.[4]
History of Jaisalmer
Medieval history
The state of Jaisalmer had its foundations in what remains of the Empire ruled by the Bhati dynasty from the mid-12th century CE until 1947.[5] Early Bhati rulers ruled over large empire stretching from Ghazni[6] in modern-day Afghanistan to Sialkot, Lahore and Rawalpindi in modern-day Pakistan[7] to Bhatinda, Muktsar & Hanumangarh in Modern day India.[8] The empire crumbled over time because of continuous invasions from the central Asia. According to Satish Chandra, the Hindu Shahis of Afghanistan made an alliance with the Bhati rulers of Multhan, because they wanted to end the slave raids made by the Turkic ruler of Ghazni, however the alliance was defeated by Alp Tigin in 977 CE.[9] Bhati dominions continued to be shifted towards the South as they ruled Multan, then finally got pushed into Cholistan and Jaisalmer where Rawal Devaraja built Dera Rawal / Derawar.[10] Jaisalmer was the new capital founded in 1156 by Maharawal Jaisal Singh and the state took its name from the capital.

Modern history
On 11 December 1818 Jaisalmer became a British protectorate in the Rajputana Agency.[11][10]
Traditionally, in the Middle Ages, the main source of income for the kingdom was levies on caravans, but the economy was heavily affected when Bombay emerged as a major port and sea trade replaced the traditional land routes. Maharawal Ranjit Singh and Bairi Sal Singh attempted to turn around the economic decline but the dramatic reduction in trade impoverished the kingdom. A severe drought and the resulting famine from 1895 to 1900, during the reign of Maharawal Salivahan Singh, only made matters worse by causing widespread loss of the livestock that the increasingly agriculturally based kingdom relied upon.
The attempts of Maharawal Jawahir Singh (1914–1949) at modernization were also not entirely successful in turning the kingdom's economy around, and the drylands of Jaisalmer remained backward compared with other regions of Rajputana, especially the neighbouring state of Jodhpur. Nonetheless, the extensive water storage and supply, sanitation, and health infrastructures developed in the 1930s by the prime minister Dewan Bahadur Brijmohan Nath Zutshi provided significant relief during the severe droughts of 1941 and 1951. Maharawal During 1930–1947, Jawahir Singh and his ministers also promoted technical education and the academic disciplines of civil and mechanical engineering in the state.
After the departure of the British from India in 1947, the Maharawal signed an Instrument of Accession to the new Union of India, while retaining some internal autonomy until the 1950s.
List of rulers
Rawals
(1153–1168), official founder of the kingdom
- Rawal Shalivahan Singh II (1168–1200)
- Rawal Bijal Singh (1200–1200)
- Rawal Kailan Singh (1200–1219)
- Rawal Chachak Dev Singh (1219–1241)
- Rawal Karan Singh I (1241–1271)
- Rawal Lakhan Sen (1271–1275)
- Rawal Punpal Singh (1275–1276)
- Rawal Jait Singh I (1276–1294)
- Rawal Mulraj Singh I (1294–1295)
- Rawal Durjan Sal (Duda) (1295–1306)
- Rawal Gharsi Singh (1306–1335)
- Rawal Kehar Singh II (1335–1402)
- Rawal Lachman Singh (1402–1436)
- Rawal Bersi Singh (1436–1448)
- Rawal Chachak Dev Singh II (1448–1457)
- Rawal Devidas Singh (1457–1497)
- Rawal Jait Singh II (1497–1530)
- Rawal Karan Singh II (1530–1530)
- Rawal Lunkaran Singh (1530–1551)
- Rawal Maldev Singh (1551–1562)
- Rawal Harraj Singh (1562–1578)
- Rawal Bhim Singh (1578–1624)
- Rawal Kalyan Das (1624–1634)
- Rawal Manohar Das (1634–1648)
- Rawal Ramchandra Dev (1648–1651)
- Rawal Sabal Singh (1651–1661)
Maharawals
- Maharawal Raghunath Singh of Jaisalmer (1661–1702)
- Maharawal Jaswant Singh of Jaisalmer (1702–1708)
- Maharawal Budh Singh (1708–1722)
- Maharawal Akhi Singh (1722–1762)
- Maharawal Mulraj II (1762–1820)
- Maharawal Gaj Singh (1820–1846)
- Maharawal Ranjit Singh of Jaisalmer (1846–1864)
- Maharawal Bairi Sal (1864–1891)
- Maharawal Shalivahan Singh III (1891 –1914)
- Maharawal Jawahir Singh (1914–1947)
- Girdhar Singh (1949–1950), last ruler of kingdom merge state with Rajasthan Union in 1949 CE.
Titular rulers
- Raghunath Singh (1950–1982)
- Brijraj Singh (1982–2020)
- Chaitanya Raj Singh (since 2020)[12]
Dewans
- List of Dewans (chief ministers)
- Mohata Nathmal (1885–1891)
- Mehta Jagjiwan (1890–1903)
- Thakur Kushal Singh (acting) (1890?–1900)
- Rawatmal Purohit Khetrapalia (acting) (1900–1909)
- Lakshmi Das Sapat (1909–1911)
- Mohammed Niyaz Ali Kazi (1911–1912)
- Murarji Rooji (1912–1930)
- M.L. Khosala
- Pandit Jamana Lal
- Munshi Nand Kishore
- Lala Rakhpat Raj
- P.K. Shurugula
- Brij Mohan Nath Zutshi
- Anand Swaroop
- Onkar Singh
- Lakhpat Rai Sikund (1940–1942)
See also
References
- ↑ Schwartzberg, Joseph E. (1978). A Historical atlas of South Asia. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 147, map XIV.4 (a). ISBN 0226742210.
- ↑ "Jaisalmer". www.crwflags.com. Retrieved 16 April 2021.
- ↑ Imperial Gazetteer of India, v. 24, p. 386.
- ↑ "Imperial Gazetteer2 of India, Volume 14, page 2 -- Imperial Gazetteer of India -- Digital South Asia Library".
- ↑ Sukhdev (2 October 2023). "Which dynasty ruled to Jaisalmer princely state?". Studentera. Retrieved 28 November 2023.
- ↑ "Rajasthan or the Central and Western Rajpoot States, Volume 2, page 197-198". Higginbotham And Co. Madras. 14 August 2018.
- ↑ "Imperial Gazetter of India, Volume 21, page 272 - Imperial Gazetteer of India - Digital South Asia Library". Dsal.uchicago.edu. 18 February 2013. Retrieved 22 November 2013.
- ↑ "Bhatinda Government: District at A glance- Origin". Bhatinda Government. 14 August 2018. Archived from the original on 10 January 2011. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ↑ Medieval India 1206-1526 part one, pg.17 by Satish Chandra
- 1 2 "Provincial Gazetteers Of India: Rajputana". Government of India. 14 August 2018.
- ↑ Princely States of India
- ↑ "Chaitanya Raj Singh becomes the 44th Maharawal of Jaisalmer". firstindia.co.in. Retrieved 11 September 2022.
External links
 Media related to Jaisalmer State at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Jaisalmer State at Wikimedia Commons- . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 15 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 129.