John Longstaff | |
|---|---|
 Portrait of Longstaff by George Coates, 1918, National Library of Australia | |
| Born | John Campbell Longstaff 10 March 1861 |
| Died | 1 October 1941 (aged 80) Melbourne, Victoria, Australia |
| Nationality | Australian |
| Known for | Painting |
Sir John Campbell Longstaff (10 March 1861 – 1 October 1941) was an Australian painter, war artist and a five-time winner of the Archibald Prize for portraiture. His cousin Will Longstaff was also a painter and war artist.
Longstaff was known for being fashionable and for being one of the most prolific portrait painters of the early 20th century.[1]
Biography
Longstaff was born at Clunes, Victoria, second son of Ralph Longstaff, storekeeper and Janet (Jessie) Campbell. John was educated at a boarding school in Miners Rest and Clunes State School. He studied 1883-87[2] at the Melbourne National Gallery School where, despite his father's initial disapproval of his artistic ambitions,[3] Longstaff's talent was recognised by George Folingsby.[3]
He joined the inaugural meeting in May 1883 of the bohemian Buonarotti Club with Alexander Colquhoun, Fred M. Williams and Tom Humphrey.[4] French painter Jules Lefebvre's controversial 1875 nude Chloé was being shown that month in Victoria's National Gallery, and the Sunday Observance League objected to the trustees' decision to open the exhibition on a Sunday. When it was covered with a black curtain, Longstaff, with eight other Gallery School students, two of whom were Buonarotti Club members Colquhoun and McCubbin, protested.[5]
Europe
Longstaff continued in the Club as a senior member until its demise in 1887 when he was given a well-attended farewell at the Melbourne Coffee Palace on 23 August 1887, before sailing to London. The occasion was his winning the National Gallery of Victoria's first travelling scholarship for his 1887 narrative painting Breaking the News which he sold for 100 guineas,[6] and which inspired a 1912 film of the same name.[7] He had married Rosa Louisa (Topsy) Crocker on 20 July that year at Powlett Street, East Melbourne and with his new wife sailed on the Valetta from Melbourne for London in September 1887.[1] In January 1888 they travelled to Paris, where Longstaff exhibited in the Paris Salon. He later moved to London, where he painted many portraits.
Longstaff returned to Australia in 1894 and was given several commissions. He occupied a studio at Grosvenor Chambers in Melbourne from 1897 to 1900. The National Gallery of Victoria assumed ownership of The Sirens under terms of the scholarship and bought his large landscape Gippsland, Sunday night, 20 February 1898. He travelled to London again in 1901, where he exhibited with the Royal Academy.
War artist
Longstaff was appointed an official war artist with the Australian Infantry Force in the First World War.[8] He made several portraits of officers in the military. On his return to Australia he won several awards and was given distinguished positions, such as his appointment to President of the Victorian Artists Society in 1924 and Trustee of the National Gallery of Victoria in 1927. He was knighted in the 1928 New Year Honours List, the first Australian artist to have had this honour.
Portraitist
In 1924, Longstaff met Miss Jessica Harcourt, at the time a theatre programme seller, and later actress, in Sydney and later called "Australia's loveliest girl". He was struck by her beauty and painted her twice. In 1925 he exhibited Harcourt's portrait with Twenty Melbourne Painters at the Athenaeum Hall. Longstaff was happy with his subject, regarding Harcourt as "almost a perfect type of feminine beauty", and it was considered "one of the best things he had ever done."[9]
His 1929 portrait of the artist Ellis Rowan was the first nationally funded memorial portrait of a woman in Australia, to which people of all the states subscribed in honour of a woman considered to be of outstanding qualities..[10]
The Art Gallery of South Australia holds his portraits of Paris Nesbit and The Artist's Wife.
Longstaff's portraits of women were the subject of the 2012 exhibition Portrait of a Lady at the Shepparton Art Museum.
Biography
His biography Portrait in Youth, written by Nina Murdoch was published in 1948. His 1920 portrait of Nina Murdoch hangs in Reading Room of the National Library, Canberra.[11]
Archibald prize
His Archibald Prize winning pieces:
- 1925 - Portrait of Maurice Moscovitch
- 1928 - Portrait of Dr Alexander Leeper
- 1929 - W A Holman, KC
- 1931 - Sir John Sulman
- 1935 - A B ('Banjo') Paterson
Gallery

 Lady In Grey, 1890, National Gallery of Victoria
Lady In Grey, 1890, National Gallery of Victoria The Young Mother, 1891, National Gallery of Victoria
The Young Mother, 1891, National Gallery of Victoria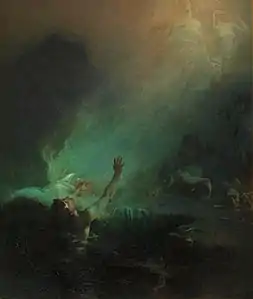 The Sirens, 1892, National Gallery of Victoria
The Sirens, 1892, National Gallery of Victoria The Artist's Wife, 1896, Art Gallery of South Australia
The Artist's Wife, 1896, Art Gallery of South Australia Gippsland, Sunday night, February 20th, 1898, 1898, National Gallery of Victoria
Gippsland, Sunday night, February 20th, 1898, 1898, National Gallery of Victoria
.jpg.webp) Arrival of Burke, Wills and King at the deserted camp at Cooper's Creek, Sunday evening, 21 April 1861, 1907, National Gallery of Victoria
Arrival of Burke, Wills and King at the deserted camp at Cooper's Creek, Sunday evening, 21 April 1861, 1907, National Gallery of Victoria Dr Alexander Leeper, National Gallery of Victoria, 1928
Dr Alexander Leeper, National Gallery of Victoria, 1928
References
- Leigh Astbury, 'Longstaff, Sir John Campbell (1861–1941)', Australian Dictionary of Biography, Volume 10, MUP, 1986, pp 141–142.
- 1 2 Splatt, William; Burton, Barbara (1977). A Treasury of Australian Landscape Painting. Rigby. p. 35.
- ↑ McCulloch, Alan; McCulloch, Susan; McCulloch Childs, Emily (2006). The new McCulloch's encyclopedia of Australian art (4th ed.). Fitzroy: AUS Art Editions ; The Miegunyah Press. p. 625. ISBN 0-522-85317-X. OCLC 80568976.
- 1 2 Percival Serle, ed. (1949). "Longstaff, Sir John". Dictionary of Australian Biography. Angus and Robertson, Sydney. Retrieved 12 July 2007.
- ↑ Mead, Stephen F. (December 2011). "The Search for Artistic Professionalism in Melbourne: the activities of the Buonarotti Club, 1883 -1887". The Latrobe Journal. 88.
- ↑ Holt, Stephanie (1994). "Chloe: a curious history". In Hoorn, Jeanette (ed.). Strange Women: essays in art and gender. Carlton, Vic.: Melbourne University Press. p. 134.
- ↑ "Melbourne Tea-Table Talk". The West Australian. 16 May 1887. p. 3. Retrieved 21 March 2023.
- ↑ "Distribution Of Prizes". The Australasian. 30 April 1887. p. 43. Retrieved 21 March 2023.
- ↑ 'Camofleur', "Musketeers of Brush and Pencil with the A.I.F.: Art Under Fire: The Battlefield as Studio", The (Melbourne) Herald, (1 February 1919), p. 4.
- ↑ "Art Exhibition". Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848–1957). 15 September 1925. p. 6. Retrieved 22 August 2020.
- ↑ "ELLIS ROWAN MEMORIAL PORTRAIT". Sydney Morning Herald. 6 December 1929. Retrieved 21 March 2023.
- ↑ Murdoch, Madoline (Nina) (1890–1976). Australian Dictionary of Biography. Retrieved on 1 November 2021.
External links
- John Longstaff at Artcyclopedia
- LONGSTAFF, Sir John at the Australian War Memorial Archived 7 August 2005 at the Wayback Machine
- Portrait of Jessica Harcourt, 1925, National Gallery of Victoria
- Catalogue for Portrait of a Lady exhibition, 2012, Shepparton Art Museum Archived 15 March 2020 at the Wayback Machine