| Komeutyuyam Range | |
|---|---|
| Комеутюямский хребет | |
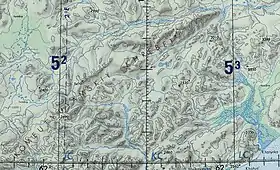 Komeutyuyam Range ONC map section | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Volokvyneitkon |
| Elevation | 1,142.7 m (3,749 ft)[1] |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 150 km (93 mi) NE/SW |
| Width | 40 km (25 mi) NW/SE |
| Geography | |
 Location in Chukotka Autonomous Okrug  Komeutyuyam Range (Kamchatka Krai)  Komeutyuyam Range (Far Eastern Federal District) | |
| Location | Chukotka Autonomous Okrug Kamchatka Krai, Russia |
| Range coordinates | 62°31′40″N 173°46′47″E / 62.52778°N 173.77972°E |
| Parent range | Koryak Highlands East Siberian Mountains |
| Geology | |
| Orogeny | Alpine orogeny |
| Age of rock | Cretaceous[2] |
| Climbing | |
| Easiest route | From Khatyrka |
The Komeutyuyam Range (Russian: Комеутюямский хребет; Chinese: 科梅乌秋亚姆斯基山) is a range of mountains in Chukotka Autonomous Okrug and Kamchatka Krai, Russian Far East.
Administratively the northern section of the range belongs to the Anadyr District of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, and the southern to Olyutorsky District of Kamchatka Krai.[3]
Geography
The Komeutyuyam Range is part of the Koryak Highland system. It stretches parallel to the Bering Sea coast, about 50 kilometres (31 mi) inland, in a NE/SW direction between the western end of the Ukvushvuynen Range in the north and the Pikas Range in the south. The valley of the Pikasvayam, the largest tributary of the Ukelayat, marks its southern end.[3]
The highest point of the range is Mt Volokvyneitkon (гора Волоквынейткон) — or Mt Valvykvyneitkon (гора Валвыквынейткон),[4] a 1,142 metres (3,747 ft) high peak, located in the southwestern sector of the range, near the limit between Chukotka Autonomous Okrug and Kamchatka Krai. The same peak has a height of 1,144 metres (3,753 ft) in the Topographic USSR Chart.[5]
Rivers Opuka and Iomrautvaam have their sources in the southern slopes of the Komeutyuyam and the Khatyrka flows along the northern slopes and bends southeastwards at the northeastern end of the range.[4][5]
See also
References
- ↑ проект закона - Законодательное Собрание Камчатского края
- ↑ Калясников Ю.А. Наноминералогия воды и биосферные процессы. Публикуется по тексту: Калясников Ю.А. Наноминералогия воды и биосферные процессы: 2-е изд., перераб. и доп. Магадан: СВНЦ ДВО РАН, 2000. 64 с.
- 1 2 Google Earth
- 1 2 Atlas of Russia
- 1 2 "Топографска карта P-59_60 - Topographic USSR Chart (in Russian)". Retrieved 17 February 2022.