| Koreanosaurus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Fossil holotype | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | †Ornithischia |
| Family: | †Thescelosauridae |
| Subfamily: | †Orodrominae |
| Genus: | †Koreanosaurus Huh et al., 2011 |
| Species: | †K. boseongensis |
| Binomial name | |
| †Koreanosaurus boseongensis Huh et al., 2011 | |
Koreanosaurus (lit. 'Korean lizard') is a genus of orodromine neornithischian dinosaur. One species has been described, Koreanosaurus boseongensis.
Discovery
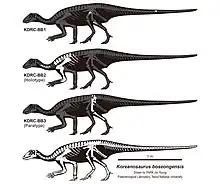
In 2003, three specimens of Koreanosaurus were found in the Late Cretaceous-age Seonso Conglomerate from the southern coast of the Bibong-ri dinosaur egg site, Boseong, Korean Peninsula.[2] These specimens include the holotype KDRC-BB2, a partial upper skeleton lacking the skull, and two additional specimens which contains portions of the pelvic girdle and lower leg (KDRC-BB1 and KDRC-BB3).[3] The type species was named after its locality (Boseong site 5). This taxon was initially named and described in a master's thesis by Dae-Gil Lee in 2008,[4] and was officially published by Min Huh, Dae-Gil Lee, Jung-Kyun Kim, Jong-Deock Lim and Pascal Godefroit in 2011.[3]
Description
Koreanosaurus was a relatively small dinosaur, reaching 2–2.4 meters (6.6–7.9 ft) in body length.[5][6] Based on its taxonomic position and the existence of small burrows from the Seonso Conglomerate, Koreanosaurus is likely a burrowing dinosaur.[3] Unlike its orodromine relatives, Koreanosaurus is assumed to have been a quadruped.[7]
Classification

Koreanosaurus was considered to be a basal member of the Ornithopoda by the authors, forming a clade with Zephyrosaurus schaffi, Orodromeus makelai and Oryctodromeus cubicularis from which they deduced a burrowing lifestyle.[3] Han et al. found it plausible that Koreanosaurus might be a member of Jeholosauridae or closely related to it.[8]
References
- ↑ Kim, J.K.; Kwon, Y.E.; Lee, S.G.; Kim, C.Y.; Kim, J.G.; Huh, M.; Lee, E.; Kim, Y.J. (2017). "Correlative microscopy of the constituents of a dinosaur rib fossil and hosting mudstone: Implications on diagenesis and fossil preservation". PLOS One. 13 (3): e0195421. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0186600. PMC 5648225.
- ↑ 전남대 허민 교수팀, 한국 이름명 공룡 복원. Yonhap (in Korean). 2010-11-01. Archived from the original on 2011-10-02. Retrieved 2011-05-04.
- 1 2 3 4 Min Huh; Dae-Gil Lee; Jung-Kyun Kim; Jong-Deock Lim; Pascal Godefroit (2011). "A new basal ornithopod dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous of South Korea" (PDF). Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 259 (1): 1–24. doi:10.1127/0077-7749/2010/0102.
- ↑ Lee G., 2008, The ornithopod dinosaur (Ornithopoda: Hypsilophodontidae) from the Late Cretaceous Seonso Conglomerate of Boseong County, Korea, master's thesis Chonnam National University
- ↑ Huh, M.; Kim, J.G. (2010). "Koreanosaurus boseongensis" (in Korean). 한국고생물학회 정기총회 및 학술발표회. pp. 21–26.
- ↑ Holtz, Thomas R. Jr. (2012). Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-Date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers of All Ages (PDF).
Winter 2011 Appendix
- ↑ Fearon, J.L.; Varricchio, D.J. (2015). "Morphometric analysis of the forelimb and pectoral girdle of the Cretaceous ornithopod dinosaur Oryctodromeus cubicularis and implications for digging". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 35 (4): e936555. doi:10.1080/02724634.2014.936555.
- ↑ Han, Feng-Lu; Paul M. Barrett; Richard J. Butler; Xing Xu (2012). "Postcranial anatomy of Jeholosaurus shangyuanensis (Dinosauria, Ornithischia) from the Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation of China". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 32 (6): 1370–1395. doi:10.1080/02724634.2012.694385. S2CID 86754247.

