Jonas Patrik Ljungström | |
|---|---|
 Jonas Patrick Ljungström, c. 1870s | |
| Born | 12 March 1827 |
| Died | 22 October 1898 (aged 71) |
| Nationality | Swedish |
| Occupation(s) | Cartographer, geodesist, teacher |
Jonas Patrik Ljungström (12 March 1827 – 22 October 1898) was a Swedish cartographer, geodesist, and teacher at the Royal Institute of Technology.[1]
Biography
Jonas Patrik Ljungström was born 12 March 1827 in Uddevalla as the son of jeweler Johan Patrik Ljungström, and Maria Christina (née Spaak). His great grandfather was the Protestant reformer Peter Spaak, and his third great-grandfather early industrialist Abraham Hülphers the Elder. He married Amalia (née Falck), and their issue included Georg Ljungström, Oscar Ljungström, Birger Ljungström, and Fredrik Ljungström.
After examination in Stockholm in 1849, Ljungström served as land surveyor for the Gothenburg and Bohus County from 1864, and as cartographer at the governmental agency for cartography in Stockholm 1873–1888. Parallel to this, he developed land survey and precision instruments at his own manufactory that cooperated with the early manufactory of L. M. Ericsson. Furthermore, he taught at the Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm.
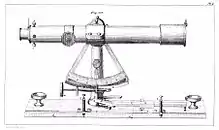

Ljungström's multiple technical innovations won prizes at the General Industrial Exposition of Stockholm (1866), the General Art and Industrial Exposition of Stockholm (1897), Exposition Universelle (1878), Exposition Universelle (1900), the Brussels Geographic Conference (1876), the Centennial Exposition in Philadelphia (1876), and the World's Columbian Exposition in Chicago (1893). While in Philadelphia in 1876 he met the Swedish physicist Salomon August Andrée who remained a friend of the family until his death, teaching Ljungström's sons Birger and Fredrik in physics.
The most successful of his inventions, the distance tube land surveying precision instrument, endured in professional use until the 1950s. Noted by John Ericsson (1803–1889) as "an innovative mind of extraordinary capability and extensive mechanical wit", Ljungström's works are represented by the Swedish National Museum of Science and Technology,[2] as well as by regional cultural heritage museums.[3][4]
Works
- Beskrifning öfver distanstub med sjelfreglerande skala jemte sättet för instrumentets justering och användande (1877)[5]
Distinctions
 Silver medal at the Exposition Universelle (1878)
Silver medal at the Exposition Universelle (1878) Member of Academie Agricole Manufacturière et Commerciale (1878)
Member of Academie Agricole Manufacturière et Commerciale (1878) Gold medal of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences (1877)
Gold medal of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences (1877) Wallmark Prize of Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences (1877)
Wallmark Prize of Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences (1877) Gold medal at the Centennial Exposition in Philadelphia (1876)
Gold medal at the Centennial Exposition in Philadelphia (1876)
References
- ↑ "226 (Sveriges statskalender / 1881)". runeberg.org.
- ↑ "Distanstub, i låda". digitaltmuseum.se.
- ↑ "foremalspost". Archived from the original on 2009-02-21. Retrieved 2018-02-21.
- ↑ "New Page 1". web.telia.com.
- ↑ LIBRIS - Beskrifning öfver distanstub ... 1877.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help)
Further reading
- Andersson, Johan Oskar (1876). Geodetisk mätningskunskap (in Swedish). Albert Bonniers förlag – via Project Runeberg.
- Ljungström, Olof (1999). Fredrik Ljungström 1875–1964 – Uppfinnare och inspiratör (in Swedish). Svenska mekanisters riksförening. ISBN 9789163076398.
External links
- Anderson, P. A. "Nyare hjälpmedel och metoder vid gruvmätning". Teknisk tidskrift.
- Gustafsson, Carolina. "Areas in the record of properties – what qualities do they have?"(in Swedish)
- Photo, Lantmätare Jonas Patrik Ljungström (1827 – 1898). Bohuslän Museum.
- Photo, Lantmätare Jonas Patrik Ljungström (1827–1898). Bohuslän Museum.