Kürten | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
Location of Kürten within Rheinisch-Bergischer Kreis district  | |
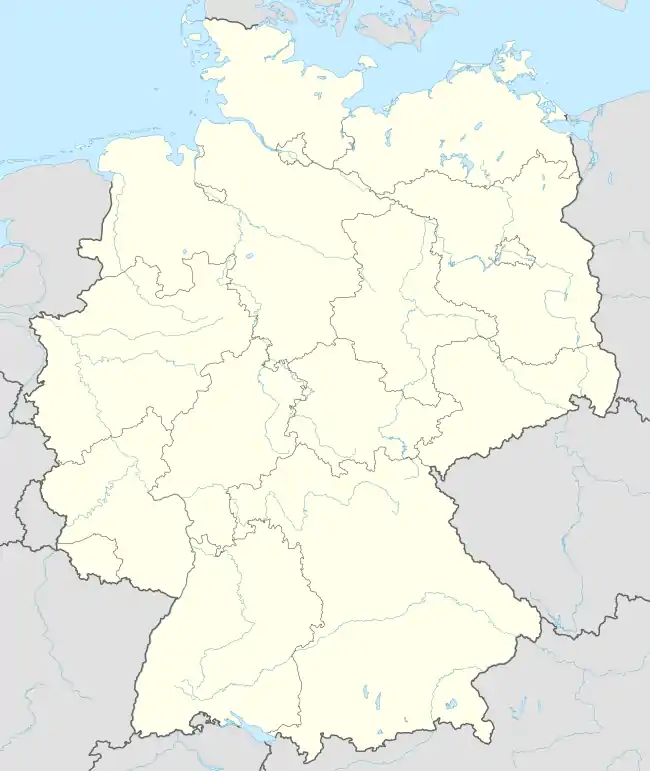 Kürten 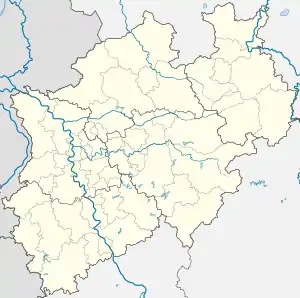 Kürten | |
| Coordinates: 51°02′59″N 07°16′00″E / 51.04972°N 7.26667°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | North Rhine-Westphalia |
| Admin. region | Köln |
| District | Rheinisch-Bergischer Kreis |
| Subdivisions | 69 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–25) | Willi Heider[1] (Ind.) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 67.5 km2 (26.1 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 300 m (1,000 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 150 m (490 ft) |
| Population (2021-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 19,832 |
| • Density | 290/km2 (760/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 51515 |
| Dialling codes | 02268, 02207 |
| Vehicle registration | GL |
| Website | www.kuerten.de |
Kürten is a village and a municipality in the Rheinisch-Bergischer Kreis, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.
Geography
Kürten is situated approximately 25 km east of Cologne.
Neighbouring places
Nearby cities include Bergisch Gladbach, Overath, Wermelskirchen, and Wipperfürth. Neighboring municipalities are Lindlar and Odenthal.
Constituent villages, localities, and communities
The municipality includes 69 districts (Ortsteile):
Ahlendung - Bechen - Biesenbach - Biesfeld - Bilstein - Blissenbach - Bornen - Breibach - Broch - Broich - Broichhausen - Burgheim - Busch - Dahl - Delling - Dörnchen - Dorpe - Duhr - Dürscheid - Eichhof - Eisenkaul - Engeldorf - Enkeln - Forsten - Furth - Hachenberg - Hahn - Heidergansfeld - Hembach - Herrscherthal - Herweg - Höchsten - Hufe - Hungenbach - Hutsherweg - Jähhardt - Junkermühle - Kalsbach - Kochsfeld - Kohlgrube - Laudenberg - Miebach - Müllenberg - Nassenstein - Nelsbach - Oberbersten - Oberbörsch - Oberkollenbach - Oeldorf - Offermannsberg - Offermannsheide - Olpe - Olperhof - Petersberg - Richerzhagen - Schanze - Schnappe - Schwarzeln - Selbach - Spitze - Sülze - Sürth - Unterbersten-Unterbörsch - Unterossenbach - Viersbach - Waldmühle - Weiden - Weier - Wolfsorth.
Twin towns
 Rodengo-Saiano, (Italy) since 1999
Rodengo-Saiano, (Italy) since 1999
Population
Kürten is one of the historically slow-growing localities in the Bergische Land. Only since the 1960s has the number of inhabitants risen significantly.
| Year | Population |
| 1829 | 2,373 |
| 1925 | 2,329 |
| 1938 | 2,684 |
| 1946 | 3,903 |
| 1953 | 3,617 |
| Year | Population |
| 1979 | 16,243 |
| 1983 | 16,919 |
| 1990 | 17,516 |
| 2001 | 20,005 |
| 2003 | 20,040 |
| Year | Population |
| 2004 | 20,116 |
| 2005 | 20,077 |
History
Origin of the place name
Up until 1930 the place name "Kürten" was written with a "C".
Already in the high Middle Ages—around 1300—the Liber Valoris (a listing of all churches as a basis for collecting the crusade tithe) registers the place "Curtine" as the location of a church. The church itself was devoted to John the Baptist. This name could suggest that the location of today's place of worship possibly already served as a baptismal site at the time of Christianization.
There are two interpretations for the origin of the name.
The conventional version holds that the name developed from medieval Latin curtis, meaning "courtyard", "socage farm", "princely court", or "place where court is held": In the terminology of the later Middle Ages, toward the 14th century, in Latin documents curtis designates the open space within an enclosed courtyard, where jurors met and the court of justice was held.
On the other hand, the resident local historian Theo Stockberg, after many years of comparative etymological research on names of the settlements and fields of the Bergisches Land, holds the view that Kürten is derived from "Op de Corte", which means more or less: "on the short (watercourse)". A wellspring does in fact exist in the original settlement area, from which today a reed-banked brook flows from the summit above the school complex into the river Sülz.
Archives of the municipality
The Kürten municipality archives predominantly contain administrative documents, beginning at present after the Code Civil under Napoleonic rule of administrative structuring (starting in 1804). Inventory 1 covers the documents from 1804 to 1918, Inventory 2 refers to the collection from the end of the First to the end of the Second World War; from 1945 Inventory 3 begins. Owing to a lack of written evidence from the time before Napoleon, the archives can provide information about local historical affairs only over the past 200 years. In the year 2000 a sheaf of 160 much older official documents were deposited in the municipal archives: Nine original documents from the sixteenth century, on the one hand church documents from Olpe, and on the other hand feudal court records. These are original papers from the 16th to the 19th century, and in particular from the time around 1780. The oldest document in the collection, a court record, originated from as early as 1572.
Chronology
1171 First documented mention of the municipal area of Olpe
1175 First documented mention of the municipal area of Bechen
1308 First documented mention of Kürten: "Curtine" is catalogued in the Liber Valoris as the location of a church.
1300 The Counts (later Dukes) of Berg introduce an Ämterverfassung (jurisdictional constitution), which remains valid for 500 years.
1555 Reference to the old seal of the Kürten Landgeding (regional court).
1699 Kürten is the location of a law court (cf. local-name interpretation of Curtis, cf. medieval record for Curtine). Reference to a manor house with a patronage of living and a legal jury, to which Biesfeld and Offermannsheide are also assigned.
1739 Records of the association of the parish of Kürten with the Steinbach authority.
1806 Elector Max Joseph von Kurpfalz-Bayern surrendered the Duchy of Berg to Napoleon. In 1808 a Grand Duchy under Joachim Murat was created and the administration was reformed (Mairies = mayoralties).
1815 Kürten and Olpe are attached to Prussia.
1929 The jurisdictions of Kürten (consisting of the municipalities of Kürten and Bechen) and Olpe (consisting of the municipalities Olpe and Wipperfeld) are combined.
1947 The municipality becomes part of the newly formed Federal State of North Rhine-Westphalia. Refugees from former eastern German regions lead to a distinct increase in the population.
1965 World-famous classical music composer Karlheinz Stockhausen has a house built in Kürten, designed to his specifications by the architect Erich Schneider-Wessling. In 1998, Stockhausen founded the Stockhausen Courses, held annually in Kürten.
1975 In the course of the kommunalen Neugliederung (repartitioning of communities) the former municipality of Kürten and significant parts of the municipalities of Bechen and Olpe are merged into the new municipality of Kürten (Köln-Gesetz, § 11 Abs. 1). Into this new municipality, parts of the then city of Bensberg (amongst others, Dürscheid) and smaller areas of the (at that time partial) municipalities of Lindlar, Odenthal, and Wipperfeld are integrated. In the course of restructuring of the Kürten Authority, the greater part of Wipperfeld became part of the city of Wipperfürth.
2000 The reconstruction achievements in all regions of the Federal Republic of Germany in the second half of the 20th century open up also in Kürten, up to the 1990s, a comparatively undreamt-of infrastructural and economic upswing, accompanied with an increase in the population from scarcely 4,000 people in the post-war period to over 20,000 citizens in the year 2000. In a counter-action, since the turn of the century indications of a decrease in growth are becoming stronger, with the ever-shrinking means of household budgets.
2008 The "Karlheinz-Stockhausen-Platz" is dedicated in Kürten on 22 August, the 80th anniversary of the late composer's birth (Press release).
Coat of arms
The upper half of the coat of arms displays the Lion of Berg. The heron in the lower part of the escutcheon alludes to the abundance of fish in the numerous brooks in the area. The official blazon reads:
In geteiltem Schild oben in Silber ein zwiegeschwänzter, blau bewehrter und gekrönter roter Löwe, unten in Rot ein silberner Fischreiher, der einen silbernen Fisch im Schnabel trägt.
Or, in English blazon:
Party per fess Argent and Gules, in the chief a demi-lion rampant Gules with double tail, langued, membered and crowned Azure, in base a heron bearing in its bill a fish Argent.
The municipal coat of arms corresponds in all essentials to the original seal of the Law-courts of Cürten from 1598. In 1925 an act from 1742 was discovered in the Staatsarchiv in Düsseldorf, which bears the impression of this legal seal. The coat of arms was first bestowed on the municipality of Kürten by a decree of the Prussian State Ministry of 5 October 1926, and a second time on the Amt of Kürten, this time by a charter from the central government of the State of North Rhine–Westphalia dated 8 December 1949. The coat of arms remained valid up until the local reorganization on 1 January 1975: At this point in time the present submunicipalities of Bechen and Olpe were included in the armorial charter. In reaction to the altered local-political situation, Kürten received a newly redesigned municipal coat of arms, which was authorized in its present form by a charter from the district president in Cologne, dated 15 March 1982. Traditionally the Bergische Lion forms one part of the configuration of coats of arms belonging to the communities of the original County of Berg. For this reason the cities and municipalities of this region retain this charge as part of the armorial achievement, supplemented with independent local symbols in order to differentiate the coats of arms from each other.
Politics
Since the general election in 2004, the Mayor has been Ulrich Iwanow (BFB).
- Local council:
- CDU 39.00% (13 seats)
- The Bürger für Bürger (Citizens for Citizens) BFB 26.75% (9 seats)
- SPD 14.75% (5 seats),
- FDP 13.14% (5 seats)
- Alliance 90/Green Party 6.37% ( 2 seats)
Elections in 2014:
- CDU 16 seats
- SPD 6 seats
- Bündnis 90/Grüne 4 seats
- FDP 4 seats
- BfB 8 seats
References
- ↑ Wahlergebnisse in NRW Kommunalwahlen 2020, Land Nordrhein-Westfalen, accessed 29 June 2021.
- ↑ "Bevölkerung der Gemeinden Nordrhein-Westfalens am 31. Dezember 2021" (in German). Landesbetrieb Information und Technik NRW. Retrieved 20 June 2022.