| KIAA1958 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | KIAA1958 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 617390 HomoloGene: 136743 GeneCards: KIAA1958 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein KIAA1958 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIAA1958 gene.[3] Orthologs of KIAA1958 go as far back in evolution to chordates, although, it is closer in homology to primates than any other orthologs. KIAA1958 has no known paralogs.
Gene
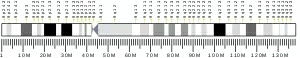
KIAA1958 is located on the long arm of chromosome 9 (9.q32) in humans on the plus strand from 115249248 to 115427597.[4] Its mRNA has 2683 bp.[3] The gene has these neighbors on chromosome 9:
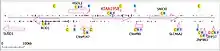
HSDL2: Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-like protein 2 plays a role in nucleotide binding, oxidoreductase activity, and sterol binding.[5]
C9orf147: Chromosome 9 open reading frame 147 has an unknown function.[6]
C9orf80: Chromosome 9 open reading frame 80 is a component of the SOSS complex, a multiprotein complex that functions downstream of the MRN complex to promote DNA repair and G2/M checkpoint. The SOSS complex associates with single-stranded DNA at DNA lesions and influences diverse endpoints in the cellular DNA damage response including cell cycle checkpoint activation, recombinational repair and maintenance of genomic stability.[7]
SNX30: Sorting nexin-30 may be linked to phosphatidylinositol binding.[8]
Expression
KIAA1958 is expressed in the highest quantities in the larynx as proposed by EST.[9] The highest expression in developmental stage is the blastocyst and for health state, it is most found in uterine tumors.[9] Data from NCBI GEO Profile[10] shows that KIAA1958 expression includes many of the tissue types in the human body. Using EMBL-EBI, KIAA1958 was found to be overexpressed in pseudopod RNA during the migration of the metastatic cancer cells.[11] KIAA1958 was also overexpressed in Stat5/ab and stat 3 which are transcription factors reported to be critical for the growth and viability of prostate cancer cells[11] and both the embryonic stem cell and the pluripotent stem cell.[11]
Protein
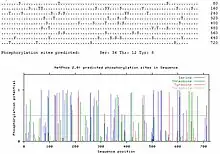
KIAA1958 is composed of 716 amino acids and weighs 79212 Da with an iso-electric point of 6.375.[12] Although not much is known about the KIAA1958 protein, scientific predictions have been made using supercomputers for predictions of KIAA1958's structure and function. KIAA1958 undergoes post-translational modifications. The most interesting modification is phosphorylation. In comparison to other proteins, KIAA1958 has a substantially significant amount of serines phosphorylated during post-translational modification. 36 serines are predicted to be phosphorylated.
Structure
PELE on SDSC Biology WorkBench is supercomputer that is able to predict secondary structure of the KIAA1958 protein.[13] According to this tool, the protein's secondary structure is a combination of alpha helices and beta sheets, in almost equal amount and spread out almost evenly throughout the protein.
Interactions
There is no known proof that KIAA1958 interacts with any other proteins at this time.[14]
Homology
| Genus and Species | Common Name | Accession Number | Seq. Length | Seq. Identity | Seq. Similarity |
| Pan troglodytes | Chimpanzee | XM_528391 | 7945 bp | 99% | 99% |
| Mus musculus | Mouse | BAC38268 | 719 a | 97% | 98% |
| Callithrix jacchus | Common marmoset | XM_002743204 | 2346bp | 97% | 82% |
| Pongo abelii | Sumatran Orangutan | XM_002820112 | 1120bp | 96% | 4% |
| Sus scrofa | Wild boar | XM_003122070 | 2502 bp | 93% | 81% |
| Ailuropoda melanoleuca | Giant Panda | XM_002925938 | 2151 bp | 85% | 91% |
| Nomascus leucogenys | White cheeked gibbon | XM_003263945 | 950 bp | 93% | 5% |
| Oryctolagus cuniculus | European rabbit | XM_002707990 | 2223 bp | 93% | 43% |
| Loxodonta africana | African bush elephant | XM_003407521 | 2388 bp | 93% | 80% |
| Cricetulus griseus | Chinese hamster | XM_003505508 | 2534 bp | 92% | 42% |
| Equus caballus | Horse | XM_001916302 | 2536 bp | 91% | 93% |
| Bos taurus | Cow | XM_876102.5 | 2480 bp | 91% | 81% |
| Rattus norvegicus | Rat | XM_002726532 | 1364 bp | 91% | 36% |
| Cavia porcellus | Guinea pig | XM_003463791 | 2217 bp | 91% | 43% |
| Monodelphis domestica | Opossum | XM_001375976 | 2217 bp | 78% | 41% |
| Branchiostoma floridae | Lancelet | XP_002611438 | 719 a | 29% | 48% |
| Amphimedon queenslandica | Sponge | XP_003390994 | 388 a | 25% | 48% |
| Acyrthosiphon pisum | Pea aphid | XP_001943720 | 1197 aa | 24% | 43% |
| Oikopleura dioica | Chordate | CBY34656 | 629 a | 22% | 43% |
| Ciona intestinalis | Vase tunicate | XP_002125964 | 1004 aa | 23% | 43% |
| Xenopus (silurana) tropicalis | Western Clawed frog | AAI61073 | 679 a | 23% | 43% |
| Halocynthia roretzi | Sea pineapple | BAB40645 | 980 a | 23% | 45% |
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000165185 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- 1 2 "Homo sapiens KIAA1958 (KIAA1958), mRNA". NCBI. Retrieved 20 April 2012.
- ↑ "Homo sapiens gene KIAA1958, encoding KIAA1958". AceView. Retrieved 19 April 2012.
- ↑ "Q6YN16 (HSDL2_HUMAN) Reviewed, UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot". UniProt. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ↑ "Homo sapiens gene C9orf147, encoding chromosome 9 open reading frame 147". AceView. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ↑ "Q9NRY2 (SOSSC_HUMAN) Reviewed, UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot". Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ↑ "Q5VWJ9 (SNX30_HUMAN) Reviewed, UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot". Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- 1 2 "Unigene EST profile". Unigene. Retrieved 8 May 2012.
- ↑ "Geo Profiles". NCBI. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
- 1 2 3 "Gene Expression Profiles". Embl-Ebi. Retrieved 8 May 2012.
- ↑ "Biology WorkBench". SDSC. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- ↑ "Biology Workbench". SDSC Biology WorkBench. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
- ↑ "Protein Interactions". String. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
Further reading
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, Macek B, Kumar C, Mortensen P, Mann M (November 2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983. S2CID 7827573.