
Jetan, also known as Martian chess, is a chess variant first published in 1922. It was created by Edgar Rice Burroughs as a game played on Barsoom, his fictional version of Mars. The game was introduced in The Chessmen of Mars, the fifth book in the Barsoom series. Its rules are described in Chapter 2 and in the Appendix of the book, with an actual game partly described in Chapter 17.
Description
Board and pieces
Jetan is played on a black and orange checkered board of 10 ranks by 10 files, with orange pieces on the "north" side and black pieces on the "south".
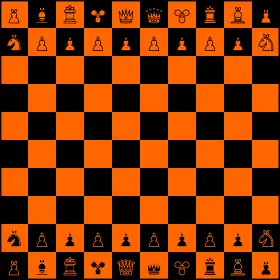
Each player has the following playing pieces: one Chief, one Princess, two Fliers; two Dwars (Captains); two Padwars (Lieutenants); two Warriors; two Thoats (Mounted Warriors); and eight Panthans (Mercenaries). The Chief, Princess, Fliers, Dwars, Padwars and Warriors are positioned along the rank closest to the player with the Chief at left center, the Princess at right center, and the Fliers, Dwars, Padwars and Warriors arranged to flank each, with the Fliers innermost and the Warriors outermost. The Thoats and Panthans are positioned along the next rank out from the player with the Thoats flanking the Panthans. The complete arrangement of each side follows:
T p p p p p p p p T W P D F C P F D P W
There has in the past been considerable confusion regarding the rules of Jetan, but research has shown that most such problems can be cleared up through careful analysis of the text in The Chessmen of Mars.[1] This article is based primarily on the Appendix in The Chessmen of Mars, but takes the abovementioned research into consideration.
Movement
Jetan pieces move one, two or three steps for every move. Two- and three-steppers may change their direction of movement at each step in the course of a move, so long as this is in a direction permitted for that piece. No piece can cross the same square of the board twice during the course of a move. The Princess and the Flier may jump over a piece that is in their path.
A capture is made when a piece lands on a square occupied by an opposing piece with its final step or jump; the Princess may not capture.
The pieces move as follows:
- Chief: three steps in any direction or combination of directions.
- This is equivalent to three moves of a chess king, except that it cannot double back and may only capture at the third step.
- Princess: three steps in any direction or combination of directions; it may jump over other pieces but cannot capture.
- It may make one ten space "escape" at any time during gameplay, jumping to any unoccupied and unthreatened space on the board.
- Flier: three steps diagonally; it may jump over other pieces.
- Per Burroughs, in an older version of Jetan these pieces were called Odwars.
- Dwar: three steps orthogonally.
- Padwar: two steps diagonally.
- Warrior: two steps orthogonally.
- A quote from Chapter 2 in The Chessmen of Mars that can be interpreted as a different type of move for the Warrior has been shown to be based on a typographical error.[1]
- Thoat: one orthogonal and one diagonal step.
- In Chapter 2 of his text, Burroughs mentions that the Thoat can jump, but this is not mentioned in the more detailed Appendix. Most players disregard this.
- Panthan: one single step forward, sideways or diagonally forward.
By analogy to standard chess, it is assumed that a piece that moves multiple squares can capture an opposing piece only by finishing its move on the opposing piece's square. In other words, a piece can capture only once per turn. Burroughs was explaining his chess rules for an Earth audience familiar with standard chess. He deliberately stated that the Princess and the Flier may jump over a piece that is in their path. The only reasonable interpretation is that the Chief, Dwar, Padwar, and Warrior are blocked by pieces in their path (as are the queen, rook, and bishop in standard chess). It is unreasonable to suppose that Burroughs could have meant that the Flier jumps over intervening pieces while the Chief captures all intervening pieces, as this would be so different from standard chess that he would have stated this, had it been his intention.
It is not explicitly stated in Burroughs' text that a piece entitled to a two-space or three-space move must move the full amount, but implicit information suggests that this is the case.[1] For example, the Padwar at [P] is entitled to a two-space diagonal move, so in the diagram below, it must end its move on the spaces marked [2]; if all the spaces marked [1] are occupied by friendly or opposing pieces, or if all the spaces marked [2] are occupied by friendly pieces, then the Padwar is blocked and unable to move.
2 2 2 1 1 2 P 2 1 1 2 2 2
Ending the game
In Burroughs's description, Jetan is won when either a Chief captures the opposing Chief, or when any piece captures the opposing Princess. The game is drawn if each player is reduced to three or fewer pieces of equal value and it is not won within the next ten moves, or if a Chief is taken by any piece other than a Chief.
Some consider these rules to result in too many draws[2][3] so a number of variants have been proposed to address this issue, the simplest being that the capture of a Chief by a piece other than a Chief merely retires the Chief without drawing or ending the game.
Jetan in Burroughs's novels
According to The Chessmen of Mars, Jetan was said to represent an ancient war between the Yellow and Black races of Barsoom. This explains why the orange pieces begin on the "north" side and black pieces on the "south," because Barsoom's Yellow and Black races inhabit its north and south polar regions, respectively.
The second half of The Chessmen of Mars takes place in the city of Manator, where the most popular civil event involves human beings fighting to the death in a life-sized Jetan game viewed by hundreds of spectators. The "board" is large enough that some of the pieces are mounted on Thoats and yet still fit in a single "square." However, this life-and-death version departs from the rules of Jetan in one very significant way: when one piece lands on a square occupied by another, the first does not automatically replace the second. Rather, the two pieces fight to the death, and the winner of the sword fight wins the square. The lone exception involves the Princess: if one side's piece lands on a square occupied by the other side's Princess, no battle occurs, and the first side wins the game.
Wagering and scoring
In his Appendix, Edgar Rice Burroughs writes: "The Martians gamble at Jetan in several ways. Of course the outcome of the game indicates to whom the main stake belongs; but they also put a price upon the head of each piece, according to its value, and for each piece that a player loses he pays its value to his opponent."[4] But Burroughs never specified any exact rules for gambling, nor did he give the point values for the various pieces.
Although gambling is optional per Burroughs' rules, some fans have developed several rule variants for gambling, with names such as Ransom and Pay to move,[5] which have sometimes been used when playing the game.
Many suggestions have been made for the respective values of the pieces. The list below is based on Cazaux & Knowlton.[6]
- Padwar: 1.7
- Warrior: 1.9
- Panthan: 2.0
- Dwar: 4.9
- Thoat: 5.6
- Flier: 9.5
- Chief: no set value
- Princess: no set value
Computer implementations
Jetan has been adapted to the computer medium on several occasions. Some variants of Jetan on the computer are:
- Jetan (Silversoft, 1993) by Paul Burgess; for MS-DOS; downloadable from Burgess' home page.
- Jetan (Softdisk, 1993) by David Moorman; this program for the Commodore 64 disk magazine Loadstar had no computer opponent.
- Tommy's Martian Chess (Tommy's Toys, 1997) by Thomas Lee Winslow; an MS-DOS shareware program that is no longer available for purchase. The try-out version can be downloaded from the Internet Archive.
- Two versions have been created for the Zillions of Games board game engine, one by Jean-Louis Cazaux and Jens Markmann, the other by L. Lynn Smith.
Similar games in other fiction
Burroughs inspired many other writers of the sword and planet genre. Some such writers have also included chess-like games in their writing, often with a living version. Instances of such possible homage include:
- Lin Carter's Darza, from Renegade of Callisto, eighth volume in his Callisto series.
- Kenneth Bulmer's Jikaida, from A Life for Kregen, 19th volume in his Dray Prescot series.
- John Norman's Kaissa, mentioned many times in his Gor series, although never fully described.
- S. M. Stirling's Atanj, from In the Courts of the Crimson Kings, his own Burroughs-influenced novel of an alternate Mars, also not fully described.
See also
- Martian chess – a board game by Andrew Looney
References
- 1 2 3 Ekman, Fredrik. "Exploring Jetan". ERBzine. Bill Hillman. Retrieved 25 December 2019.
- ↑ Gollon, John (1968). Chess Variations: Ancient, Regional, and Modern. Charles E. Tuttle Company. pp. 209–213. ISBN 978-1-4629-1220-9.
- ↑ Cazaux, Jean-Louis; Bodlaender, Hans L. "Jetan". The Chess Variant Pages. Fergus Duniho. Retrieved 25 December 2019.
- ↑ Burroughs, Edgar Rice (1922). The Chessmen of Mars. Project Gutenberg. Retrieved 26 December 2019.
- ↑ Smith, Larry Lynn (2003). Handscomb, Kerry (ed.). "The Wager of Jetan". Abstract Games. Carpe Diem Publishing (14): 27–28. ISSN 1492-0492.
- ↑ Cazaux, Jean-Louis; Knowlton, Rick (2017). A World of Chess: Its Development and Variations through Centuries and Civilizations. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland & Company. pp. 314–316. ISBN 978-0-7864-9427-9.
External links
- The Rules of Jetan edited by Fredrik Ekman, ERBzine
- Jetan at BoardGameGeek