Juazeiro | |
|---|---|
City | |
 Juazeiro skyline seen from São Francisco river | |
 Flag  Seal | |
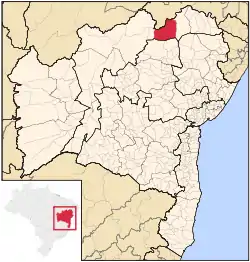 | |
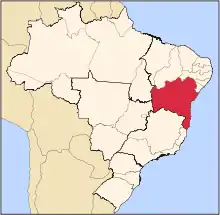
 Juazeiro Location in Brazil | |
| Coordinates: 09°25′50″S 40°30′10″W / 9.43056°S 40.50278°W | |
| Country | |
| Region | Northeast |
| State | Bahia |
| Mesoregion | Vale São-Franciscano da Bahia |
| Microregion | Juazeiro |
| Founded | May 9, 1833 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Suzana Ramos |
| Area | |
| • Total | 6,500.520 km2 (2,509.865 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 368 m (1,207 ft) |
| Population (2020 est.[2]) | |
| • Total | 218,162 |
| Time zone | UTC−3 (BRT) |
| HDI (2010)[3] | 0.677 |
| Website | Official Website |
Juazeiro, formerly also known as Joazeiro,[4] is a municipality in the state of Bahia, in the northeastern region of Brazil.
The city is twinned with Petrolina, in the state of Pernambuco. The two cities are connected by a modern bridge crossing the São Francisco River. Together they form the metropolitan region of Petrolina-Juazeiro, an urban conglomerate of close to 500,000 inhabitants.
History
It was founded in 1833 and became a city on July 15, 1878. Its name comes from the Juá tree which grows in the region.
Organization
Its city districts are Abóbora, Carnaíba, Itamotinga, Junco, Juremal, Massaroca, and Pinhões.
Geography
Climate
The annual average temperature is 26 °C or 78.8 °F. Although it lies on the São Francisco River and the Curaçá River, Juazeiro is one of the driest places in Brazil, with a hot semi-arid climate (Köppen BSh) that is very close to being classified as a hot arid climate (BWh).
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 35.3 (95.5) |
35.4 (95.7) |
34.9 (94.8) |
33.4 (92.1) |
30.8 (87.4) |
29.5 (85.1) |
29.1 (84.4) |
30.4 (86.7) |
33.2 (91.8) |
35.6 (96.1) |
36.3 (97.3) |
35.2 (95.4) |
33.3 (91.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 27.6 (81.7) |
27.7 (81.9) |
27.4 (81.3) |
26.5 (79.7) |
24.9 (76.8) |
23.6 (74.5) |
22.8 (73.0) |
23.4 (74.1) |
25.4 (77.7) |
27.4 (81.3) |
28.2 (82.8) |
27.4 (81.3) |
26 (79) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 20.8 (69.4) |
21.2 (70.2) |
21.1 (70.0) |
20.7 (69.3) |
19.7 (67.5) |
18.2 (64.8) |
17.2 (63.0) |
17.4 (63.3) |
18.9 (66.0) |
20.4 (68.7) |
21 (70) |
20.8 (69.4) |
19.8 (67.6) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 69.4 (2.73) |
71.1 (2.80) |
96.2 (3.79) |
40.9 (1.61) |
7.9 (0.31) |
2.6 (0.10) |
3.2 (0.13) |
1.9 (0.07) |
4 (0.2) |
9.9 (0.39) |
46.6 (1.83) |
60.6 (2.39) |
414.3 (16.35) |
| Source: [5][6][7][8] | |||||||||||||
Transport

There are highway connections with several capitals of the Northeast and railroad connections to the coast are made by the Ferrovia Centro-Atlântica. The railroad connection ends at the fluvial port of Juazeiro.
Economy
Like its sister city Petrolina, Juazeiro has experienced great growth in the last decade due to the irrigation of the semi-arid soils with water from the São Francisco River. Fruit cultivation is important to such an extent that Juazeiro entitles itself "Capital of Irrigated Fruit", which is exported between the Petrolina Airport to United States and/or Europe. For more detailed information on the development of this fertile valley see the article on Petrolina.
The main agricultural products in planted area according to the IBGE in 2003:
- bananas: 18 km2
- coconut: 2.72 km2
- guava: 2.5 km2
- lemon: 2 km2
- papaya: 0.45 km2
- mango: 60 km2
- passion fruit: 0.9 km2
- grapes: 21 km2
- sugarcane: 152.53 km2
- onions: 3.4 km2
- beans: 4.04 km2
- manioc: 4.2 km2
- watermelon: 4.5 km2
- melon: 1.95 km2
- tomato: 0.32 km2
Sport
Both the city's professional football teams play at the Estádio Adauto Moraes: Juazeiro SC founded 1995, and SD Juazeirense founded in 2006.
Notable people
Juazeiro is the birthplace of the following famous people:
- Dani Alves: right back footballer of the Brazilian national team, formerly of Bahia, FC Barcelona, and Sevilla, Pumas of UNAM Mexico City, Juventus, PSG and São Paulo FC.
- Luís Pereira: Brazilian former professional footballer, winner of three national championships
- Nixon, Brazilian former professional footballer.
- Petros, brazilian football player.
See also
References
- ↑ "Área territorial oficial" [Official Territorial Area] (in Portuguese). Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics(IBGE). 2002-10-10. Retrieved 2010-12-05.
- ↑ IBGE 2020
- ↑ "Ranking decrescente do IDH-M dos municípios do Brasil" (PDF) (in Portuguese). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). 2010. Retrieved 2013-08-07.
- ↑
- Lamoureaux, Andrew Jackson (1911), , in Chisholm, Hugh (ed.), Encyclopædia Britannica, vol. 3 (11th ed.), Cambridge University Press, p. 210
- ↑ "PRECIPITACAO MENSAL - ESTADO DA BAHIA". Departmento de Ciencas Atmosfericas. Archived from the original on February 20, 2018.
- ↑ "TEMPERATURA MAXIMA MENSAL E ANUAL DA BAHIA". Departmento de Ciencas Atmosfericas. Archived from the original on February 20, 2018.
- ↑ "TEMPERATURA COMPENSADA MENSAL E ANUAL DA BAHIA". Departmento de Ciencas Atmosfericas. Archived from the original on December 30, 2021.
- ↑ "TEMPERATURA MINIMA MENSAL E ANUAL DA BAHIA". Departmento de Ciencas Atmosfericas. Archived from the original on December 6, 2021.
- ↑ (in Portuguese), IBGE, 2003 https://web.archive.org/web/20070109005631/http://www.ibge.gov.br/cidadesat/default.php, archived from the original on 2007-01-09
{{citation}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)