| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Service type | Limited express |
| Locale | Tokaido Main Line, Fukuchiyama Line, Sanin Main Line |
| First service | 12 March 2011 |
| Current operator(s) | JR West |
| Route | |
| Termini | Shin-Ōsaka Kinosaki Onsen |
| Technical | |
| Rolling stock | 287 series/289 series EMUs |
| Track gauge | 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) |
| Electrification | 1,500 V DC overhead |
The Kounotori (こうのとり, Kōnotori) is a limited express train service operated by the West Japan Railway Company (JR West) between Shin-Ōsaka and Kinosaki Onsen in Japan since 12 March 2011. It replaced the previous Kitakinki services.[1]
The name means "stork", and was chosen because the stork is the prefectural bird of Hyōgo, and the city of Toyooka in particular has close involvement with stork breeding programmes.[1]
Service pattern and station stops

14 down services (Kounotori 1–27) from Shin-Osaka and 13 up services (Kounotori 2–26) to Shin-Osaka run daily, with the journey time from Shin-Osaka to Kinosaki Onsen taking approximately 2 hours 45 minutes.[2]
Kounotori services stop at the following stations. (Stations in parentheses are not served by all trains.)[2]
Shin-Ōsaka - Ōsaka - Amagasaki - Takarazuka - Sanda - (Shin-Sanda) - (Aino) - Sasayamaguchi - (Tanikawa) - Kaibara - (Kuroi) - Fukuchiyama - (Wadayama) - (Yōka) - (Ebara) - (Toyooka) - (Kinosaki Onsen)
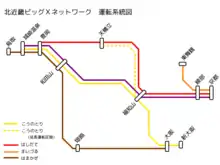
Kounotori, Kinosaki, Hashidate, Maizuru, and Hamakaze constitute the Kitakinki Big X Network of limited express services connecting the northern Kinki (Kitakinki) region with the Keihanshin metropolitan area.
Rolling stock
The following rolling stock is used on Kounotori services.[3]
- 287 series EMUs (since 12 March 2011)
- 289 series EMUs (from 31 October 2015)
289 series EMUs converted from former dual-voltage 683 series trainsets were introduced on Kounotori services from 31 October 2015, replacing the remaining JNR-era 381 series trains.[4]
Former rolling stock
- 183 series 4/6-car EMUs (12 March 2011 – 15 March 2013)[5]
- 381 series 4/6-car EMUs (from 12 March 2011 to 31 May 2011, and from 1 June 2012 to 30 October 2015)[6][7][8]
 183 series 6-car set, April 2012
183 series 6-car set, April 2012 381 series 6-car set, March 2011
381 series 6-car set, March 2011
See also
References
- 1 2 "JR西日本 287系デビュー時に特急「北近畿」を「こうのとり」に改呼" [JR West to rename "Kitakinki" as "Kounotori" with debut of 287 series]. Tetsudō Daiya Jōhō Magazine. Vol. 39, no. 320. Japan: Kōtsū Shimbun. December 2010. p. 73.
- 1 2 JR Timetable, February 2011 issue
- ↑ 平成23年春ダイヤ改正について [Spring 2011 timetable revision details] (PDF). JR West news release (in Japanese). West Japan Railway Company. 17 December 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 January 2011. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ↑ JR西日本 289系 10月31日から運転開始 [JR West 289 series to enter service from 31 October]. Tetsudo Hobidas (in Japanese). Japan: Neko Publishing Co., Ltd. 21 August 2015. Retrieved 21 August 2015.
- ↑ "JR西日本の183系が定期運用を終了" [JR West 183 series withdrawn from scheduled services]. Japan Railfan Magazine Online (in Japanese). Japan: Koyusha Co., Ltd. 17 March 2013. Retrieved 17 March 2013.
- ↑ 新型車両(287 系)追加投入の詳細 [Details of further introduction of new (287 series) trains] (PDF). JR West news release (in Japanese). West Japan Railway Company. 28 April 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 2 May 2011.
- ↑ "JR西日本 381系福知山車FE編成が営業運転開始" [JR West: Fukichiyama-based 381 series FE sets enter service]. Tetsudō Daiya Jōhō Magazine. Vol. 41, no. 340. Japan: Kōtsū Shimbun. August 2012. p. 75.
- ↑ 381系が関西地区の定期運用から離脱 [381 series removed from scheduled Kansai area services]. Japan Railfan Magazine Online (in Japanese). Japan: Koyusha Co., Ltd. 31 October 2015. Retrieved 1 November 2015.
External links
- JR West 287 series Kounotori Archived 2 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine (in Japanese)
- JR West 289 series Kounotori Archived 8 February 2018 at the Wayback Machine (in Japanese)