| Kaibara Domain 柏原藩 | |
|---|---|
| under Tokugawa shogunate Japan | |
| 1598–1871 | |
| Capital | Kaibara jin'ya |
| Area | |
| • Coordinates | 35°7′43.8″N 135°4′55.9″E / 35.128833°N 135.082194°E |
| • Type | Daimyō |
| Historical era | Edo period |
• Established | 1598 |
• Oda clan | 1598 |
• Tenryō | 1650 |
• Oda clan | 1695 |
• Disestablished | 1871 |
| Today part of | part of Hyōgo Prefecture |
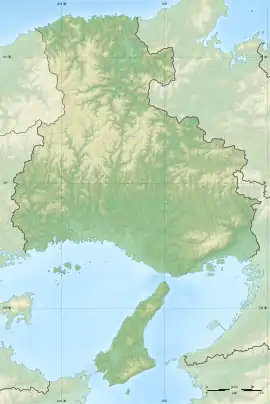


Kaibara Domain (柏原藩, Kaibara-han) was a feudal domain under the Tokugawa shogunate of Edo period Japan, located in Tajima Province in what is now the central portion of modern-day Hyōgo Prefecture. It was centered around Kaibara jin'ya, located in what is now the city of Tanba, Hyōgo.[1][2][3]
History
In 1598, Oda Nobunaga’s younger brother, Oda Nobukane was transferred from Ise Province to Tanba Province to establish the 36,000 koku Kaibara Domain. Although he sided with the losing Western Army during the Battle of Sekigahara, he was allowed to retain his domain, and afterwards continued in the service of Toyotomi Hideyori at Osaka Castle. He died in 1614 before the Siege of Osaka, and his son and grandson continued to rule the domain. In 1650, the 3rd daimyo, Oda Nobukatsu died without heir and the domain was abolished and administered as tenryō directly by the Tokugawa shogunate.
Oda Tananaga was the fifth son of Oda Nobukatsu, the younger brother of Oda Nobunaga. He was daimyō of Uda-Matsuyama Domain in Yamato Province. In 1694, the 4th daimyo of that domain, Oda Nobutake, went insane and killed a number of his close retainers before committing suicide. The shogunate demoted his son, Oda Nobuyasu, by reducing his kokudaka from 28,000 to 20,000 koku and ordering his transfer to the restored Kaibara Domain. The situation for the new domain was grim, as there was neither castle or jin'ya to be occupied, and the land was wasteland due to recurrent flooding and droughts. In 1696 the domain had to plea for relief from taxation. The issue of financial crisis continued through successive daimyō, with the domain forced to dismiss most of its retainers, reduce stipends for the remainder and borrow heavily. The situation was not helped by the 5th daimyō, Oda Nobumori, whose profligate spending on his mistress and his continuing meddling in political affair led to an uprising, followed by peasant revolts in 1824 and 1833 due to inflation. The 8th daimyō, Oda Nobunori, managed to implement reforms centered on fiscal frugality and he constructed a han school. His successor, Oda Nobutami, continued these reforms. In the Bakumatsu period, Oda Nobutami and his successor Oda Nobuchika supported the sonnō jōi movement and was an early supporter of the imperial cause. In 1869, he became imperial governor and relocated to Tokyo on the abolition of the han system in 1871. Kabara Domain became “Kaibara Prefecture” in 1871.
Kaibara Domain Jin'ya
Permission to construct the jin'ya was not granted by the shogunate until 1713, some 19 years after the transfer. The main building was destroyed by a fire in 1818 and reconstructed in 1820. It was largely dismantled after the Meiji restoration and now only about one-fifth of the original structure remains. Most of the site is now occupied by an elementary school. The front gate of the jin'ya, a nagayamon dates from the original 1714 construction. The site was designated a National Historic Site in 1971.[4]
Holdings at the end of the Edo period
As with most domains in the han system, which consisted of several discontinuous territories calculated to provide the assigned kokudaka, based on periodic cadastral surveys and projected agricultural yields.[5][6]
- Tanba Province
- 9 villages in Ikaruga District
- 4 villages in Amata District
- 43 villages in Hikami District
List of daimyō
# Name Tenure Courtesy title Court Rank kokudaka  Oda clan, 1598-1650 (Tozama)
Oda clan, 1598-1650 (Tozama)1 Oda Nobukane (織田信包) 1598 - 1614 Sakonoechūshō (左近衛中将) Junior 3rd Rank (従三位) 36,000 koku 2 Oda Nobunori (織田信則) 1614 - 1630 Gyobu-daifu (刑部大輔) Junior 4th Rank, Lower grade (従四位下) 36,000 koku 3 Oda Nobukatsu (織田信則) 1630 - 1650 Kazusa-no-suke (上総介) Junior 5th Rank, Lower grade (従五位下) 36,000 koku  tenryō 1650-1695
tenryō 1650-1695 Oda clan, 1695-1871 (Tozama)
Oda clan, 1695-1871 (Tozama)1 Oda Nobuyasu (織田信休) 1695 - 1722 Ōmi-no-kami (近江守) Junior 5th Rank, Lower grade (従五位下) 20,000 koku 2 Oda Nobutomo (織田信朝) 1722 - 1737 Izumo-no-kami (出雲守) Junior 5th Rank, Lower grade (従五位下) 20,000 koku 3 Oda Nobuhisa (織田信旧) 1737 - 1783 Yamashiro-no-kami (山城守) Junior 5th Rank, Lower grade (従五位下) 20,000 koku 4 Oda Nobuyori (織田信憑) 1783 - 1827 Izumo-no-kami (出雲守) Junior 4th Rank, Lower grade (従四位下) 20,000 koku 5 Oda Nobumori (織田信守) 1827 - 1829 Yamashiro-no-kami (山城守) Junior 5th Rank, Lower grade (従五位下) 20,000 koku 6 Oda Nobumoto (織田信古) 1829 - 1842 Ōmi-no-kami (近江守) Junior 5th Rank, Lower grade (従五位下) 20,000 koku 7 Oda Nobutada (織田信貞) 1842 - 1846 Izumo-no-kami (出雲守) Junior 5th Rank, Lower grade (従五位下) 20,000 koku 8 Oda Nobunori (織田信敬) 1846 - 1854 Izumo-no-kami (出雲守) Junior 5th Rank, Lower grade (従五位下)) 20,000 koku 9 Oda Nobutami (織田信民) 1854 - 1865 Yamashiro-no-kami (山城守) Junior 5th Rank, Lower grade (従五位下) 20,000 koku 10 Oda Nobuchika (織田信親) 1854 - 1861 Izumo-no-kami (出雲守) Junior 5th Rank, Lower grade (従五位下)) 20,000 koku
See also
Further reading
- Bolitho, Harold. (1974). Treasures Among Men: The Fudai Daimyo in Tokugawa Japan. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-01655-0; OCLC 185685588
References
- ↑ Nakayama, Yoshiaki (2015). 江戸三百藩大全 全藩藩主変遷表付. Kosaido Publishing. ISBN 978-4331802946.(in Japanese)
- ↑ Nigi, Kenichi (2004). 藩と城下町の事典―国別. Tokyodo Printing. ISBN 978-4490106510.
- ↑ Papinot, E (1910). Historical and Geographic Dictionary of Japan. Tuttle (reprint) 1972.
- ↑ "柏原陣屋跡" (in Japanese). Agency for Cultural Affairs. Retrieved August 20, 2020.
- ↑ Mass, Jeffrey P. and William B. Hauser. (1987). The Bakufu in Japanese History, p. 150.
- ↑ Elison, George and Bardwell L. Smith (1987). Warlords, Artists, & Commoners: Japan in the Sixteenth Century, p. 18.