上黒岩岩陰遺跡 | |
 Kamikuroiwaiwakage Site | |
 Kamikuroiwaiwakage Site  Kamikuroiwaiwakage Site (Japan) | |
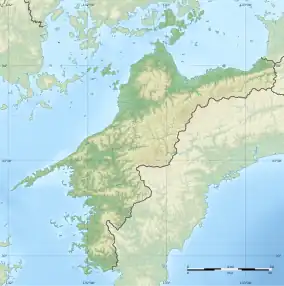
| Location | Kumakōgen, Ehime, Japan |
|---|---|
| Region | Shikoku |
| Coordinates | 33°37′4.2″N 132°57′39.1″E / 33.617833°N 132.960861°E |
| Type | settlement |
| History | |
| Periods | Jōmon period |
| Site notes | |
| Public access | Yes |
The Kamikuroiwaiwakage Site (上黒岩岩陰遺跡, Kamikuroiwaiwakage iseki) is an archaeological site consisting of a Jōmon period rock shelter dwelling in the Mikawa neighborhood of the typo of Kumakōgen, Ehime Prefecture in the island of Shikoku Japan. The site was designated a National Historic Site of Japan in 1971.[1]
The Kamikuroiwaiwakage Site is on a river terrace on the right bank of the Kuma River about three kilometers from Misannohe, where the Omogo Valley, which originates at the southwestern foot of Mt. Ishizuchi, joins the Kuma River. It is in the shadow of a 30-meter-high limestone outcrop, the center of the ruins extends from the north end to the southwest side of the rock wall. The site was discovered in 1961 by a junior high school student living nearby. Archaeological excavations have been conducted five times since 1970, with stratigraphic examination of over 14 layers indicated that it had been occupied from the early to late Jōmon period. Artifacts were found in all layers, and included Jōmon pottery with fine ridge line designs, tongued points, arrowhead grinders, sharpeners, gravel implements, and seven stone slabs inscribed on chlorite schist. A total of 28 sets of human remains were also found, notably a female human hipbone with a deer-antler javelin stuck in it, believed to have been part of a posthumous ritual, as well as a female statue carved into a stone using a sharp flake stone tool, which may have been a ritual object. This was the first time that this kind of Venus figurine was excavated in Japan. Objects such as bracelets, neck ornaments, and ear ornaments made from seashell or bone were also excavated. The same soil layer also unearthed the world's oldest piece of earthenware at the time of its discovery, radiocarbon dated to approximately 14,500 years ago. A variety of animal remains were unearthed, including that of deer, wild boar, kamoshika, Japanese macaque, Japanese raccoon dog, Japanese wolf, Siberian lynx, Japanese river otter, Asian black bear, rabbit, giant flying squirrel, and mice and a huge number of Semisulcospira libertina snail shells. Of domestic animals, the excavation of a dog (Jōmon dog), is noteworthy.[2]
The site was designated as a prefectural historic site in November 1962 in 1964 Mikawa Village made 379.6 square meters of land public. It was designated as a national historic site on May 27, 1971. The excavated items are displayed at the Kamikuroiwa Iwankage Ruins Archaeological Museum (上黒岩岩陰遺跡考古館) on site.[2]
The site is located about 80 minutes from Matsuyama City Hall or about 10 minutes from Kumakogen Town Hall, on Japan National Route 33.
See also
References
External links
- Kumakōgen home page (in Japanese)